Radom
| Radom | |||
|---|---|---|---|
|
| |||
| |||
 Radom | |||
| Coordinates: 51°24′N 21°10′E / 51.400°N 21.167°E | |||
| Country | Poland | ||
| Voivodeship | Masovian | ||
| County | city county | ||
| Established | 13th century | ||
| Town rights | 1364 | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Radosław Witkowski (Civic Platform) | ||
| Area | |||
| • City | 111.71 km2 (43.13 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2013) | |||
| • City | 219,703 | ||
| • Density | 2,000/km2 (5,100/sq mi) | ||
| • Metro | 371,000 | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postal code | 26-600 to 26-618 | ||
| Area code(s) | +48 48 | ||
| Car plates | WR | ||
| Website | http://www.radom.pl | ||
Radom ([ˈradɔm]; Yiddish: ראָדעם Rodem) is a city in east-central Poland with 219,703 inhabitants (2013). It is located 100 kilometres (62 miles) south of Poland's capital, Warsaw, on the Mleczna River, in (as of 1999) the Masovian Voivodeship, having previously been the capital of Radom Voivodeship (1975–1998). Despite being part of the Masovian Voivodeship, the city historically belongs to Lesser Poland. For centuries, Radom was part of the Sandomierz Voivodeship of the Kingdom of Poland and the later Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. It was an important center of administration, having served as seat of the Crown Council. The Pact of Vilnius and Radom was signed there in 1401, and the Nihil novi and Łaski's Statute were adopted by the Sejm at Radom's Royal Castle in 1505. In 1976, it was a center of anti Communist street protests.
The city is home to the biennial Radom Air Show, the largest and best-attended air show in Poland, held during the last weekend of August. "Radom" is also the popular unofficial name for a semiautomatic 9 mm Para pistol of Polish design (the Model 35/ViS-35) which was produced from 1935 to 1944 at the national arsenal located in the city. The Łucznik Arms Factory (still located in Radom) continues to produce modern military firearms.
The international Radom Jazz Festival and the International Gombrowicz Theater Festival are held in the city.
History
Radom's original settlement dates back to the 8th–9th century. It was an early mediaeval town in the valley of the Mleczna River (on the approximate site of present-day Old Town). In the second half of the 10th century, it became a gord, called Piotrówka, which was protected by a rampart and a moat. Due to convenient location on the edge of a large wilderness, and its proximity to the border of Lesser Poland and Mazovia, Radom quickly emerged as an important administrative center of the early Kingdom of Poland. Piotrówka was probably named after St. Peter church, which in 1222 was placed under the authority of a Benedictine Abbey in nearby Sieciechów. The church no longer exists; the oldest still-extant church in Radom is St. Wacław, founded in the 13th century by Prince of Sandomierz Leszek I the White. The first documented mention of Radom comes from the year 1155, in a bull of Pope Adrian IV (villam iuxta Rado, que vocatur Zlauno, or a village near Radom, called Sławno). By 1233, Radom was the seat of a castellan. The name of the city comes from the ancient Slavic given name Radomir, and Radom means a gord, which belongs to Radomir.
In the second half of the 13th century, Radom was granted a Środa Śląska town charter by Prince Bolesław V the Chaste, although no documents exist to confirm the exact date of this event. The town prospered in the 14th century, when in 1350 King Kazimierz Wielki established the so-called New Town, with a royal castle, a defensive wall, and a town hall. There was also a market square and a grid plan of the streets, patterned after Gothic German towns. The area of New Town was 9 hectares, and the length of the defensive wall was 1,100 meters. Radom had three gates, named after main merchant roads: Iłża Gate, Piotrków Trybunalski Gate, and Lublin Gate. The defensive wall was further protected by 25 fortified towers. New Town had the Church of John the Baptist, and the Royal Castle was built between the church and the moat.
In 1364, Radom’s obsolete Środa Śląska rights were replaced with more modern Magdeburg rights, and residents gained several privileges as a result. At that time, Radom was located along the so-called Oxen Trail, from Ruthenian lands to Silesia. In 1376, the city became the seat of a starosta, and entered the period of its greatest prosperity.
