Kh-38
| Kh-38 | |
|---|---|
|
Kh-38ME | |
| Type | Tactical air-to-surface missile |
| Place of origin | Russia |
| Service history | |
| In service | 2012 |
| Used by | Russia |
| Production history | |
| Designer | Tactical Missiles Corporation JSC |
| Designed | 2007 |
| Manufacturer | Tactical Missiles Corporation JSC |
| Produced | 2013 |
| Specifications | |
| Weight | 520 kg (1,150 lb) |
| Length | 4.2 m (13 ft 9 in) |
| Diameter | 0.31 m (12.2 in) |
| Warhead | HE fragmentation, cluster warhead, armor-piercing |
| Warhead weight | up to 250 kg (551 lb) |
Detonation mechanism | Contact fuse |
|
| |
| Engine | Solid rocket motor |
| Wingspan | 1.14 m (44.9 in) |
Operational range | up to 40 km (21.6 nmi) |
| Speed | Mach 2.2 |
Guidance system | Laser, active radar, IR, satellite, depending on variant |
Launch platform | Su-34, PAK FA, Ka-52K |
The Kh-38/Kh-38M (Russian: Х-38) is a family of air-to-surface missiles meant to succeed the Kh-25 family of missiles.
Design
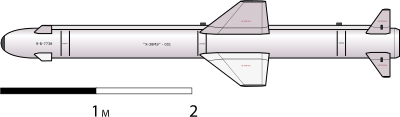
The basic configuration of the Kh-38M was revealed at the 2007 Moscow Air Show (MAKS). The modular guided air-to-surface missile is meant to succeed the venerable Kh-25 missile family. The missile is designed to be carried by the fifth-generation PAK FA fighter aircraft. The missile has folding wings and tail fins for internal carriage, and would have a variety of seeker heads for different variants.[1]
Variants
- Kh-38MAE - inertial, active radar homing
- Kh-38MKE - inertial, satellite guidance
- Kh-38MLE - inertial, laser guidance
- Kh-38MTE - inertial, infrared guidance
- Kh-36 Grom-1 AS-23 tactical cruise missile / AGM Air to Surface with 130–260 km range and
- Kh-36P Grom-2 AS-23B / KAB- guided bomb gliding LGB version, 250 and 500 kg, various aim guidance, both created on the base of Kh-38M short-range tactical missile and also have a modular structure, warheads and seekers, can be propelled modified, shown at MAKS 2015
- Kh-38M2 improvement of Kh-38M, optoelectronic IR UV (CCD also ?) sensors
See also
References
- ↑ Barrie, Douglas and Komarov, Alexey. "War on Two Fronts for Russia's Missile Builders ". Aviation Week, 10 September 2007. Retrieved: 25 May 2014.
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 10/29/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.
