University of Warsaw
| Uniwersytet Warszawski | |
 | |
| Latin: Universitas Varsoviensis | |
| Type | Public |
|---|---|
| Established | 1816 (200 years ago) |
| Endowment | PLN 1,132,000,000[1] (approx. USD 373,000,000) |
| Rector | Marcin Pałys |
Administrative staff | 5,531 |
| Students | 51,700[2] |
| Postgraduates | 3,800 (2014) |
| 3,200 (2014) | |
| Location | Warsaw, Poland |
| Campus | Urban |
| Affiliations | EUA, Socrates-Erasmus, EAIE, UNICA |
| Website | www.uw.edu.pl |
| University rankings | |
|---|---|
| Global | |
| ARWU[3] | 301–400 |
| QS[4] | 351–400 |
| Times[5] | 351–400 |
The University of Warsaw (Polish: Uniwersytet Warszawski, Latin: Universitas Varsoviensis), established in 1816, is the largest[6] university in Poland. It employs over 6,000 staff including over 3,100 academic educators. It provides graduate courses for 53,000 students (on top of over 9,200 postgraduate and doctoral candidates). The University offers some 37 different fields of study, 18 faculties and over 100 specializations in Humanities, technical as well as Natural Sciences.[6]
It was founded as a Royal University on 19 November 1816, when the Partitions of Poland separated Warsaw from the oldest and most influential Jagiellonian University located in Kraków. Tsar Alexander I granted permission for the establishment of five faculties – law and political science, medicine, philosophy, theology and the humanities. The university expanded rapidly, but was closed during November Uprising in 1830. It was reopened in 1857 under the name Akademia Medyko-Chirurgiczna (Academy of Medicine) based in the nearby Staszic Palace with only medical and pharmaceutical faculties. All Polish-language campuses were closed in 1869 after the failed January Uprising, but the university managed to train 3,000 students, many of whom were important part of the Polish intelligentsia, meanwhile the Main Building was reopened as the Imperial Russian University aimed at training military personnel. Over 70% of students were of Polish nationality, but after the revolution in 1905, the proportion dropped below 10% as a result of the boycott. The university was resurrected during the First World War and the number of students in 1918 was estimated at 4,500. After Poland's independence in 1918 the new government focused on improving the university, and in the early 1930s it became the country's largest. New faculties were established and the curriculum was extended. The university was named after Chief-of-State and Marshal of Poland Józef Piłsudski after his death in 1935. Following the Second World War and the devastation of Warsaw, the University successfully reopened in 1945.
Today, the University of Warsaw consists of 126 buildings and educational complexes with over 18 faculties: biology, chemistry, journalism and political science, philosophy and sociology, physics, geography and regional studies, geology, history, applied linguistics and Slavic philology, economics, philology, pedagogy, Polish language, law and public administration, psychology, applied social sciences, management and mathematics, computer science and mechanics.