Poland's Golden Age
King Władysław Jagiełło granted several privileges to the city. Jagiełło himself frequently travelled from Kraków to Vilnius, and liked to stay at Radom Castle en route. On March 18, 1401, the Pact of Vilnius and Radom was signed, which strengthened the Polish–Lithuanian union. Immediately after the Pact, preparations for the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War began. King Casimir IV Jagiellon frequently visited Radom, along with his wife, Elizabeth of Austria. Here, the King would host foreign envoys, from such countries as the Crimean Khanate, the Kingdom of Bohemia, and the Duchy of Bavaria. On November 18, 1489, Johann von Tiefen, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, paid homage to King Jagiellon at Radom Castle. Mikołaj Radomski, one of the earliest Polish composers, comes from Radom. In 1468, the complex of a Bernardine church and monastery was founded here by King Jagiellon, with support of the local starosta, Dominik z Kazanowa. The complex was originally made of wood (until 1507).
In 1481, Radom became the residence of Prince Kazimierz, the son of King Jagiellon, who ruled the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The young prince died of tuberculosis, and later became patron saint of both the city of Radom (since 1983), and the Roman Catholic Diocese of Radom (since 1992). During the reign of Alexander Jagiellon, the Nihil novi act was adopted by the Polish Sejm in a meeting at Radom Castle. Furthermore, at the same meeting, the first codification of law published in the Kingdom of Poland was accepted. Radom remained one of the most important urban centers of Sandomierz Voivodeship, the seat of a county, and of the Treasure Tribunal (1613-1764), which controlled taxation. Several kings visited the city, including Stephen Bathory and his wife Anna Jagiellon, Sigismund III Vasa, and August III Sas. In 1623 many residents died in an epidemic, and in 1628, half of Radom burned in a fire.
The period of prosperity ended during the Swedish invasion of Poland. The Swedish army captured the city without a fight in November 1655. At first the invaders behaved correctly, as King Charles X Gustav still sought alliances within the Polish-Lithuanian nobility; the situation changed, however, in early 1656, when anti-Swedish uprisings broke out in southern Lesser Poland and quickly spread across the country. Radom was looted and almost completely destroyed in August 1656. Its population shrank from some 2,000 before the war, to 395 in 1660, with only 37 houses still standing. Swedish soldiers burned the royal castle and the monastery. With the Polish population in decline, the number of Jewish settlers grew by the early 18th century. In 1682 the first Piarists arrived, and in 1737-1756, opened a college.
.jpg)
Radom remained within the Sandomierz Voivodeship of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth until the third partition of Poland (1795). For a few years (1795 - 1809) it was part of the Austrian province of West Galicia, and then (1809 - 1815) part of the Duchy of Warsaw, which named it capital of the Radom Department. From 1815 the city belonged to Russian-controlled Congress Poland, remaining a regional administrative center. In 1816 - 1837 it was the capital of the Sandomierz Voivodeship, whose capital, despite the name, was at Radom. In 1837 - 1844 it was the capital of the Sandomierz Governorate, and from 1844 until the oubreak of World War I, the capital of the Radom Governorate. The city was an important center of the November Uprising. Its obsolete and ruined fortifications were destroyed upon order of Mayor Józef Królikowski. In the early days of the January Uprising, Marian Langiewicz visited Radom, preparing the rebellion. In 1867 a sewage system was built. Streets were gradually paved, and in 1885, a rail line from Dąbrowa Górnicza to Dęblin was completed, via Radom. In the early 20th century a power plant was built. The city was captured by the Austro-Hungarian Army in July 1915. An Austrian garrison remained until November 1918.
Modern era
In the Second Polish Republic Radom became part of Kielce Voivodeship. In 1932 the City County of Radom was created, and the following year, its rail connection with Warsaw was completed. In the late 1930s, due to the government project known as the Central Industrial Area, several new factories were built; by 1938, the population had grown to 80,000. The city was also a military garrison, serving as headquarters of the 72nd Infantry Regiment. On September 8, 1939, during World War II, Radom was captured by the Wehrmacht. The German occupiers carried out several executions of civilians, and formed the Radom Ghetto, with a population of 34,000 Jews, most of whom perished at the Treblinka extermination camp. Radom was also a center of Polish resistance, with numerous Home Army units operating in the area. On September 9, 1945, the city was briefly seized by the Cursed soldiers, who broke into a local prison, releasing a number of Home Army soldiers.
Up to the Second World War, like many other cities in interwar Poland, Radom had a large Jewish population. According to the Russian census of 1897, out of the total population of 28,700, Jews constituted 11,200 (~39% percent).[1][2]
Current events
In 2007, two pilots died in an accident at the Air Show, resulting in the cancellation of the rest of the event. On 30 August 2009, also during the air show, another two pilots who represented Belarus were killed when their plane crashed.
Radom was one of the main centres of the strike action taken by Polish health care workers in 2007.
