Oxford railway station
| Oxford | |
|---|---|
|
Oxford station from the south with platforms 4 (left) and 3 (right) | |
| Location | |
| Place | Oxford |
| Local authority | City of Oxford |
| Coordinates | 51°45′12″N 1°16′13″W / 51.7534°N 1.2703°WCoordinates: 51°45′12″N 1°16′13″W / 51.7534°N 1.2703°W |
| Grid reference | SP504063 |
| Operations | |
| Station code | OXF |
| Managed by | Great Western Railway |
| Number of platforms | 3 |
| DfT category | B |
|
Live arrivals/departures, station information and onward connections from National Rail Enquiries | |
| Annual rail passenger usage* | |
| 2010/11 |
|
| 2011/12 |
|
| 2012/13 |
|
| 2013/14 |
|
| 2014/15 |
|
| History | |
| Original company | Great Western Railway |
| Pre-grouping | Great Western Railway |
| Post-grouping | Great Western Railway |
| 1852 | Opened |
| 1971 | Rebuilt |
| 1990 | Rebuilt |
| National Rail – UK railway stations | |
| * Annual estimated passenger usage based on sales of tickets in stated financial year(s) which end or originate at Oxford from Office of Rail and Road statistics. Methodology may vary year on year. | |
|
| |
Oxford railway station is a mainline railway station serving the city of Oxford, England. It is about 0.5 miles (800 m) west of the city centre, north-west of Frideswide Square and the eastern end of Botley Road. It is on the line for trains between London Paddington and Hereford via Worcester Shrub Hill. It is a starting point for fast and local trains to London Paddington (and, planned from December 2016, to London Marylebone), and for local trains to Reading, Worcester and Banbury. It is also on the north/south Cross Country Route from Manchester Piccadilly and Newcastle via Birmingham New Street and Reading to Bournemouth. The station is managed by Great Western Railway, and also served by CrossCountry and Chiltern Railways trains. Immediately to the north is Sheepwash Channel Railway Bridge over the Sheepwash Channel.
History

The Great Western Railway (GWR) opened to Oxford on 12 June 1844[1] with a terminus station in what is now Western Road, Grandpont. In 1845 the Oxford and Rugby Railway (ORR) began to build its line, starting from a junction at New Hinksey 0.75 miles (1.2 km) south of the GWR terminus. The junction was known as Millstream Junction, and was between the future sites of Hinksey Halt and Abingdon Road Halt, both of which were opened in 1908. The GWR took over the ORR while it was still being built, and opened the line as far as Banbury on 2 September 1850. For just over two years, trains from Oxford to Banbury started at Grandpont, and had to reverse at Millstream Junction in order to continue their journey.[2]
The ORR line included a new through station in Park End Street, so when this opened with the extension of the line from Banbury to Birmingham on 1 October 1852, the original Grandpont terminus was closed to passenger services.[1][3] The old station at Grandpont became a goods depot, but was closed completely on 26 November 1872, the day that the broad gauge tracks were removed north of Didcot. The site of the station was then sold, as was the trackbed from Millstream Junction, some 66 chains (1,300 m) in length.[4][5]
Major subsequent changes were removal of the last 7 ft 0 1⁄4 in (2,140 mm) gauge tracks in 1872 and of the train shed in 1890–1. The station was substantially rebuilt by the Western Region of British Railways in 1971, further improvements being carried out during 1974 including the provision of a new travel centre,[6] and the new main building and footbridge were added in 1990 by Network South East.
The station has always been busy. In addition to current services, formerly there were others over the Wycombe Railway, Oxford, Witney and Fairford Railway, and Blenheim and Woodstock Branch Line. [lower-alpha 1] Through trains from the north to the Southern Railway also typically changed locomotives at Oxford.
It was for a time known as Oxford General station to distinguish it from the London and North Western Railway's Oxford Rewley Road terminus of the Varsity Line to Cambridge, which was adjacent and came under joint management in 1933. On 1 October 1951 British Railways closed Rewley Road station to passengers and transferred its services to the former GWR station.[1]

South of the station immediately west of the railway tracks is Osney Cemetery, established in 1848 just before the current station site. Nearby is the site of the former Osney Abbey.