The University of Warsaw is one of the top Polish universities. It was ranked by Perspektywy magazine as best Polish university in 2010, 2011 and 2014.[7][8] International rankings such as ARWU and University Web Ranking [9] rank the university as the best Polish higher level institution. On the list of 100 best European universities compiled by University Web Ranking, the University of Warsaw was placed as 61st. QS World University Rankings positioned the University of Warsaw as the best higher level institution among the world's top 400.[10]
History
Beginnings under Alexander I
In 1795 the partitions of Poland left Warsaw with access only to the Academy of Vilnius; the oldest and most influential Polish academic center, Jagiellonian University in Kraków, became part of Habsburg Austria. In 1815, the newly established autonomous Congress Poland de facto belonging to the Russian Empire found itself without a university at all, as Vilnius was incorporated into Russia. The first to be established in Congress Poland were the Law School and the Medical School. In 1816 Tsar Alexander I permitted the Polish authorities to create a university, comprising five departments: Law and Administration, Medicine, Philosophy, Theology, and Art and Humanities. The university soon grew to 800 students and 50 professors. After most of the students and professors took part in the November 1830 Uprising the university was closed down.[11] After the Crimean War, Russia entered a brief period of liberalization, and the permission was given to create a Polish medical and surgical academy (Akademia Medyko-Chirurgiczna) in Warsaw. In 1862 departments of Law and Administration, Philology and History, and Mathematics and Physics were opened. The newly established academy gained importance and was soon renamed the "Main School" (Szkoła Główna). However, after the January 1863 Uprising the liberal period ended and all Polish-language schools were closed down again. During its short existence, the Main School educated over 3,000 students, many of whom became part of the backbone of the Polish intelligentsia.[12]

The Main School was replaced with a Russian-language "Imperial University of Warsaw". Its purpose was to provide education for the Russian military garrison of Warsaw, the majority of students (up to 70% out of an average of 1,500 to 2,000 students) were Poles. The tsarist authorities believed that the Russian university would become a perfect way to Russify Polish society and spent a significant sum on building a new university campus. However, various underground organizations soon started to grow and the students became their leaders in Warsaw. Most notable of these groups (the supporters of Polish revival and the socialists) joined the ranks of the 1905 Revolution. Afterwards a boycott of Russian educational facilities was proclaimed and the number of Polish students dropped to below 10%. Most of the students who wanted to continue their education left for Galicia and Western Europe.[13]
After the fall of the January Uprising (1863–1864), the Tsarist authorities' decided to convert the Main School into a Russian-language university, which functioned under the name of Imperial University for 46 years. There were two times when the question of moving the university into Russia was considered. During the 1905–1907 revolution, such a proposal was made by some of the professors, in the face of a boycott of the university by Polish students. Talks on that subject were conducted with a number of Russian cities, including Voronezh and Saratov. The Russian government finally decided to keep a university in Warsaw, but as a result of the boycott, the university was Russian not only in the sense of the language used, but also of the nationality of its professors and students.[13]
For the second time the question emerged during the First World War, when the military and political situation forced the Russian authorities to evacuate. Beginning from the autumn of 1915, there were two Universities of Warsaw: one Polish, in Warsaw, and another Russian, in Rostov-on-Don which functioned until 1917. On 5 May 1917 the Russian Provisional Government decided to close the University of Warsaw. The decision took effect on 1 July 1917; on the same day, the University of the Don, now called Rostov State University (Southern Federal University since 2006), was inaugurated.[14]
During World War I Warsaw was seized by Germany in 1915. In order to win the Poles for their case and secure the Polish area behind the front lines the governments of Germany and Austria-Hungary allowed for a certain liberalization of life in Poland. In accordance with the concept of Mitteleuropa, German military authorities permitted several Polish social and educational societies to be recreated. One of these was University of Warsaw. The Polish language was reintroduced, and the professors were allowed to return to work. In order not to let the Polish patriotic movement out of control the number of lecturers was kept low (usually not more than 50), but there were no limits on the number of students. Until 1918 their number rose from a mere 1,000 to over 4,500.[15]
Second Polish Republic

After Poland regained its independence in 1918, the University of Warsaw began to grow very quickly. It was reformed; all the important posts (the rector, senate, deans and councils) became democratically elected, and the state spent considerable amounts of money to modernize and equip it. Many professors returned from exile and cooperated in the effort. By the late 1920s the level of education in Warsaw had reached that of western Europe.[16]
By the beginning of the 1930s the University of Warsaw had become the largest university in Poland, with over 250 lecturers and 10,000 students. However, the financial problems of the newly reborn state did not allow for free education, and students had to pay a tuition fee for their studies (an average monthly salary, for a year). Also, the number of scholarships was very limited, and only approximately 3% of students were able to get one. Despite these economic problems, the University of Warsaw grew rapidly. New departments were opened, and the main campus was expanded.[16] After the death of Józef Piłsudski the senate of the University of Warsaw changed its name to "Józef Piłsudski University of Warsaw" (Uniwersytet Warszawski im. Józefa Piłsudskiego). The Sanacja government proceeded to limit the autonomy of the universities. Professors and students remained divided for the rest of the 1930s as the system of segregated seating for Jewish students, known as ghetto benches, was implemented customarily, not institutionally, which should be noted; comparable to the era of the Civil rights movement in the United States.
