Maxillary nerve
| Maxillary nerve | |
|---|---|
 Alveolar branches of superior maxillary nerve and pterygopalatine ganglion. | |
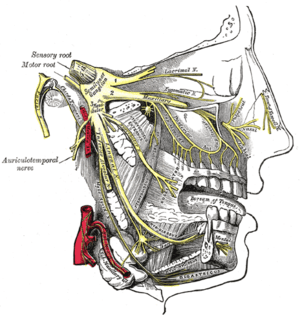 Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion. | |
| Details | |
| From | Trigeminal nerve |
| To | Infraorbital nerve, zygomatic nerve, posterior superior alveolar nerve, palatine nerve, nasopalatine nerve, sphenopalatine ganglion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Nervus maxillaris |
| MeSH | A08.800.800.120.760.550 |
| TA | A14.2.01.037 |
| FMA | 52724 |
The maxillary nerve (CN V2) is one of the three branches or divisions of the trigeminal nerve, the fifth (V) cranial nerve. It comprises the principal functions of sensation from the maxillary, nasal cavity, sinuses, the palate and subsequently that of the mid-face,[1] and is intermediate, both in position and size, between the ophthalmic nerve and the mandibular nerve.[2] Its function is the transmission of sensory fibers from the maxillary teeth, the skin between the palpebral fissure and the mouth, and from the nasal cavity and sinuses.[3]
Structure
It begins at the middle of the trigeminal ganglion as a flattened plexiform band, and, passing horizontally forward, it leaves the skull through the foramen rotundum, where it becomes more cylindrical in form, and firmer in texture. It then crosses the pterygopalatine fossa, inclines lateralward on the back of the maxilla, and enters the orbit through the inferior orbital fissure. It then runs forward on the floor of the orbit, at first in the infraorbital groove and then in the infraorbital canal remaining outside the periosteum of the orbit. It then emerges on the face through the infraorbital foramen and terminates by dividing into palpebral, lateral nasal and labial branches. The nerve is accompanied by the infraorbital branch of (the third part of) the maxillary artery and the accompanying vein.
Branches
Its branches may be divided into four groups, depending upon where they branch off: in the cranium, in the pterygopalatine fossa, in the infraorbital canal, or on the face.
In the cranium
- Middle meningeal nerve in the meninges
From the pterygopalatine fossa
- Zygomatic nerve (zygomaticotemporal nerve, zygomaticofacial nerve), through the inferior orbital fissure
- Nasopalatine nerve, through the sphenopalatine foramen
- Posterior superior alveolar nerve
- Greater and lesser palatine nerves
- Pharyngeal nerve
In the infraorbital canal
On the face
Function
The Maxillary nerve gives cutaneous branches to the face. It also carries parasympathetic preganglionic fibers (sphenopalatine) and postganglionic fibers (zygomatic, greater and lesser petrosal and nasopalatine) to and from the pterigopalatine ganglion.
Additional Images
- Maxillary nerve
See also
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
Books
- Feneis, Heinz; Dauber, Wolfgang (2007). Pocket Atlas of Human Anatomy (5th ed.). Thieme. pp. 400–401.
External links
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/h_n/cn/cn1/cnb2.htm
- cranialnerves at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (VII)