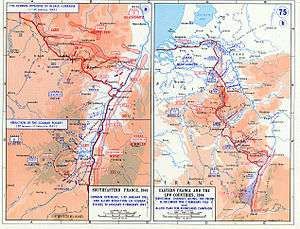
Operation Nordwind
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Operation North Wind (Unternehmen Nordwind) was the last major German offensive of World War II on the Western Front. It began on 31 December 1944 in Alsace and Lorraine in northeastern France, and ended on 25 January.
Objectives
In a briefing at his military command complex at Adlerhorst, Adolf Hitler declared in his speech to his division commanders on 28 December 1944 (three days prior to the launch of Operation Nordwind): "This attack has a very clear objective, namely the destruction of the enemy forces. There is not a matter of prestige involved here. It is a matter of destroying and exterminating the enemy forces wherever we find them." [4]:499
The goal of the offensive was to break through the lines of the U.S. Seventh Army and French 1st Army in the Upper Vosges mountains and the Alsatian Plain, and destroy them. This would leave the way open for Operation Dentist (Unternehmen Zahnarzt), a planned major thrust into the rear of the U.S. Third Army which would lead to the destruction of that army.[4]:494
Offensive
On 31 December 1944, German Army Group G—commanded by Generaloberst Johannes Blaskowitz—and Army Group Oberrhein ("Upper Rhein")—commanded by Reichsführer-SS Heinrich Himmler—launched a major offensive against the thinly stretched, 110 kilometres (68 mi)-long front line held by the U.S. 7th Army. Operation Nordwind soon had the understrength U.S. 7th Army in dire straits. The 7th Army —at the orders of U.S. General Dwight D. Eisenhower— had sent troops, equipment, and supplies north to reinforce the American armies in the Ardennes involved in the Battle of the Bulge.
On the same day that the German Army launched Operation Nordwind, the Luftwaffe (German Air Force) committed almost 1,000 aircraft in support. This attempt to cripple the Allied air forces based in northwestern Europe was known as Operation Bodenplatte, which failed without having achieved any of its key objectives.
The initial attack was conducted by three Corps of the German 1st Army of Army Group G, and by 9 January, the XXXIX Panzer Corps was heavily engaged as well. By 15 January at least seventeen German divisions (including units in the Colmar Pocket) from Army Group G and Army Group Oberrhein, including the 6th SS Mountain, 17th SS Panzergrenadier, 21st Panzer, and 25th Panzergrenadier Divisions were engaged in the fighting. Another, smaller, attack was made against the French positions south of Strasbourg, but it was finally stopped.
The U.S. VI Corps—which bore the brunt of the German attacks—was fighting on three sides by 15 January. With casualties mounting, and running severely short on reinforcements, tanks, ammunition, and supplies, Eisenhower, fearing the outright destruction of the U.S. 7th Army, rushed already battered divisions hurriedly relieved from the Ardennes, southeast over 100 km (62 mi), to reinforce the 7th Army. Their arrival was delayed, and the American forces were forced to withdraw to defensive positions on the south bank of the Moder River on 21 January. The German offensive finally drew to a close on 25 January, after the US 222nd Infantry Regiment stopped their advance near Haguenau, and earning the Presidential Unit Citation in the process. This was the same day that the reinforcements began to arrive from the Ardennes. Strasbourg was saved but the Colmar Pocket was a danger which had to be eliminated.
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Zabecki, David T. (2014). Germany at War: 400 Years of Military History. ABC-CLIO. Retrieved 17 July 2016.
- ↑ Warlord Games & Peter Dennis (2014). Bolt Action: Battleground Europe: D-Day to Germany. Osprey Publishing.
- ↑ Captured in Hatten, Danny S. Parker
- 1 2 Clarke, Jeffrey J.; Smith, Robert Ross (1993). Riviera to the Rhine (CMH Pub 7-10). Washington, DC: Center of Military History, Unites States Army. Retrieved 1 May 2016.
Bibliography
- Engler, Richard. The Final Crisis: Combat in Northern Alsace, January 1945. Aberjona Press. 1999. ISBN 978-0-9666389-1-2
- Clarke, Jeffrey J. and Smith, Robert Ross. Riviera to the Rhine (CMH Pub 7-10, GPO S/N: 008-029-00213-2). Center of Military History, Unites States Army: Washington, DC, 1993.
- Nordwind & the US 44th Division *Battle History of the 44th I.D.
- Whiting, Charles (1992). The Other Battle of the Bulge: Operation Northwind. Avon Books. ISBN 0380716283. OCLC 211992045.
External links
- Cirillo, Roger. The Ardennes-Alsace. The U.S. Army Campaigns of World War II. United States Army Center of Military History. CMH Pub 72-26.
- The NORDWIND Offensive (January 1945) on the website of the 100th Infantry Division Association contains a list of German primary sources on the operation.