World War II
- For more details on this period see: Underground Education in Poland During World War II
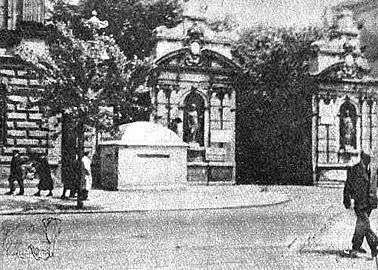
After the Polish Defensive War of 1939 the German authorities of the General Government closed all the institutions of higher education in Poland. The equipment and most of the laboratories were taken to Germany and divided amongst the German universities while the main campus of the University of Warsaw was turned into military barracks.[17]
German racial theories assumed that no education of Poles was needed and the whole nation was to be turned into uneducated serfs of the German race. Education in Polish was banned and punished with death. However, many professors organized the so-called "Secret University of Warsaw" (Tajny Uniwersytet Warszawski). The lectures were held in small groups in private apartments and the attendants were constantly risking discovery and death. However, the net of underground faculties spread rapidly and by 1944 there were more than 300 lecturers and 3,500 students at various courses.
Many students took part in the Warsaw Uprising as soldiers of the Armia Krajowa and Szare Szeregi. The German-held campus of the University was turned into a fortified area with bunkers and machine gun nests. It was located close to the buildings occupied by the German garrison of Warsaw. Heavy fights for the campus started on the first day of the Uprising, but the partisans were not able to break through the gates. Several assaults were bloodily repelled and the campus remained in German hands until the end of the fights. During the uprising and the occupation 63 professors were killed, either during fights or as an effect of German policy of extermination of Polish intelligentsia. The University lost 60% of its buildings during the fighting in 1944. A large part of the collection of priceless works of art and books donated to the University was either destroyed or transported to Germany, never to return.
In the People's Republic

After World War II it was not clear whether the university would be restored or whether Warsaw itself would be rebuilt. However, many professors who had survived the war returned, and began organizing the university from scratch. In December 1945, lectures resumed for almost 4,000 students in the ruins of the campus, and the buildings were gradually rebuilt. Until the late 1940s the university remained relatively independent. However, soon the communist authorities started to impose political controls, and the period of Stalinism started. Many professors were arrested by the Urząd Bezpieczeństwa (Secret Police), the books were censored and ideological criteria in employment of new lecturers and admission of students were introduced. On the other hand, education in Poland became free of charge and the number of young people to receive the state scholarships reached 60% of all the students. After Władysław Gomułka's rise to power in 1956, a brief period of liberalization ensued, though communist ideology still played a major role in most faculties (especially in such faculties as history, law, economics and political science). International cooperation was resumed and the level of education rose.[18]
By mid-1960s the government started to suppress freedom of thought, which led to increasing unrest among the students. A political struggle within the communist party prompted Zenon Kliszko to ban the production of Dziady by Mickiewicz at the Polish Theatre, leading to 1968 Polish political crisis coupled with anti-Zionist and anti-democratic campaign and the outbreak of student demonstrations in Warsaw, which were brutally crushed – not by police, but by the ORMO reserve militia squads of plain-clothed workers.[19] As a result, a large number of students and professors were expelled from the university. Nonetheless, the University remained the centre of free thought and education. What professors could not say during lectures, they expressed during informal meetings with their students. Many of them became leaders and prominent members of the Solidarity movement and other societies of the democratic opposition which led to the collapse of communism. The scientists working at the University of Warsaw were also among the most prominent printers of books forbidden by censorship.[20]
Campus
| University rankings (overall) | |
|---|---|
| ARWU (2011/12, national) | 1–2 |
| ARWU (2011/12, world) | 301–400 |
| QS (2012/13, national) | 1 |
| QS (2012/13, world) | 398 |
| THE (2012/13, national) | 1 |
| THE (2012/13, world) | 351–400 |
| Webometrics (January 2013, world) | 234 |
University of Warsaw owns a total of 126 buildings. Further construction and a vigorous renovation program is underway at the main campus. The university is spread out over the city, though most of the buildings are concentrated in two areas.
