HMG-CoA
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
(9R,21S)-1-[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-
(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy- 3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydrofuran-2-yl]- 3,5,9,21-tetrahydroxy-8,8,21-trimethyl- 10,14,19-trioxo-2,4,6-trioxa-18-thia- 11,15-diaza-3,5-diphosphatricosan-23- oic acid 3,5-dioxide | |
| Identifiers | |
| 1553-55-5 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:61659 |
| ChemSpider | 392859 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.014.820 |
| 3040 | |
| MeSH | HMG-CoA |
| PubChem | 445127 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C27H44N7O20P3S | |
| Molar mass | 911.661 g/mol |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
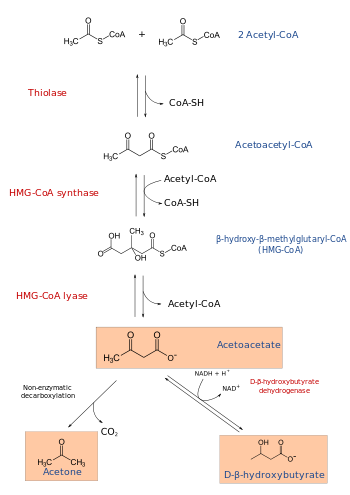
HMG-CoA (or 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A) is an intermediate in the mevalonate and ketogenesis pathways. It is formed from acetyl CoA and acetoacetyl CoA by HMG-CoA synthase. The researches of Minor J. Coon and Bimal Kumar Bachhawat in the 1950s at University of Illinois led to its discovery.[1][2]
It is also an intermediate in the metabolism of leucine. Its immediate precursor is 3-methylglutaconyl CoA.
Mevalonate pathway
Main article: Mevalonate pathway
HMG-CoA reductase converts it into mevalonic acid.

Mevalonate pathway
Ketogenesis pathway
HMG-CoA lyase breaks it into acetyl CoA and acetoacetate.
References
- ↑ Debi P. Sarkar (2015). "Classics in Indian Medicine" (PDF). The National Medical Journal of India (28): 3.
- ↑ Avadhesha Surolia (1997). "An outstanding scientist and a splendid human being" (PDF). Glycobiology. 7 (4): v–ix.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 9/24/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.