Climate
Radom has a humid continental climate (Köppen: Dfb).
| Climate data for Radom | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −4.7 (23.5) |
−3.3 (26.1) |
2.1 (35.8) |
8.4 (47.1) |
13.2 (55.8) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.0 (64.4) |
17.4 (63.3) |
13.7 (56.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
3.2 (37.8) |
−1.9 (28.6) |
7.6 (45.7) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 26 (1.02) |
25 (0.98) |
28 (1.1) |
37 (1.46) |
59 (2.32) |
76 (2.99) |
79 (3.11) |
66 (2.6) |
45 (1.77) |
36 (1.42) |
38 (1.5) |
34 (1.34) |
549 (21.61) |
| Source: Climate-Data.org[3] | |||||||||||||
Tourist attractions

- St Waenceslaus church in the Old Town Square: founded by Leszek I the White, built in the 13th century in gothic style
- St John the Baptist church: founded by Casimir III, built in the years 1360–1370 in gothic style, and re-constructed many times
- Bernardine church and monastery: founded by Casimir IV of Poland, built in the years 1468–1507
- Holy Trinity Church: built in the years 1619–1627 in the baroque style, burned in a fire and was rebuilt in the years 1678–1691
- Gąska's and Esterka's Houses: 16th / 17th century
- Evangelical Church of the Augsburg Confession: built in 1785
- Building of city council: built in the years 1825–1827, designed in classical style by Antonio Corazzi
- City hall: built in the years 1847–1848
- Cathedral of Virgin Mary: built in the years 1899–1908 in neo-gothic style
- Tool gates: built in the 19th century in classical style
- Radom Air Show: the most popular air show in Poland.
- Radom Air Show
 Patrouille de France, 2005
Patrouille de France, 2005- Patrouille de France, 2011
 Gazelle, 2005
Gazelle, 2005- Red Arrows, 2009
.jpg) Frecce Tricolori, 2011
Frecce Tricolori, 2011%2C_Radom_AirShow_2005%2C_Poland.jpg) F-16, 2005
F-16, 2005
Culture
.jpg)
.jpg)
Philharmonic
- Radom Chamber Orchestra established in 2007 [4]
Cinemas
Theatre
- Jan Kochanowski Theatre [6]
Museums and art galleries
- Jacek Malczewski Museum [7]
- Modern art museum [8]
- Scouting Museum
- "Elektrownia" - Power station built in 1903, renewed as a Modern art gallery
- Cultural Heritage Gallery of Radom
- Skansen in Radom [9]
Transport
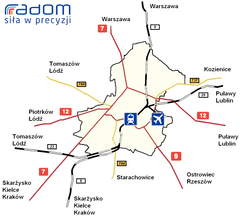
Radom is an important railroad junction, where two lines meet: east - west connection from Lublin to Łódź, and north - south from Warsaw to Kielce, and Kraków. The city is also located along European route E77, here the European route E371 begins, which runs southwards, to Slovakia. The famous Radom Air Show takes place at Radom Airport, an airport located 3.5 km (2 mi) from the center of Radom.
- Transport in Radom - Gallery
 Radom Airport
Radom Airport Bus Solaris Urbino 12
Bus Solaris Urbino 12_Inside.jpg) Train connecting Radom and Warsaw
Train connecting Radom and Warsaw Biking in Radom
Biking in Radom
Education

Radom is home to about 20 schools of higher education:
- Instytut Teologiczny Uniwersytetu Kardynała Stefana Wyszyńskiego w Radomiu - department of theology
- Kolegium Nauczycielskie [10]
- Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków Obcych [11]
- Niepubliczne Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków Obcych [12]
- Niepubliczne Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków Obcych TWP [13]
- Radom Technical University (Politechnika Radomska) [14]
- University College of Environmental Sciences (Wyższa Szkoła Ochrony Środowiska) [15]
- Radomska Szkoła Zarządzania
- Warsaw Agricultural University - department in Radom (Szkoła Główna Gospodarstwa Wiejskiego w Warszawie)
- College of the Maria Curie-Skłodowska University (Kolegium licencjackie Uniwersytetu Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej) [16]
- Warsaw University - department in Radom (Uniwersytet Warszawski)[17][18]
- Maria Curie-Skłodowska University - department in Radom (Uniwersytet Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej) [19]
- Wyższa Inżynierska Szkoła Bezpieczeństwa i Organizacji Pracy [20]
- Higher Business College (Wyższa Szkoła Biznesu) [21]
- Higher Financial and Banking College (Wyższa Szkoła Finansów i Bankowości) [22]
- Higher Merchant College (Wyższa Szkoła Handlowa) [23]
- Higher Seminary (Wyższe Seminarium Duchowne) [24]
- Higher Journalis College (Wyższa Szkoła Dziennikarska) [25]
- Zespół Szkół Medycznych [26]
Other

- At the Western part of Radom, there is a facility for commercial LF transmission (not broadcasting), the Radom longwave transmitter
- The Łucznik Arms Factory in Radom produces a range of military firearms such as assault rifles
- The book, Outcry - Memoirs of Manny Steinberg, chronicles a young Jewish man's life and trials during the Nazi occupation of Radom and beyond. Published by Share Publishing, Menlo Park, CA
Sports

- RoSa Sport Radom - men's basketball team, founded in 2004, currently in 1st league.