Main campus


The main campus of the University of Warsaw is in the city center, adjacent to the Krakowskie Przedmieście street. It comprises several historic palaces, most of which had been nationalized in the 19th century. The chief buildings include:
- Kazimierzowski Palace (Pałac Kazimierzowski) – the seat of the rector and the senate;
- Uruski Palace (Pałac Uruskich) – left side of main gate entrance, houses the Department of Geography and Regional Studies
- the Old Library (Stary BUW) – since recent refurbishment, a secondary lecture building;
- the Main School (Szkoła Główna) – former seat of the Main School until the January 1863 Uprising, later the faculty of biology; now, since its refurbishment, the seat of the institute of archaeology;
- Auditorium Maximum – the main lecture hall, with seats for several hundred students.
The Warsaw University Library building is a short walk downhill from the main campus, in the Powiśle neighborhood.
Natural sciences campus
The second important campus is located near Banacha and Pasteura streets. It is home to the departments of chemistry, physics, biology, mathematics, computer science and geology, and contains several other university buildings such as the Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematical and Computational Modelling, the Environmental Heavy Ion Laboratory that houses a cyclotron and a facility for the production of PET radiopharmaceuticals, and a sports facility. Several new buildings have been constructed within this campus in the recent years, and the Department of Physics moved here from its previous location at Hoża street.
Together with buildings of other institutions, such as the Institute of Experimental Biology, Radium Institute and the Medical University of Warsaw, the campus is part of an almost contiguous area of scientific and educational facilities covering approximately 43 hectares (110 acres).
Faculties
- Applied Linguistics and East-Slavonic Philology[21]
- Applied Social Sciences and Resocialization
- Biology[22]
- Chemistry[23]
- Economic Sciences[24]
- Education
- Geography and Regional Studies[25]
- Geology[26]
- History[27]
- Journalism and Political Science[28]
- Law and Administration[29]
- Management[30]
- Mathematics, Informatics, and Mechanics[31]
- Modern Languages
- Oriental Studies[32]
- Philosophy and Sociology[33]
- Physics[34]
- Polish Studies
- Psychology[35]
Other institutes
- American Studies Center
- British Studies Centre
- Centre de Civilisation Française et d'Études Francophones auprès de l'Université de Varsovie
- Centre for Archaeological Research at Novae
- Centre for Environmental Study
- Centre for Europe
- Centre for European Regional and Local Studies (EUROREG)[36]
- Centre for Foreign Language Teaching
- Centre for Inter-Faculty Individual Studies in the Humanities[37]
- Centre for Latin-American Studies (CESLA)
- Centre for Open Multimedia Education
- Centre for the Study of Classical Tradition in Poland and East-Central Europe
- Centre of Studies in Territorial Self-Government and Local Development
- Chaire UNESCO du Developpement Durable de l`Universite de Vaersovie
- Comité Polonais de l'Alliance Français
- Digital Economy Lab (DELab) – joint institute with Google [38]
- Erasmus of Rotterdam Chair
- Heavy Ion Laboratory
- Individual Inter-faculty Studies in Mathematics and Natural Sciences[39]