Plans
Further expansion
Passenger traffic at Oxford is growing rapidly. In the nine years 2003–12 the number of passengers using the station increased by 71%[9] and from 2012 to 2015 by a further 6.4% (base 2012).
In November 2009 it was announced that Oxford station would be expanded. A £10 million joint development between Network Rail and Oxfordshire County Council would create a new platform on part of the station’s long-stay car park. The new platform (south of platform 1) would allow trains to arrive and depart from the same track and reduce the need for empty trains to be shunted around the station. Currently, in busy periods trains can be kept waiting outside of the station for a platform to become available.
A new covered footbridge would also be built over Botley Road to link the station building with the new platform, replacing the existing footbridge to the car park. The new platform was to have been brought into use during 2011, and was to be part of the city and county councils' West End Area Action Plan for the western part of the city centre, which also considers other rail projects such as Evergreen 3 and the Paddington – Oxford electrification.[10]
Planning permission has been granted for the expansion to support the proposed Chiltern Railway's service to London Marylebone [11] with a proposed launch date for the service of 12 December 2016.[12] Meanwhile, Oxford City Council, Oxfordshire County Council and Network Rail have developed a masterplan for further development of the station.[13]
Chiltern Railways has raised the possibility of developing a service between Oxford and the Cowley branch line.[14]
Flood remediation work south of the station at Hinksey will see services at the station curtailed & replaced by buses to/from Didcot Parkway for two weeks in July and August 2016. This will see the trackbed raised by 2 feet (0.65 m) and new culverts installed to reduce the impact of flooding from the nearby River Thames upon the railway (which has caused service interruptions on several occasions in recent years). Concurrent bridge repair work at Hanborough and signalling alterations at Banbury will also be carried out over this period. The £18 million scheme was completed on 15 August 2016.[15]
Project Evergreen 3
In August 2008 Chiltern Railways announced Project Evergreen 3, a proposal to construct a 0.25 miles (400 m) chord between the Oxford to Bicester Line and the Chiltern Main Line, to allow a new Oxford to London Marylebone service to run via Bicester Village and High Wycombe. Work began in 2014:[16] the project has been completed as far as Oxford Parkway railway station and the Oxford Parkway/Bicester/Marylebone service commenced on 26 October 2015. The line between Bicester and Oxford Parkway has been doubled and a new station has been built at Oxford Parkway. Services will start from Oxford to Marylebone in December 2016, delayed from Spring 2016 as locals objected to the extra noise that would be caused.[17][18] Network Rail completed the final stages of track relaying in the Wolvercote Tunnel & Peartree areas in September 2016, which will allow operator Chiltern to begin services from here to Oxford Parkway starting at the December 2016 timetable change.[19]
From 2019, this route out of Oxford will be shared with the western section of East West Rail [20] on the former Varsity Line to Winslow, Bletchley, Milton Keynes Central and Bedford.
The scheme also includes two new platforms at Oxford station, to be built on the site of the disused parcels depot. The new platforms will initially be five carriages in length, but provision will be made for them to be extended southwards to eight carriages.[21]
Services
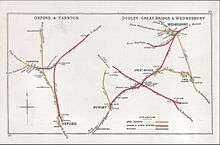
Railways around Oxford | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Legend
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preceding station | |
Following station | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banbury or Tackley | Chiltern Railways Stratford-upon-Avon – Oxford Limited Service[lower-alpha 2] |
Terminus | ||
| Oxford Parkway | Chiltern Railways Interim bus service |
Terminus | ||
| Banbury | CrossCountry Manchester – Bournemouth |
Reading | ||
| CrossCountry Newcastle – Reading and beyond |
||||
| Hanborough or Terminus | Great Western Railway Cotswold Line |
Didcot Parkway or Reading | ||
| Tackley or Terminus |
Great Western Railway Cherwell Valley Line |
Radley | ||
| Future services | ||||
| Oxford Parkway | Chiltern Railways London Marylebone – Oxford |
Terminus | ||
| Oxford Parkway | East West Rail Reading - Bedford or Milton Keynes Central |
Didcot Parkway | ||
| Historical railways | ||||
| Wolvercot Platform Line open; station closed |
Great Western Railway Great Western Main Line |
Hinksey Halt Line open; station closed | ||
Notes
- ↑ The recently published Lost Railways of Oxfordshire[7] gives information on all three of these services and The Woodstock Branch[8] gives an overview of how the service to Oxford changed over the line's life.
