Project Gasbuggy
Coordinates: 36°40′41″N 107°12′33″W / 36.678037°N 107.209205°W
| Project Gasbuggy | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Information | |
| Country | United States |
| Test series |
Operation Crosstie Operation Plowshare |
| Test site | Carson National Forest |
| Date | December 10, 1967 |
| Test type | Underground |
| Yield | 29 kt |
Project Gasbuggy was an underground nuclear detonation carried out by the United States Atomic Energy Commission on December 10, 1967 in rural northern New Mexico. It was part of Operation Plowshare, a program designed to find peaceful uses for nuclear explosions.[1]
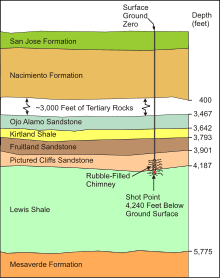
Gasbuggy was carried out by the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory and the El Paso Natural Gas Company, with funding from the Atomic Energy Commission. Its purpose was to determine if nuclear explosions could be useful in fracturing rock formations for natural gas extraction.[2] The site, lying in the Carson National Forest, is approximately 34 km (21 mi) southwest of Dulce, New Mexico and 87 km (54 mi) east of Farmington, and was chosen because natural gas deposits were known to be held in sandstone beneath Leandro Canyon.[3] A 29 kt (120 TJ) device was placed at a depth of 1,288 m (4,227 ft) underground,[4] then the well was backfilled before the device was detonated; a crowd had gathered to watch the detonation from atop a nearby butte.

The detonation took place after a couple of delays, the last one caused by a breakdown of the explosive refrigeration system. The detonation produced a rubble chimney that was 24 m (80 ft) wide and 102 m (335 ft) high above the blast center.[5]
After an initial surface cleanup effort the site sat idle for over a decade. A later surface cleanup effort primarily tackled leftover toxic materials. In 1978, a marker monument was installed at the Surface Ground Zero (SGZ) point that provided basic explanation of the historic test. Below the main plaque lies another which indicates that no drilling or digging is allowed without government permission.
The site is publicly accessible via the Carson National Forest, F.S. 357 dirt road/Indian J10 that leads into the Carson National Forest.
Following the Project Gasbuggy test, two subsequent nuclear explosion fracturing experiments were conducted in western Colorado in an effort to refine the technique. They were Project Rulison in 1969 and Project Rio Blanco in 1973. In both cases the gas radioactivity was still seen as too high and in the last case the triple-blast rubble chimney structures disappointed the design engineers. Soon after that test the ~ 15-year Project Plowshare program funding dried up.
These early fracturing tests were later superseded by hydraulic fracturing (fracking) technologies.
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Crosstie Gasbuggy. |
- ↑ Peter Metzger (February 22, 1970). "Project Gasbuggy And Catch-85*: *That's krypton-85, one of the radioactive by-products of nuclear explosions that release natural gas Project Gasbuggy and Catch-85 "It's 95 per cent safe? We worry about the other 5"". New York Times: SM14.
- ↑ Project Gasbuggy. Popular Mechanics, September 1967.
- ↑ A Good Start for Gasbuggy. Time, December 22, 1967.
- ↑ Project Gasbuggy, Atomictourist.com. Size and depth as per placard at the site.
- ↑ Gasbuggy Nuclear Test Site. Center for Land Use Interpretation. Accessed April 11, 2011.