- Institute of Americas and Europe
- Institute of International Relations – host of GMAPIR
- The Robert B.Zajonc Institute for Social Studies[40]
- Inter-faculty Study Programme in Environmental Protection
- Interdisciplinary Centre for Behavioural Genetics
- Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematical and Computational Modelling[41]
- Physical Education and Sports Centre
- Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology
- University Centre for Technology Transfer
- University College of English Language Teacher Education
- University of Warsaw for Foreign Language Teacher Training and European Education
Institutions
- Academic Radio Kampus 97,1 FM[42]
- Institute of Information Science and Book Studies[43]
- The Institute of Polish Language and Culture 'Polonicum'[44]
- University of Warsaw Libraries[45]
Notable alumni
- Jerzy Andrzejewski (1909–1983), author
- Krzysztof Kamil Baczyński (1921–1944), poet, Home Army soldier killed in the Warsaw Uprising
- Menachem Begin (1913–1992), 6th Prime Minister of Israel (1977–1983), Nobel Peace Prize winner (1978)
- David Ben-Gurion (1886–1973), 1st Prime Minister of Israel (1948–53; 1955–63)
- Emanuel Ringelblum (1900–1944), historian, founder Emanuel Ringelblum Archives of Warsaw Ghetto[46]
- Tadeusz Borowski (1922–1951), poet, writer
- Kazimierz Brandys (1916–2000), writer
- Marian Brandys (1912–1998), writer, journalist
- Frédéric Chopin (1810–1849), pianist, composer
- Włodzimierz Cimoszewicz (b. 1950), politician, Prime Minister of Poland (1996–1997), Marshal of the Sejm (2005)
- Joseph Epstein (1911–1944), communist leader of French resistance
- Bronisław Geremek (1932–2008), historian, politician
- Witold Gombrowicz (1904–1969), writer
- Hanna Gronkiewicz-Waltz (b. 1952), politician, President of the National Bank of Poland (1992–2001), Mayor of Warsaw (since 2006)
- Jan T. Gross (b. 1947), historian, writer, Princeton University professor
- Gustaw Herling-Grudziński (1919–2000), journalist, writer, Gulag survivor
- Zofia Helman (b. 1937), Polish musicologist
- Leonid Hurwicz (1917–2008), economist, mathematician, Nobel Prize in Economics winner (2007)
- Czesław Janczarski (1911–1971), poet and Russian literature translator
- Jarosław Kaczyński (b. 1949), politician, Prime Minister of Poland (2006–2007)
- Lech Kaczyński (1949–2010), politician, Mayor of Warsaw (2002–2005), President of Poland (2005–2010)
- Aleksander Kamiński (1903–1978), writer, leader of Polish Scouting and Guiding Association
- Ryszard Kapuściński (1932–2007), writer and journalist
- Mieczysław Karłowicz (1876–1909), composer
- Jan Karski (1914–2000), Polish resistance fighter
- Leszek Kołakowski (1927–2009), philosopher, historian of philosophy
- Bronisław Komorowski (b. 1952), politician, Marshal of the Sejm (2007–2010), President of Poland (2010–2015)
- Alpha Oumar Konaré, (b. 1946), 3rd President of Mali (1992–2002)
- Janusz Korwin-Mikke (b. 1942), conservative-liberal politician and journalist
- Marek Kotański (1942–2002), psychologist and streetworker
- Jacek Kuroń (1934–2004), historian, author, social worker and politician
- Jan Józef Lipski (1926–1991), literature historian, politician
- Jerzy Łojek (1932–1986), historian, writer
- Tadeusz Mazowiecki (1927–2013), author, social worker, journalist, Prime Minister of Poland (1989–1991)
- Adam Michnik (b. 1946), journalist
