Olivine
| Olivine | |
|---|---|
 | |
| General | |
| Category |
Nesosilicate Olivine group Olivine series |
| Formula (repeating unit) | (Mg, Fe)2SiO4 |
| Strunz classification | 9.AC.05 |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic |
| Identification | |
| Color | Yellow to yellow-green |
| Crystal habit | Massive to granular |
| Cleavage | Poor |
| Fracture | Conchoidal – brittle |
| Mohs scale hardness | 6.5–7 |
| Luster | Vitreous |
| Streak | None |
| Diaphaneity | Transparent to translucent |
| Specific gravity | 3.2–4.5[1][2][3][4] |
| Optical properties | Biaxial (+) |
| Refractive index |
nα = 1.630–1.650 nβ = 1.650–1.670 nγ = 1.670–1.690 |
| Birefringence | δ = 0.040 |
| References | [5][6][7] |
The mineral olivine (pronunciation: /ˈɒlᵻˌviːn/) is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula (Mg+2, Fe+2)2SiO4. Thus it is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface.
The ratio of magnesium and iron varies between the two endmembers of the solid solution series: forsterite (Mg-endmember: Mg2SiO4) and fayalite (Fe-endmember: Fe2SiO4). Compositions of olivine are commonly expressed as molar percentages of forsterite (Fo) and fayalite (Fa) (e.g., Fo70Fa30). Forsterite has an unusually high melting temperature at atmospheric pressure, almost 1,900 °C (3,450 °F), but the melting temperature of fayalite is much lower (about 1,200 °C [2,190 °F]). The melting temperature varies smoothly between the two endmembers, as do other properties. Olivine incorporates only minor amounts of elements other than oxygen, silicon, magnesium and iron. Manganese and nickel commonly are the additional elements present in highest concentrations.
Olivine gives its name to the group of minerals with a related structure (the olivine group) which includes tephroite (Mn2SiO4), monticellite (CaMgSiO4) and kirschsteinite (CaFeSiO4).
Olivine's crystal structure incorporates aspects of the orthorhombic P Bravais lattice, which arise from each silica (SiO4) unit being joined by metal divalent cations with each oxygen in SiO4 bound to 3 metal ions. It has a spinel-like structure similar to magnetite but uses one quadravalent and two divalent cations M2+2 M+4O4 instead of two trivalent and one divalent cations.[8]
Olivine gemstones are called peridot and chrysolite.
Identification and paragenesis


Olivine is named for its typically olive-green color (thought to be a result of traces of nickel), though it may alter to a reddish color from the oxidation of iron.
Translucent olivine is sometimes used as a gemstone called peridot (péridot, the French word for olivine). It is also called chrysolite (or chrysolithe, from the Greek words for gold and stone). Some of the finest gem-quality olivine has been obtained from a body of mantle rocks on Zabargad island in the Red Sea.
Olivine occurs in both mafic and ultramafic igneous rocks and as a primary mineral in certain metamorphic rocks. Mg-rich olivine crystallizes from magma that is rich in magnesium and low in silica. That magma crystallizes to mafic rocks such as gabbro and basalt. Ultramafic rocks such as peridotite and dunite can be residues left after extraction of magmas, and typically they are more enriched in olivine after extraction of partial melts. Olivine and high pressure structural variants constitute over 50% of the Earth's upper mantle, and olivine is one of the Earth's most common minerals by volume. The metamorphism of impure dolomite or other sedimentary rocks with high magnesium and low silica content also produces Mg-rich olivine, or forsterite.
Fe-rich olivine is relatively much less common, but it occurs in igneous rocks in small amounts in rare granites and rhyolites, and extremely Fe-rich olivine can exist stably with quartz and tridymite. In contrast, Mg-rich olivine does not occur stably with silica minerals, as it would react with them to form orthopyroxene ((Mg,Fe)2Si2O6).
Mg-rich olivine is stable to pressures equivalent to a depth of about 410 km (250 mi) within Earth. Because it is thought to be the most abundant mineral in Earth’s mantle at shallower depths, the properties of olivine have a dominant influence upon the rheology of that part of Earth and hence upon the solid flow that drives plate tectonics. Experiments have documented that olivine at high pressures (e.g. 12 GPa, the pressure at depths of about 360 km (220 mi)) can contain at least as much as about 8900 parts per million (weight) of water, and that such water contents drastically reduce the resistance of olivine to solid flow; moreover, because olivine is so abundant, more water may be dissolved in olivine of the mantle than contained in Earth's oceans.[9]
Extraterrestrial occurrences
Mg-rich olivine has also been discovered in meteorites,[11] on the Moon[12] and Mars,[13][14] falling into infant stars,[15] as well as on asteroid 25143 Itokawa.[16] Such meteorites include chondrites, collections of debris from the early Solar System; and pallasites, mixes of iron-nickel and olivine.