- ↑ Currently one train per weekday from Stratford-upon-Avon to Oxford which returns as a stopping service to Banbury.[22]
References
- 1 2 3 Butt, R.V.J. (1995). The Directory of Railway Stations. Yeovil: Patrick Stephens Ltd. p. 179. ISBN 1-85260-508-1. R508.
- ↑ MacDermot, E.T. (1927). History of the Great Western Railway, vol. I: 1833–1863. Paddington: Great Western Railway. p. 300.
- ↑ MacDermot 1927, pp. 322, 324–327
- ↑ Cooke, B.W.C., ed. (November 1957). "The Why and the Wherefore: Original Station at Oxford". The Railway Magazine. Westminster: Tothill Press. 103 (679): 816.
- ↑ MacDermot, E.T. (1931). History of the Great Western Railway, vol. II: 1863–1921. Paddington: Great Western Railway. pp. 65–66, 599.
- ↑ Slater, J.N., ed. (July 1974). "Notes and News: Travel Centre for Oxford Station". Railway Magazine. London: IPC Transport Press Ltd. 120 (879): 361. ISSN 0033-8923.
- ↑ Moors, Terry (2009). Lost Railways of Oxfordshire (First ed.). Newbury, Berkshire: Countryside Books. ISBN 978 1 84674 110 4.
- ↑ Lingard, Richard (1973). The Woodstock Branch (First ed.). Oxford: Oxford Publishing Co. ISBN 978 0 902888 23 4.
- ↑ Office of the Rail Regulator data: see infobox at head of article.
- ↑ Little, Reg (26 November 2009). "Grand plans for Oxford's train station". The Oxford Times. Oxford: Newsquest (Oxfordshire) Ltd. pp. 1, 3.
- ↑ "Oxford City planning approval". Oxford City Council planning. Oxford City Council. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "Press release 20 Jan 2016". Press Releases Chiltern Railways. Chiltern Railways. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "Masterplan". Oxford Station masterplan. Oxford City Council. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "Chiltern railways to Cowley". Two new railway stations planned for Oxford. rail.co.uk. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ↑ "Network Rail to carry out flood alleviation work to improve railway reliability for passengers"Network Rail press release 26 July 2016; Retrieved 1 August 2016
- ↑ "Closure of Oxford to Bicester". Future engineering work. Network Rail. Retrieved 29 January 2016.
- ↑ "Oxford-Marylebone service delayed until December".
- ↑ "Chiltern's Oxford city centre-London services pushed to December".
- ↑ "Oxford to Marylebone track now complete"Network Rail Media Centre press release 21 September 2016; Retrieved 22 September 2016
- ↑ "East West Rail". Home - East West Rail. East West Rail Consortium. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
- ↑ "Chiltern Railways plan to make Bicester well connected". Railnews. 2008-08-29. Retrieved 2008-09-07.
- ↑ "December 2015 Timetable" (PDF). Winter and Spring Train Times. Chiltern Railways. Retrieved 24 January 2016.
Bibliography
- Vaughan, Adrian (1994). The Heart of the Great Western. Great Addington: Silver Link Publishing. ISBN 1-85794-026-1.
- Waters, Laurence (1986). Rail Centres: Oxford. Ian Allan. ISBN 0-7110-1590-2.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Oxford railway station. |