- Karol Modzelewski (b. 1937), historian, politician
- Jerzy Neyman (1894–1981), mathematician, statistician, University of California professor
- Jan Olszewski (b. 1930), lawyer, politician, Prime Minister of Poland (1991–1992)
- Janusz Onyszkiewicz (b. 1937), politician
- Maria Ossowska (1896–1974), sociologist
- Bolesław Piasecki (1915–1979), politician
- Bohdan Paczyński (1940–2007), astronomer
- Longin Pastusiak (b. 1935), politician, Marshal of the Senate of the Republic of Poland (2001–2005)
- Krzysztof Piesiewicz (b. 1945), lawyer, screenwriter
- Adam Przeworski (b. 1940), political scientist, New York University professor
- Bolesław Prus (1847–1912), writer
- Józef Rotblat (1908–2005), physicist, Nobel Peace Prize winner (1995)
- Stefan Sarnowski (b. 1939), philosopher
- Stanisław Sedlaczek (1892–1941), social worker, leader of Polish Scouting and Guiding Association
- Yitzhak Shamir (1915–2012), 7th Prime Minister of Israel (1983–1984 and 1986–1992)
- Dmitry Strelnikoff (b. 1969), Russian writer, biologist, journalist for the media
- Alfred Tarski (1902–1982), logician, mathematician, member of the Lwów-Warsaw school of logic
- Władysław Tatarkiewicz (1886–1980), philosopher, historian of esthetics
- Julian Tuwim (1894–1953), poet and writer
- Alfred Twardecki (b. 1962), archaeologist, historian of antiquity, museologist
- Janusz Andrzej Zajdel (1938–1985), physicist and science-fiction writer
- Anna Zawadzka (1919–2004), social worker, leader of Polish Scouting and Guiding Association
- Ludwik Zamenhof (1859–1917), physician, inventor of Esperanto
- Maciej Zembaty (1944–2011), poet, writer, translator of Leonard Cohen's works
- Rafał A. Ziemkiewicz (b. 1964), writer
- Florian Znaniecki (1882–1958), philosopher and sociologist
- Lech Gardocki (b. 1944) lawyer, judge, former First President of the Polish Supreme Court
- Monika Jaruzelska (b. 1963) fashion designer, journalist, daughter of former Polish President Wojciech Jaruzelski
Notable staff
Professors
- Osman Achmatowicz (1899–1988), chemist, rector of the Technical University of Łódź (1946–1953)
- Szymon Askenazy (1866–1935), historian
- Karol Borsuk (1905–1982), mathematician
- Jan Niecisław Baudouin de Courtenay (1845–1929), linguist, introduced the concept of a phoneme
- Zygmunt Bauman (b. 1925), sociologist
- Tomasz Dietl (b.1950), physisct, Laureate of Agilient Technologies Europhysics Prize of The European Physical Society (2005)
- Benedykt Dybowski (1833–1930), biologist and explorer of Siberia and Baikal area
- Michel Foucault (1926–1984), French philosopher, at the University dean-faculty of the French Centre 1958–1959
- Stanisław Grabski (1871–1949), economist
- Henryk Jabłoński (1909–2003), historian, nominal head of state of Poland (1972–1985)
- Feliks Pawel Jarocki (1790–1865), zoologist
- Leszek Kołakowski (1927–2009), philosopher
- Kazimierz Kuratowski (1896–1980), mathematician
- Joachim Lelewel (1786–1861), historian, politician and freedom fighter
- Antoni Leśniowski (1867–1940), surgeon and medic, one of the discoverers of Crohn's disease
- Edward Lipiński (1888–1986), economist, founder of the Main Statistical Office
- Jan Łukasiewicz (1878–1956), mathematician and logician
- Leszek Marks (b. 1951), geologist
- Kazimierz Michałowski (1901–1981), archaeologist, explorer of Deir el Bahari and Faras
- Andrzej Mostowski (1913–1975), mathematician
- Maria Ossowska (1896–1974), sociologist
