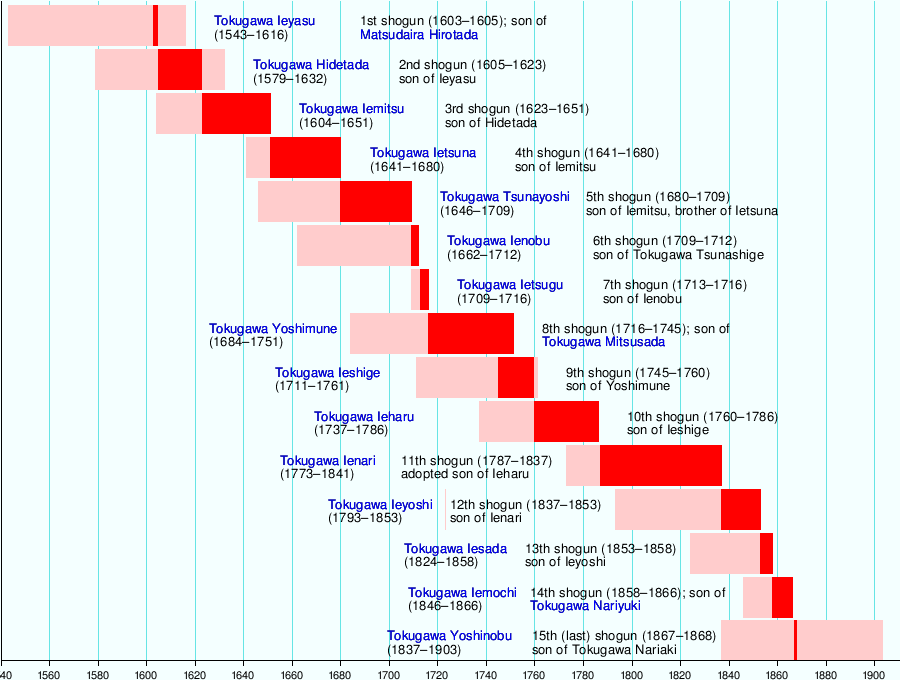
Tokugawa Hidetada
| Tokugawa Hidetada | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 2nd Edo shogun | |
|
In office 1605–1623 | |
| Monarch | Go-Yōzei |
| Preceded by | Tokugawa Ieyasu |
| Succeeded by |
Shogun: Tokugawa Iemitsu |
| Personal details | |
| Born | May 2, 1579 |
| Died | March 14, 1632 (aged 52) |
| Relations |
Father: Tokugawa Ieyasu Mother: Saigō-no-Tsubone |
| Children |
Senhime by Oeyo Tamahime by Oeyo Katsuhime by Oeyo Hatsuhime by Oeyo Chomaru (1601-1602) by Oshizu Tokugawa Iemitsu by Oeyo Tokugawa Tadanaga by Oeyo Hoshina Masayuki by Oshizu Others |
Tokugawa Hidetada (徳川 秀忠, May 2, 1579 – March 14, 1632) was the second shogun of the Tokugawa dynasty, who ruled from 1605 until his abdication in 1623. He was the third son of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the first shogun of the Tokugawa shogunate.
Early life (1579–1593)
Tokugawa Hidetada was born to Tokugawa Ieyasu and the Lady Saigō (the first of his many consorts) on May 2, 1579. This was shortly before Lady Tsukiyama, Ieyasu's official wife, and their son Tokugawa Nobuyasu were executed on suspicion of plotting to assassinate Oda Nobunaga, who was Nobuyasu's father-in-law and Ieyasu's ally. By killing his wife and son, Ieyasu declared his loyalty to Nobunaga. In 1589, Hidetada's mother fell ill, her health rapidly deteriorated, and she died at Sunpu Castle.