- Radomiak Radom - men's football team, founded in 1910, currently playing in 3rd league.
- Czarni Radom - men's volleyball team, founded in 1921, currently playing in 1st league.
- Jadar Radom former men's volleyball team, played in 1st league in 2006-10.
- Broń Radom - men's football team, founded in 1926, currently in 3rd league.
Politics
Members of Parliament (Sejm) elected from Radom constituency
- Ewa Kopacz (PO)
- Dariusz Bąk (PIS)
- Mirosław Maliszewski (PSL)
- Czesław Czechyra (PO)
- Marek Suski (PIS)
- Marek Wikiński (SLD),
- Radosław Witkowski (PO)
- Krzysztof Sońta (PIS)
International relations
Twin towns — Sister cities
Radom is twinned with:[27][28]
|
Notable people
Notable people who have been born, have lived or have worked in Radom:
|
|
See also
References
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Radom. |
- ↑ Joshua D. Zimmerman, Poles, Jews, and the politics of nationality, Univ of Wisconsin Press, 2004, ISBN 0-299-19464-7, Google Print, p.16
- ↑ See also: Alfred Lipson, ed. and comp., The Book of Radom: The Story of a Jewish Community in Poland Destroyed by the Nazis (New York, 1963), based on Sefer Radom, ed. Yitsḥak Perlov (Tel Aviv, 1961); Sebastian Piątkowski, Dni życia, dni śmierci: Ludność żydowska w Radomiu w latach 1918–1950 (Warsaw, 2006).
- ↑ "Climate: Radom". Climate-Data.org. Retrieved 18 April 2014.
- ↑ Radom Chamber Orchestra, www
- ↑ Helios cinemas, www
- ↑ Jan Kochanowski Theatre, www
- ↑ Jacek Malczewski Museum, www
- ↑ Modern art museum, www
- ↑ Skansen in Radom, www
- ↑ Kolegium Nauczycielskie, www
- ↑ Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków, www
- ↑ Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków, www
- ↑ Nauczycielskie Kolegium Języków TWP, www
- ↑ Politechnika Radomska, www
- ↑ Wyższa Szkoła Ochrony Środowiska, www
- ↑ Kolegium licencjackie, www
- ↑ Warsaw University department in Radom, www
- ↑ Uniwersytet Warszawski, www
- ↑ Uniwersytet Marii Curie-Skłodowskiej, www
- ↑ Wyższa Inżynierska Szkoła Bezpieczeństwa, www
- ↑ Wyższa Szkoła Biznesu, www
- ↑ Wyższa Szkoła Finansów i Bankowości, www
- ↑ Wyższa Szkoła Handlowa, www
- ↑ Wyższe Seminarium Duchowne, www
- ↑ Wyższa Szkoła Dziennikarska, www
- ↑ www
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Radom - Miasta partnerskie" [Radom - Partnership cities]. Miasto Radom [City of Radom] (in Polish). Archived from the original on 2013-04-03. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Radom - miasta partnerskie" (in Polish). radom.naszestrony.pl. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
- ↑ "Banská Bystrica Sister Cities". © 2001-2008. Retrieved 2008-10-23.
- ↑ Zachert, Uwe; Annica Kunz. "Twin cities". Landeshauptstadt Magdeburg [City of Magdeburg]. Archived from the original on 2012-09-01. Retrieved 2013-08-07.
 Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Radom". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Radom". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. Media related to Radom at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Radom at Wikimedia Commons- Official web page of Radom in English
- Official web page of Radom in Polish
- Radom Culture (Polish)
- (Polish) http://www.nasz-radom.pl/
- Radom photo gallery (Polish)
- Jewish Community in Radom on Virtual Shtetl
Coordinates: 51°24′N 21°10′E / 51.400°N 21.167°E