- Stanisław Ossowski (1897–1963), sociologist
- Grigol Peradze (1899–1942), Orthodox theologian
- Leon Petrażycki (1867–1931), jurist, philosopher and logician, one of the founders of sociology of law
- Ladislaus Pilars de Pilar (1874–1952), literature professor, poet and entrepreneur
- Adam Podgórecki (1925–1998), sociologist of law
- Henryk Samsonowicz (b. 1930), historian, rector (1980–1982)
- Wacław Sierpiński (1882–1969), mathematician
- Alfred Sokołowski (18491924), physician and a pioneer in tuberculosis treatment
- Hélène Sparrow (1891–1970), bacteriologist and public health pioneer, especially typhus
- Andrzej K. Tarkowski (b.1933), zoologist, Laureate of Japan Prize (2002)
- Nikolay Yakovlevich Sonin (1849–1915), mathematician
- Jan Strelau (b. 1931), psychologist
- Jerzy Szacki (1929–2016), sociologist and historian
- Stanisław Thugutt (1873–1941), politician, rector (1919–1920)
- Włodzimierz Zonn (1905–1985), astronomer
Rectors
- Wojciech Szweykowski (1818–1831)
- Józef Karol Skrodzki (1831)
- Józef Mianowski (1862–1869)
- Piotr Ławrowski (1869–1873)
- Nikołaj Błagowieszczański (1874–1884)
- Nikołaj Ławrowski (1884–1890)
- Michaił Szałfiejew (1895)
- Pawieł Kowalewski (1896)
- Grigorij Zenger (1896)
- Michaił Szałfiejew (1898)
- Grigorij Uljanow (1899–1903)
- Piotr Ziłow (1904)
- Yefim Karskiy (1905–1911)
- Wasilij Kudrewiecki (1911–1912)
- Iwan Trepicyn (1913)
- Siergiej Wiechow (1914–1915)
- Józef Brudziński (1915–1917)
- Antoni Kostanecki (1917–1919)
- Stanisław Thugutt (1919–1920)
- Jan Karol Kochanowski (1920–1921)
- Jan Mazurkiewicz (1921–1922)
- Jan Łukasiewicz (1922–1923)
- Ignacy Koschembahr-Łyskowski (1923–1924)
- Franciszek Krzyształowicz (1924–1925)
- Stefan Pieńkowski (1925–1926)
- Bolesław Hryniewiecki (1926–1927)
- Antoni Szlagowski (1927–1928)
- Gustaw Przychocki (1928–1929)
- Tadeusz Brzeski (1929–1930)
- Mieczysław Michałowicz (1930–1931)
- Jan Łukasiewicz (1931–1932)
- Józef Ujejski (1932–1933)
- Stefan Pieńkowski (1933–1936)
- Włodzimierz Antoniewicz (1936–1939)
- Jerzy Modrakowski (1939)
- Stefan Pieńkowski (1945–1947)
- Franciszek Czubalski (1947–1949)
- Jan Wasilkowski (1949–1952)
- Stanisław Turski (1952–1969)
- Zygmunt Rybicki (1969–1980)
- Henryk Samsonowicz (1980–1982)
- Kazimierz Albin Dobrowolski (1982–1985)
- Rector electus Klemens Szaniawski (1984)
- Grzegorz Białkowski (1985–1989)
- Andrzej Kajetan Wróblewski (1989–1993)
- Włodzimierz Siwiński (1993–1999)
- Piotr Węgleński (1999–2005)
- Katarzyna Chałasińska-Macukow (2005–2012)
- Marcin Pałys (since 2012)
Staff
- Czesław Miłosz – janitor at Warsaw University Library during World War II; recipient of 1980 Nobel Prize in Literature.[47]
See also
- List of modern universities in Europe (1801–1945)
- Warsaw school of history (Askenazy school)
- Warsaw School of Mathematics
Notes
- ↑ "Finansowanie badań". Uw.edu.pl.
- ↑ http://en.uw.edu.pl/about-university/facts-and-figures/
- ↑ "Academic Ranking of World Universities 2016". Shanghai Ranking Consultancy. 2016. Retrieved August 16, 2016.
- ↑ "QS World University Rankings® 2016/17". Quacquarelli Symonds Limited. 2016. Retrieved September 6, 2016.
- ↑ "World University Rankings 2016-17". THE Education Ltd. Retrieved September 21, 2016.
- 1 2 Redakcja (2012). "About Us". University of Warsaw (UW) homepage (in Polish and English). Uniwersytet Warszawski, Warsaw. Retrieved September 9, 2012.