The traditional power base of the Tokugawa clan was Mikawa. In 1590, the new ruler of Japan, Toyotomi Hideyoshi enlisted Tokugawa Ieyasu and others in attacking the domain of the Hōjō in what became known as the Siege of Odawara (1590). Hideyoshi enlisted Ieyasu for this campaign by promising to exchange the five provinces under Ieyasu's control for the eight Kantō provinces, including the city of Edo. In order to keep Ieyasu from defecting to the Hōjō side (since the Hōjō and the Tokugawa were formerly on friendly terms), Hideyoshi took the eleven-year-old Nagamaru as a hostage. In 1592 Hideyoshi presided over Nagamaru's coming of age ceremony; it was then that Ieyasu's son dropped his childhood name, Nagamaru, and assumed the name Hidetada. He was named the heir of the Tokugawa family, being the eldest surviving son of Ieyasu, and his favorite (since Ieyasu's eldest son had been previously executed, and his second son was adopted by Hideyoshi while still an infant). In 1593, Hidetada returned to his father's side.
Military achievements (1593–1605)
In 1595, Hidetada married Oeyo of the Oda clan and they had two sons, Tokugawa Iemitsu and Tokugawa Tadanaga.[1] They also had two daughters, one of whom, Sen hime, married twice. The other daughter, Kazuko hime, married Emperor Go-Mizunoo (of descent from the Fujiwara clan).[2]
Knowing his death would come before his son Toyotomi Hideyori came of age, Hideyoshi named five regents—one of whom was Hidetada's father, Ieyasu—to rule in his son's place. Hideyoshi hoped that the bitter rivalry among the regents would prevent any one of them from seizing power. But after Hideyoshi died in 1598 and Hideyori became nominal ruler, the regents forgot all vows of eternal loyalty and were soon vying for control of the nation. Tokugawa Ieyasu was one of the strongest of the five regents, and began to rally around himself an Eastern faction. A Western faction rallied around Ishida Mitsunari. The two factions clashed at the Battle of Sekigahara, which set the stage for Tokugawa rule.
In 1600 Hidetada led 16,000 of his father's men in a campaign to contain the Western-aligned Uesugi clan in Shinano. Ieyasu then ordered Hidetada to march his troops to Sekigahara in anticipation of the decisive battle against the Western faction. But the Sanada Clan managed to tie Hidetada's forces down, meaning that he arrived too late to assist in his father's narrow but decisive victory. Hidetada and Ieyasu's relationship never recovered.
In 1603 Emperor Go-Yozei granted Ieyasu the title of shogun. Thus Hidetada became the heir to the shogunate.
Shogun (1605–1623)
In order to avoid his predecessor's fate, Ieyasu established a dynastic pattern soon after becoming shogun by abdicating in favor of Hidetada in 1605. Ieyasu retained significant power until his death in 1616; but Hidetada nevertheless assumed a role as formal head of the bakufu bureaucracy.[3]
Much to the dismay of Ieyasu, in 1612, Hidetada engineered a marriage between Sen, Ieyasu's favorite granddaughter, and Toyotomi Hideyori, who was living as a commoner in Osaka Castle with his mother. When this failed to quell Hideyori's intrigues, Ōgosho Ieyasu and Shogun Hidetada brought an army to Osaka.[4] Father and son once again disagreed on how to conduct this campaign against the recalcitrant Toyotomi forces in Osaka. In the ensuing siege Hideyori and his mother were forced to commit suicide. Even Hideyori's infant son (Kunimatsu), that he had with a concubine, was not spared. Only Sen was spared; she later remarried and had a new family.
After Ieyasu's death in 1616,[4] Hidetada took control of the bakufu. He strengthened the Tokugawa hold on power by improving relations with the Imperial court. To this end he married his daughter Kazuko to Emperor Go-Mizunoo.[4] The product of that marriage, a girl, eventually succeeded to the throne of Japan to become Empress Meishō. The city of Edo was also heavily developed under his reign.
Ogosho (1623–1632)
In Genna 9 (1623) Hidetada resigned the government to his eldest son and heir, Tokugawa Iemitsu.[5] Like his father before him, Hidetada became Ogosho or Retired Shogun, and retained effective power. He enacted draconian anti-Christian measures, which Ieyasu had only considered: he banned Christian books, forced Christian daimyo to commit suicide, ordered all other Christians to apostatize, and executed the fifty-five Christians (both Japanese and foreign) who refused to renounce Christianity or to go into hiding, in Nagasaki in 1628.
