Chromosome 17 (human)
| Chromosome 17 (human) | |
|---|---|
 Pair of human chromosome 17 (after G-banding). One is from mother, one is from father. | |
 Chromosome 17 pair in human male karyogram. | |
| Features | |
| Length (bp) | 83,257,441 |
| Number of genes | 2,010 |
| Type | Autosome |
| Centromere position | Submetacentric[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| RefSeq | NC_000017 |
| GenBank | CM000679 |
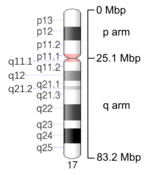
Ideogram of human chromosome 17. Mbp means mega base pair. See locus for other notation.
Chromosome 17 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 17 spans more than 83 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 2.5 and 3% of the total DNA in cells.
Identifying genes on each chromosome is an active area of genetic research. Because researchers use different approaches to predict the number of genes on each chromosome, the estimated number of genes varies. Chromosome 17 likely contains between 1,200 and 1,500 genes. It also contains the Homeobox B gene cluster.
Genes
The following are some of the genes and their corresponding Cytogenetic location on chromosome 17:
- ABI3: encoding protein ABI gene family member 3
- AZI1: encoding protein 5-azacytidine-induced protein 1
- GGT6: encoding protein Gamma-glutamyltransferase 6
- RPL23A: encoding protein 60S ribosomal protein L23a
- SPACA3: Sperm acrosome membrane-associated protein 3
- Several CC chemokines: CCL1, CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL7, CCL8, CCL11, CCL13, CCL14, CCL15, CCL16, CCL18, and CCL23
q-arm
- GRB7: Growth factor Receptor-Bound protein 7 (17q12)
- RHBDF2: Rhomboid family member 2 (17q25.3)
- RPS6KB1 or S6K: Ribosomal protein S6-kinase (17q23.1)
- SCN4A: Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subunit Alpha Nav1.4 (17q23.3)
- CBX1: chromobox homolog 1 (17q21.32)
- ACTG1: actin, gamma 1 (17q25)
- BRCA1: breast cancer 1, early onset (17q21)
- COL1A1: collagen, type I, alpha 1 (17q21.33)
- ERBB2 loca leukemia viral oncogene homolog 2, neuro/glioblastoma derived oncogene homolog (avian) (17q12)
- GALK1: galactokinase 1 (17q24)
- GFAP: glial fibrillary acidic protein (17q21)
- KCNJ2: potassium inwardly-rectifying channel, subfamily J, member 2 (17q24.3)
- MAPT gene coding for encoding tau protein (17q21.1)
- NF1: neurofibromin 1 (neurofibromatosis, von Recklinghausen disease, Watson disease) (17q11.2)
- NOG: Noggin protein (17q22)
- SLC4A1: Band 3 anion transporter protein. Solute carrier family 4, member 1 (17q21.31)
- SLC6A4: Serotonin transporter linked to Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) [2] (17q11.2)
- TMC6 and TMC8: Transmembrane channel-like 6 and 8 (epidermodysplasia verruciformis) (17q25.3)
- USH1G: Usher syndrome 1G (autosomal recessive) (17q25.1)
- RARA or RAR-alpha: Retinoic acid receptor Alpha (involved in t(15,17) with PML) (17q21)
p-arm
- SHBG: Sex hormone binding globulin (17p13.1)
- ACADVL: acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase, very long chain (17p13.1)
- ASPA: aspartoacylase (Canavan disease) (17p13.3)
- CTNS: cystinosin, the lysosomal cystine transporter (17p13)
- FLCN: folliculin (17p11.2)
- MYO15A: myosin XVA (17p11.2)
- PMP22: peripheral myelin protein 22 (17p12)
- TP53: tumor suppressor protein p53 (Li-Fraumeni syndrome), tumor suppressor gene (17p13.1)
- RAI1: retinoic acid induced 1 (17p11.2)
- USP6: Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase 6 linked to Aneurysmal bone cyst (17p13)
Diseases and disorders
The following diseases are related to genes on chromosome 17:
- 17Q21.31 Microdeletion Syndrome
- Alexander disease
- Andersen-Tawil syndrome
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé syndrome
- Bladder cancer
- Breast cancer
- Bruck syndrome
- Camptomelic dysplasia
- Canavan disease
- Cerebroretinal microangiopathy with calcifications and cysts
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, type 1
- Corticobasal degeneration
- Cystinosis
- Depression
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, classical type
- Epidermodysplasia verruciformis
- Galactosemia
- Glycogen storage disease type II (Pompe disease)
- Hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies
- Howel–Evans syndrome
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome
- Maturity onset diabetes of the young type 5
- Miller-Dieker syndrome
- Multiple synostoses syndrome
- Neurofibromatosis type I
- Nonsyndromic deafness
- Nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal dominant
- Nonsyndromic deafness, autosomal recessive
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type I
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type II
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type III
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Type IV
- Potocki-Lupski syndrome
- Proximal symphalangism
- Smith-Magenis syndrome
- Usher syndrome
- Very long-chain acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase deficiency
- Aneurysmal bone cyst
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder
References
- ↑ "Table 2.3: Human chromosome groups". Human Molecular Genetics (2nd ed.). Garland Science. 1999.
- ↑ "Obsessive Compulsive Disorder". An Online Catalog of Human Genes and Genetic Disorders.
- Gilbert F (1998). "Disease genes and chromosomes: disease maps of the human genome. Chromosome 17". Genet Test. 2 (4): 357–81. doi:10.1089/gte.1998.2.357. PMID 10464617.
- Gene Card Website http://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=SCN4A
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Human chromosome 17. |
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/8/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.