- ↑ University Ranking at Perspektywy.pl Ranking uczelni akademickich 2011 with index. (Polish).
- ↑ University Ranking at Perspektywy.pl Ranking uczelni akademickich 2014 (Polish)
- ↑ University Ranking Best Universities in Europe 2012 (Polish).
- ↑ University of Warsaw history, homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ University of Warsaw history (1816–1831), homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ University of Warsaw history (1857–1869), homepage. (Polish)
- 1 2 University of Warsaw history (1870–1915), homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ "The University of Warsaw: 'university'? 'of Warsaw'?". Cejsh.icm.edu.pl. Retrieved 2011-10-07.
- ↑ University of Warsaw history (1915–1918), homepage. (Polish)
- 1 2 University of Warsaw history (1918–1935), homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ "University of Warsaw history (1939–1944)" (in Polish). Uw.edu.pl.
- ↑ University of Warsaw history (1945–1956), homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ "March '68". Exhibition. Institute of National Remembrance. pp. 1–2. Introduction, followed by scans of articles. Retrieved June 2, 2012.
The Voluntary Reserves of the Citizens' Militia (armed with cable and truncheons) beating the students, were met with shouts of "Gestapo!", "Gestapo!"
- ↑ University of Warsaw history (1956–1989), homepage. (Polish)
- ↑ http://www.wlsifw.uw.edu.pl/
- ↑ "Strona Wydziału Biologii UW". Biol.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ http://www.chem.uw.edu.pl/index_en.htm
- ↑ "Wydział Nauk Ekonomicznych – Uniwersytet Warszawski". Wne.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Wydział Geografii i Studiów Regionalnych Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego" (in Polish). Wgsr.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Wydział Geologii Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego" (in Polish). Geo.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Wydział Historyczny UW". Wh.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Wydział Dziennikarstwa i Nauk Politycznych UW – Strona główna". Wdinp.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Faculty of Law and Administration". En.wpia.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ Marcin Jędra (2012-05-26). "Wydział Zarządzania Uniwersytetu Warszawskiego, zarządzanie, studia podyplomowe, studia licencjackie, studia magisterskie". Wz.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Wydział MIM UW – Strona główna". Mimuw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ Wydział Orientalistyczny (Polish)
- ↑ Instytut Socjologii Uniwersytet Warszawski, 2005. The Internet Archive. (English)
- ↑ Faculty of Physics University of Warsaw (English)
- ↑ Psychologia.pl (Polish) and Psychology.pl (English)
- ↑ "Centre for European Regional and Local Studies (EUROREG)". Euroreg.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2013-01-05.
- ↑ "Kolegium MISH UW". Mish.uw.edu.pl. 2007-09-30. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Digital Economy Lab (DELab)" (in Polish). uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2014-04-15.
- ↑ "MISMaP – MiÄ™dzywydziaÅ‚owe Indywidualne Studia Matematyczno-Przyrodnicze UW – MISMaP". Mismap.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2011-10-07.
- ↑ "Witamy w ISS" (in Polish). Iss.uw.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ "Strona Główna". icm.edu.pl. Retrieved 2012-07-15.
- ↑ Akademickie Radio Kampus 97,1 fm. (Polish)
- ↑ History of the Institute. The Internet Archive. (English)
- ↑ Polonicum.uw.edu.pl Archived April 5, 2004, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Buwcd.buw.uw.edu.pl Archived April 6, 2004, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Emanuel Ringelblum: The Creator of “Oneg Shabbat” Holocaust Research Project.
- ↑ Haven, Cynthia L. (2006). Czesław Miłosz: Conversations. University Press of Mississippi. pp. XXV.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to University of Warsaw. |
- Official website
- The University's computer network
- The WU Students Association
- Website of The University New Library
Coordinates: 52°14′25″N 21°1′9″E / 52.24028°N 21.01917°E
.jpg)





.jpg)
.jpg)