The spectral signature of olivine has been seen in the dust disks around young stars. The tails of comets (which formed from the dust disk around the young Sun) often have the spectral signature of olivine, and the presence of olivine was verified in samples of a comet from the Stardust spacecraft in 2006.[17] Comet-like (magnesium-rich) olivine has also been detected in the planetesimal belt around the star Beta Pictoris.[18]
Crystal structure
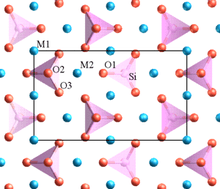
Minerals in the olivine group crystallize in the orthorhombic system (space group Pbnm) with isolated silicate tetrahedra, meaning that olivine is a nesosilicate. In an alternative view, the atomic structure can be described as a hexagonal, close-packed array of oxygen ions with half of the octahedral sites occupied with magnesium or iron ions and one-eighth of the tetrahedral sites occupied by silicon ions.
There are three distinct oxygen sites (marked O1, O2 and O3 in figure 1), two distinct metal sites (M1 and M2) and only one distinct silicon site. O1, O2, M2 and Si all lie on mirror planes, while M1 exists on an inversion center. O3 lies in a general position.
High pressure polymorphs
At the high temperatures and pressures found at depth within the Earth the olivine structure is no longer stable. Below depths of about 410 km (250 mi) olivine undergoes an exothermic phase transition to the sorosilicate, wadsleyite and, at about 520 km (320 mi) depth, wadsleyite transforms exothermically into ringwoodite, which has the spinel structure. At a depth of about 660 km (410 mi), ringwoodite decomposes into silicate perovskite ((Mg,Fe)SiO3) and ferropericlase ((Mg,Fe)O) in an endothermic reaction. These phase transitions lead to a discontinuous increase in the density of the Earth's mantle that can be observed by seismic methods. They are also thought to influence the dynamics of mantle convection in that the exothermic transitions reinforce flow across the phase boundary, whereas the endothermic reaction hampers it.[19]
The pressure at which these phase transitions occur depends on temperature and iron content.[20] At 800 °C (1,070 K; 1,470 °F), the pure magnesium end member, forsterite, transforms to wadsleyite at 11.8 gigapascals (116,000 atm) and to ringwoodite at pressures above 14 GPa (138,000 atm). Increasing the iron content decreases the pressure of the phase transition and narrows the wadsleyite stability field. At about 0.8 mole fraction fayalite, olivine transforms directly to ringwoodite over the pressure range 10.0 to 11.5 GPa (99,000–113,000 atm). Fayalite transforms to Fe
2SiO
4 spinel at pressures below 5 GPa (49,000 atm). Increasing the temperature increases the pressure of these phase transitions.
Weathering
Olivine is one of the weaker common minerals on the surface according to the Goldich dissolution series. It alters into iddingsite (a combination of clay minerals, iron oxides and ferrihydrites) readily in the presence of water.[21] The presence of iddingsite on Mars would suggest that liquid water once existed there, and might enable scientists to determine when there was last liquid water on the planet.[22]
Uses
A worldwide search is on for cheap processes to sequester CO2 by mineral reactions, called enhanced weathering. Removal by reactions with olivine is an attractive option, because it is widely available and reacts easily with the (acid) CO2 from the atmosphere. When olivine is crushed, it weathers completely within a few years, depending on the grain size. All the CO2 that is produced by burning 1 liter of oil can be sequestered by less than 1 liter of olivine. The reaction is exothermic but slow. To recover the heat produced by the reaction to produce electricity, a large volume of olivine must be thermally well-isolated. The end-products of the reaction are silicon dioxide, magnesium carbonate and small amounts of iron oxide.[23][24]
The aluminium foundry industry uses olivine sand to cast objects in aluminium. Olivine sand requires less water than silica sands while still holding the mold together during handling and pouring of the metal. Less water means less gas (steam) to vent from the mold as metal is poured into the mold.[25]
In Finland, olivine is marketed as an ideal rock for sauna stoves because of its comparatively high density and resistance to weathering under repeated heating and cooling. Olivine is also used to tap blast furnaces in the steel industry, acting as a plug, removed in each steel run.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Olivine. |
References
- ↑ Mick R. Smith (1999). Stone: Building Stone, Rock Fill and Armourstone in Construction. Geological Society of London. pp. 62–. ISBN 978-1-86239-029-4.
Specific Gravity 3.5-4.5
- ↑ Jessica Elzea Kogel (2006). Industrial Minerals & Rocks: Commodities, Markets, and Uses. SME. pp. 679–. ISBN 978-0-87335-233-8.
The specific gravity is approximately 3.2 when pure rises with increasing iron content.
- ↑ "Olivine". Science.smith.edu. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
G = 3.22 to 4.39. Specific gravity increases and hardness decreases with increasing Fe.
- ↑ "University of Minnesota's Mineral Pages: Olivine". Geo.umn.edu. Retrieved 2013-11-14.
