Primary energy
Primary energy (PE) is an energy form found in nature that has not been subjected to any conversion or transformation process. It is energy contained in raw fuels, and other forms of energy received as input to a system. Primary energy can be non-renewable or renewable.
Total Primary Energy Supply (TPES) is a term used to indicate the sum of production and imports subtracting exports and storage changes.[2]
The concept of primary energy is used in energy statistics in the compilation of energy balances, as well as in the field of energetics. In energetics, a primary energy source (PES) refers to the energy forms required by the energy sector to generate the supply of energy carriers used by human society.[3]
The use of primary energy as a measure ignores conversion efficiency. Thus forms of energy with poor conversion efficiency, particularly the thermal sources, coal, gas and nuclear are overstated, whereas energy sources such as hydroelectricity which are converted efficiently, while a small fraction of primary energy are significantly more important than their total raw energy supply may seem to imply.
PE and TPES are better defined in the context of worldwide energy supply.
Examples of sources
Primary energy sources should not be confused with the energy systems (or conversion processes) through which they are converted into energy carriers.
| Primary energy sources | converted by |
Energy systems | to | Energy carriers (main) | ||
| Non-renewable sources[nb 1] |
Fossil fuels |
Oil (or crude oil) | Oil refinery | Fuel oil | ||
| Coal or natural gas | Fossil fuel power station | Enthalpy, mechanical work or electricity | ||||
| Mineral fuels |
Natural uranium[nb 2] | Nuclear power plant (thermonuclear fission) | Electricity | |||
| Renewable sources |
Solar energy | Photovoltaic power plant (see also Solar power) | Electricity | |||
| Solar power tower, solar furnace (see also Solar thermal energy) | Enthalpy | |||||
| Wind energy | Wind farm (see also Wind power) | Mechanical work or electricity | ||||
| Falling and flowing water, tidal energy[4] | Hydropower station, wave farm, tidal power station | Mechanical work or electricity | ||||
| Biomass sources | Biomass power plant | Enthalpy or electricity | ||||
| Geothermal energy | Geothermal power station | Enthalpy or electricity | ||||
Usable energy
.png)
Primary energy sources are transformed in energy conversion processes to more convenient forms of energy (that can directly be used by society), such as electrical energy, refined fuels, or synthetic fuels such as hydrogen fuel. In the field of energetics, these forms are called energy carriers and correspond to the concept of "secondary energy" in energy statistics.
Conversion to energy carriers (or secondary energy)
Energy carriers are energy forms which have been transformed from primary energy sources. Electricity is one of the most common energy carriers, being transformed from various primary energy sources such as coal, oil, natural gas, and wind. Electricity is particularly useful since it has low entropy (is highly ordered) and can be converted into other forms of energy very efficiently.
According to the laws of thermodynamics, primary energy sources cannot be produced. They must be available to society to enable the production of energy carriers.[3]
Conversion efficiency varies; for thermal energy electricity and mechanical energy production is limited by Carnot's theorem, and generates a lot of waste heat. Other non thermal conversions can be more efficient, for example wind turbines do not capture all the wind energy, but generate very little waste heat, since wind energy is low entropy. In principle solar photovoltaic conversions could be very efficient, but current conversion can only be done well for narrow frequency ranges, whereas solar thermal is also subject to Carnot efficiency limits. Hydroelectric power is also converted very efficiently. The amount of usable energy is the exergy of a system.
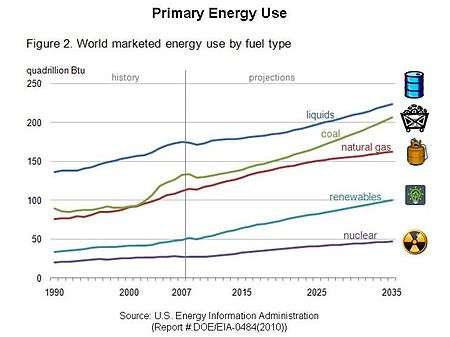
Outlook
Energy accidents and fatalities
Energy accidents are accidents that occur in systems that provide energy or power. These can result in fatalities, as can the normal running of many systems, for example those deaths due to pollution.
Globally, coal is responsible for 100,000 deaths per trillion kWh.[5]
See also
Notes
- ↑ At the scale of earth sciences, all primary energy sources can be considered to be renewable. The non-renewable essence of resources (PES) is due to the scale of needs within human society. In certain situations, the use of resources by human society is performed at a much higher rate than the minimum rate at which it can be geophysically renewed. This is the rationale behind the differentiation between non-renewable primary energy sources (oil, coal, gas, uranium) and renewable primary energy sources (wind, solar, hydro).
- ↑ Some nuclear fuels, such as plutonium or depleted uranium, are also used in nuclear fission power plants. However, they cannot be considered to be primary energy sources as they cannot be found in nature in any quantity. Indeed, there must be a consumption of natural uranium (primary energy source) in order to make these other nuclear fuels available.
References
- 1 2 "2014 Key World Energy Statistics" (PDF). http://www.iea.org/publications/freepublications/. IEA. 2014. pp. 6,8. Archived from the original on 5 May 2014. External link in
|website=(help) - ↑ "OECD Factbook 2013: Economic, Environmental and Social Statistics". 2013. Retrieved 12 April 2014.
- 1 2 Giampietro, Mario; Mayumi, Kozo (2009). The Biofuel Delusion: The Fallacy of Large Scale Agro-Biofuels Production. Earthscan, Taylor & Francis group. p. 336. ISBN 978-1-84407-681-9.
- ↑ "Energy and the Natural Environment" by David A. Dobson, Ph.D., Welty Environmental Center Feature Article, accessed July 9, 2009
- ↑ How Deadly Is Your Kilowatt? We Rank The Killer Energy Sources James Conca, June 10, 2012
- Kydes, Andy (Lead Author); Cutler J. Cleveland (Topic Editor). 2007. "Primary energy." In: Encyclopedia of Earth. Eds. Cutler J. Cleveland (Washington, D.C.: Environmental Information Coalition, National Council for Science and the Environment). [First published in the Encyclopedia of Earth June 1, 2006; Last revised August 14, 2007; Retrieved November 15, 2007.
- Øvergaard, Sara. Definition of primary and secondary energy Statistics Norway, September 2008