Provincial historic sites of Alberta



Provincial historic sites of Alberta are museums and historic sites run by the Government of Alberta.[1]
Only sites owned by the provincial government and run as a functioning historic site or museum are known as Provincial Historic Sites. Buildings and sites owned by private citizens and companies or other levels or branches of government may gain one of two levels of historic designation, "Registered Historic Resource" or "Provincial Historic Resource".[2] A concentration of several heritage buildings can be designated a "Provincial Historic Area", and there are two such areas in Alberta: downtown Fort Macleod and Old Strathcona in Edmonton. Historic designation in Alberta is governed by the Historic Resources Act.[3] The province also lists buildings deemed historically significant by municipal governments on the Alberta Register of Historic Places, which is also part of the larger Canadian Register of Historic Places although this does not imply provincial or federal government status or protection.[4] The Alberta Main Street Program helps to preserve historic buildings in the downtowns of smaller communities.[5] The Heritage Survey Program is a survey of 80,000 historic buildings in Alberta, with no protective status.[6]
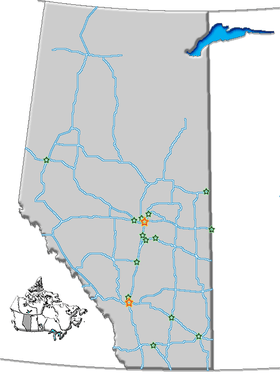
The official list as per the government of Alberta is:[7]
- Brooks Aqueduct, irrigation museum near Brooks
- Carmangay Tipi Rings - archaeological tipi ring site at Carmangay, near Calgary
- Father Lacombe Chapel / Chapelle du Père Lacombe - missionary church built by Father Albert Lacombe in 1861 in St. Albert
- Frank Slide Interpretive Centre - site of rock slide tragedy in 1903, in Frank
- Fort George and Buckingham House - fur trade post, near Elk Point
- Head-Smashed-In Buffalo Jump - (also UNESCO World Heritage Site and National Historic Site of Canada) - First Nations' history, near Fort Macleod
- Historic Dunvegan - fur trade post and mission, near Fairview
- Leitch Collieries - coal mine, Crowsnest Pass
- Lougheed House - sandstone mansion from 1891 in Calgary.
- Oil Sands Discovery Centre - oil sands mining display, Fort McMurray
- Okotoks Erratic - giant rock left by glaciers, Okotoks
- Remington Carriage Museum - collection of horse-drawn forms of transportation, Cardston
- Reynolds-Alberta Museum - machinery and transportation, aviation hall of fame, Wetaskiwin
- Royal Alberta Museum - official provincial museum (formerly Provincial Museum of Alberta), Edmonton
- Royal Tyrrell Museum - dinosaurs and palaeontology, near Drumheller
- Rutherford House - home of Albert's first premier, University of Alberta, Edmonton
- Stephansson House - home of famous Icelandic poet Stephan G. Stephansson, near Red Deer
- Turner Valley Gas Plant - site of early oil discovery, near Calgary
- Tyrrell Field Station - field station of Tyrrell Museum, near Brooks
- Ukrainian Cultural Heritage Village - recreation of early Ukrainian settlement in Canada, near Edmonton
- Victoria Settlement - early pioneer settlement, near Smoky Lake
See also
References
- ↑ Alberta Tourism, Parks, Recreation and Culture. "Museums and Historic Sites". Retrieved 2008-02-14.
- ↑ Alberta Culture and Community Spirit - Historic Resources Management - Historic Places Stewardship Section - Alberta's Historic Places Designation Program
- ↑ Alberta Queen's Printer
- ↑ Alberta Culture and Community Spirit - Historic Resources Management - Historic Places Stewardship Section - Alberta's Historic Places Designation Program - Municipal Historic Resource Designation
- ↑ The Alberta Main Street Program
- ↑ Alberta Culture and Community Spirit - Historic Resources Management - Historic Places Stewardship Section - Heritage Survey Program
- ↑ http://culture.alberta.ca/museums/historicsiteslisting/default.aspx
External links
For a partial list of privately owned buildings or other sites that are designated as "Provincial Historic Resources" see:
- Alberta Tourism, Parks, Recreation and Culture - List of Historic Resources Designated in 2001
- List of Historic Resources Designated in 2002