Polyene antimycotic
Polyene antimycotics, sometimes referred to as polyene antibiotics, are a class of antimicrobial polyene compounds that target fungi.[1] These polyene antimycotics are typically obtained from some species of Streptomyces bacteria. The polyenes bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane and thus weakens it, causing leakage of K+ and Na+ ions, which may contribute to fungal cell death. Amphotericin B, nystatin, and natamycin are examples of polyene antimycotics. They are a subgroup of macrolides.[2]
Structures
Their chemical structures feature a large ring of atoms (in essence, a cyclic ester ring) containing multiple conjugated carbon-carbon double bonds (hence polyene) on one side of the ring and multiple hydroxyl groups bonded to the other side of the ring. Their structures also often have a d-mycosamine (a type of amino-glycoside) group bonded to the molecule.[3] The series of conjugated double bonds typically absorbs strongly in the ultraviolet-visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum, often resulting in the polyene antibiotics having a yellow color.

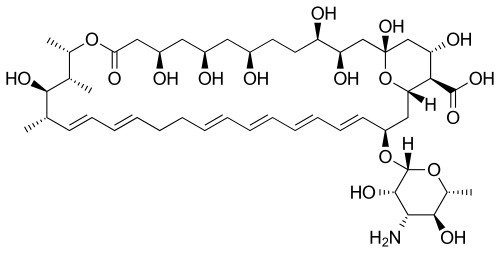
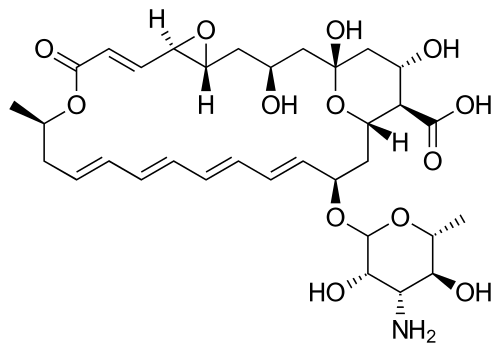
Biosynthesis
The natural route to synthesis includes polyketide synthase components.[4]
Other examples of polyenes
References
- ↑ NCBI Bookshelf (1996). "Polyene Antifungal Drugs". The University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston. Retrieved 29 January 2010.
- ↑ Hamilton-Miller (1973). "Chemistry and Biology of the Polyene Macrolide Antibiotics" (PDF). Bacteriological Reviews. American Society for Microbiology. 37 (2): 166–196. PMC 413810
 . PMID 4578757.
. PMID 4578757. - ↑ Solution NMR structure of five representative glycosylated polyene macrolide antibiotics
- ↑ Khan N, Rawlings B, Caffrey P (Jan 26, 2011). "A labile point in mutant amphotericin polyketide synthases". Biotechnol Lett. 33 (6): 1121–6. doi:10.1007/s10529-011-0538-3. PMID 21267757.