Specific Gravity: 3.2 (Mg-rich variety) to 4.3 (Iron-rich variety) (average weight)
- ↑ Olivine. Webmineral.com Retrieved on 2012-06-16.
- ↑ Olivine. Mindat.org Retrieved on 2012-06-16.
- ↑ Klein, Cornelis; C. S. Hurlburt (1985). Manual of Mineralogy (21st ed.). New York: John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-80580-7.
- ↑ Ernst, W. G. Earth Materials. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall, 1969. Print. p.65
- ↑ Smyth, J. R.; Frost, D. J.; Nestola, F.; Holl, C. M.; Bromiley, G. (2006). "Olivine hydration in the deep upper mantle: Effects of temperature and silica activity". Geophysical Research Letters. 33 (15). Bibcode:2006GeoRL..3315301S. doi:10.1029/2006GL026194.
- ↑ Brown, Dwayne (October 30, 2012). "NASA Rover's First Soil Studies Help Fingerprint Martian Minerals". NASA. Retrieved October 31, 2012.
- ↑ Fukang and other Pallasites. Farlang.com (2008-04-30). Retrieved on 2012-06-16.
- ↑ Meyer, C. (2003). "Mare Basalt Volcanism" (PDF). NASA Lunar Petrographic Educational Thin Section Set. NASA. Retrieved 23 October 2016.
- ↑ Pretty Green Mineral....Mission Update 2006... UMD Deep Impact Website, University of Maryland Ball Aerospace & Technology Corp. retrieved June 1, 2010
- ↑ Hoefen, T.M., et al. 2003. Discovery of Olivine in the Nili Fossae Region of Mars. Science 302, 627-630. "http://www.sciencemag.org/content/302/5645/627"
- ↑ Spitzer Sees Crystal Rain... NASA Website
- ↑ Japan says Hayabusa brought back asteroid grains... retrieved November 18, 2010
- ↑ Press Release 06-091. Jet Propulsion Laboratory Stardust website, retrieved May 30, 2006.
- ↑ De Vries, B. L.; Acke, B.; Blommaert, J. A. D. L.; Waelkens, C.; Waters, L. B. F. M.; Vandenbussche, B.; Min, M.; Olofsson, G.; Dominik, C.; Decin, L.; Barlow, M. J.; Brandeker, A.; Di Francesco, J.; Glauser, A. M.; Greaves, J.; Harvey, P. M.; Holland, W. S.; Ivison, R. J.; Liseau, R.; Pantin, E. E.; Pilbratt, G. L.; Royer, P.; Sibthorpe, B. (2012). "Comet-like mineralogy of olivine crystals in an extrasolar proto-Kuiper belt" (PDF). Nature. 490 (7418): 74–76. doi:10.1038/nature11469. PMID 23038467.
- ↑ Christensen, U.R. (1995). "Effects of phase transitions on mantle convection". Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 23: 65–87. Bibcode:1995AREPS..23...65C. doi:10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.000433.
- ↑ Deer, W. A.; R. A. Howie; J. Zussman (1992). An Introduction to the Rock-Forming Minerals (2nd ed.). London: Longman. ISBN 0-582-30094-0.
- ↑ Kuebler, K.; Wang, A.; Haskin, L. A.; Jolliff, B. L. (2003). "A Study of Olivine Alteration to Iddingsite Using Raman Spectroscopy" (PDF). Lunar and Planetary Science. 34: 1953.
- ↑ Swindle, T. D.; Treiman, A. H.; Lindstrom, D. J.; Burkland, M. K.; Cohen, B. A.; Grier, J. A.; Li, B.; Olson, E. K. (2000). "Noble Gases in Iddingsite from the Lafayette meteorite: Evidence for Liquid water on Mars in the last few hundred million years". Meteoritics and Planetary Science. 35 (1): 107–115. Bibcode:2000M&PS...35..107S. doi:10.1111/j.1945-5100.2000.tb01978.x.
- ↑ Goldberg, P.; Chen, Z.-Y.; O'Connor, W.; Walters, R.; Ziock, H. (2000). "CO2 Mineral Sequestration Studies in US" (PDF). Technology. 1 (1): 1–10.
- ↑ Schuiling, R. D.; Krijgsman, P. (2006). "Enhanced Weathering: An Effective and Cheap Tool to Sequester CO2". Climatic Change. 74 (1–3): 349–354. doi:10.1007/s10584-005-3485-y.
- ↑ Ammen, C. W. (1980). The Metal Caster's Bible. Blue Ridge Summit PA: TAB. p. 331. ISBN 0-8306-9970-8.
External links
- Pretty Green Mineral – Pretty Dry Mars? by Linda M.V. Martel, Planetary Science Research Discoveries, Hawai'i Institute of Geophysics and Planetology
- Olivine Page Farlang library: Historic sources + modern articles on Olivine and Peridot
- Geological information and several microscopic images University of North Dakota
