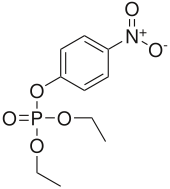
Paraoxon
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | S01EB10 (WHO) |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
311-45-5 |
| PubChem (CID) | 9395 |
| ChemSpider |
9026 |
| UNII |
Q9CX8P80JW |
| ChEBI |
CHEBI:27827 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL23838 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.005.657 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H14NO6P |
| Molar mass | 275.195 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| | |
Paraoxon is a parasympathomimetic which acts as an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor. It is an organophosphate oxon, and the active metabolite of the insecticide parathion. It is also used as an ophthalmological drug against glaucoma. Paraoxon is one of the most potent acetylcholinesterase-inhibiting insecticides available, around 70% as potent as the nerve agent sarin, and so is now rarely used as an insecticide due to the risk of poisoning to humans and other animals. It is easily absorbed through skin, and was used as an assassination weapon by the apartheid-era South African chemical weapons program Project Coast.[1]
References
| Sympathomimetics | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parasympathomimetics |
| ||||||||||
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors/ (sulfonamides) | |||||||||||
| Beta blocking agents | |||||||||||
| Prostaglandin analogues (F2α) |
| ||||||||||
| Other agents | |||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 4/2/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.