Ogosho Hidetada died in Kan'ei 9, on the 24th day of the 1st month (1632).[5] His buddhist posthumous name is Taitoku-in.[6] His ashes were ceremoniously laid to rest in the Taitoku-in Mausoleum in Edo.
Honours
- Senior First Rank (March 30, 1632; posthumous)
Eras
The years in which Hidetada was shogun are more specifically identified by more than one era name or nengō.[4]
Notable descendants
Notable descendants of Tokugawa Hidetada, by his wife Oeyo, include:
- Senhime - Daughter, married Toyotomi Hideyori and later married Honda Tadatoki
- Toyotomi Kunimatsu
- Kochiyo
- Katsuhime married Ikeda Mitsumasa
- Tamahime married Maeda Toshitsune
- Tokugawa Masako - Daughter, married Emperor Go-Mizunoo
- Tokugawa Tadanaga- Son, married Oyu, daughter of Oda Nobusada and granddaughter of Oda Nobunaga
- Tokugawa Iemitsu - Son, 3rd shogun
- Tokugawa Ietsuna - 4th shogun
- Tokugawa Tsunayoshi - 5th shogun
- Tsuruhime (1677-1686)
- Tokugawa Tokumatsu (1679-1686)
- Chosomaru (1683-1686)
- Yanagisawa Yoshisato (1686-1724)
- Tokugawa Tsunashige
- Tokugawa Ienobu - 6th shogun
- Tokugawa Iechiyo
- Tokugawa Daigoro (1709-1710)
- Tokugawa Ietsugu - 7th shogun
- Tokugawa Torakichi (1711-1712)
- Tokugawa Ienobu - 6th shogun
- Matsudaira Katahiro - 7th generation descendant
Children of Hidetada, by a concubine, include:
- Chomaru
- Hoshina Masayuki
- Hoshina Masatsune
- Hoshina Masakata
- Himehime
Notes
- ↑ Wilson, Richard L. (1985). Ogata Kenzan (1663-1743) (PhD thesis/dissertation). Lawrence, Kansas: University of Kansas. OCLC 19111312
- ↑ NHK has announced that its 2011 Taiga drama will be named Gō: Himetachi no Sengoku; and it will be based on the life of Oeyo, who was the mother of Tokugwa Masako -- see 大河ドラマ 第50 作 江(ごう) 姫たちの戦国; "Atsuhime"-Autorin für NHKs 2011er Taiga-Drama gewählt (citing Tokyograph), J-Dorama.
- ↑ Titsingh, I. (1834). Annales des empereurs du Japon, p. 409.
- 1 2 3 4 Titsingh, p. 410.
- 1 2 Screech, T. Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822. p.85.
- ↑ f1aQAgAAQBAJ Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822 at Google Books
References
- Screech, Timon. (2006). Secret Memoirs of the Shoguns: Isaac Titsingh and Japan, 1779-1822. London: RoutledgeCurzon. ISBN 0-7007-1720-X
- Titsingh, Isaac. (1822). Illustrations of Japan. London: Ackerman.
- Titsingh, Isaac, ed. (1834). [Siyun-sai Rin-siyo/Hayashi Gahō, 1652], Nipon o daï itsi ran; ou, Annales des empereurs du Japon Paris: Oriental Translation Fund of Great Britain and Ireland.
- Totman, Conrad. (1967). Politics in the Tokugawa bakufu, 1600-1843. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Wilson, Richard L. (1985). Ogata Kenzan (1663-1743) (PhD thesis/dissertation). Lawrence, Kansas: University of Kansas. OCLC 19111312
| Military offices | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Tokugawa Ieyasu |
Edo Shogun: Tokugawa Hidetada 1605–1623 |
Succeeded by Tokugawa Iemitsu |