Three-domain system
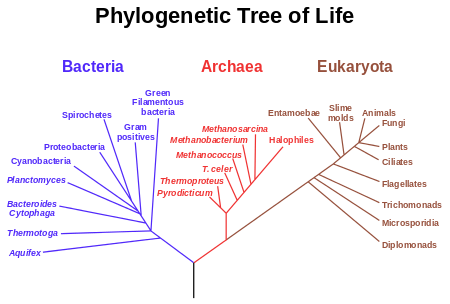
The three-domain system is a biological classification introduced by Carl Woese et al. in 1977[1][2] that divides cellular life forms into archaea, bacteria, and eukaryote domains. In particular, it emphasizes the separation of prokaryotes into two groups, originally called Eubacteria (now Bacteria) and Archaebacteria (now Archaea). Woese argued that, on the basis of differences in 16S rRNA genes, these two groups and the eukaryotes each arose separately from an ancestor with poorly developed genetic machinery, often called a progenote. To reflect these primary lines of descent, he treated each as a domain, divided into several different kingdoms. Woese initially used the term "kingdom" to refer to the three primary phylogenic groupings, and this nomenclature was widely used until the term "domain" was adopted in 1990.[2]
Classification
_crop.jpg)
The three-domain system adds a level of classification (the domains) "above" the kingdoms present in the previously used five- or six-kingdom systems. This classification system recognizes the fundamental divide between the two prokaryotic groups, insofar as archaea appear to be more closely related to eukaryotes than they are to other prokaryotic bacteria. The current system has the following listed kingdoms in the three domains:
Domain Archaea – prokaryotic, no nuclear membrane, distinct biochemistry and RNA markers from bacteria, possess unique ancient evolutionary history for which they are considered some of the oldest species of organisms on Earth; traditionally classified as archaebacteria; often characterized by living in extreme environments. Some examples of archaeal organisms are methanogens which produce the gas methane, halophiles which live in very salty water, and thermoacidophiles which thrive in acidic high temperature water.
Domain Bacteria – prokaryotic, consists of prokaryotic cells possessing primarily diacyl glycerol diester lipids in their membranes and bacterial rRNA, no nuclear membrane, traditionally classified as bacteria. Most of the known pathogenic prokaryotic organisms belong to bacteria (see [3] for exceptions), and are currently studied more extensively than Archaea. Some examples of bacteria include Cyanobacteria photosynthesizing bacteria that are related to the chloroplasts of eukaryotic plants and algae, Spirochaetes – Gram-negative bacteria that include those causing syphilis and Lyme disease, and Firmicutes – Gram-positive bacteria including Bifidobacterium animalis which is present in the human large intestine.
Domain Eukarya – eukaryotes, organisms that contain a membrane-bound nucleus. An inexhaustive list of eukaryotic organisms includes:
- Kingdom Fungi or fungi
Examples:
- Saccharomycotina – includes true yeasts
- Basidiomycota – includes mushrooms
- Kingdom Plantae or plants
Examples:
- Bryophyta – mosses
- Magnoliophyta – flowering plants
- Kingdom Animalia or animals
Examples:
- Arthropoda – includes insects, arachnids, and crustaceans
- Chordata – includes vertebrates and, as such, human beings
- Kingdom Chromalvaeolate – a group of eukaryotes that represent descent from an organism that had an endosymbiosis between a line related to a bikont and a red alga. However, the monophyly of this group is challenged.
Niches
Each of the three cell types tends to fit into recurring specialties or roles. Bacteria tend to be the most prolific reproducers, at least in moderate environments. Archaeans tend to adapt quickly to extreme environments, such as high temperatures, high acids, high sulfur, etc. This includes adapting to use a wide variety of food sources. Eukaryotes are the most flexible with regard to forming cooperative colonies, such as in multi-cellular organisms, including humans. In fact, the structure of a Eukaryote is likely to have derived from a joining of different cell types, forming organelles.
Parakaryon myojinensis (incertae sedis) is a single-celled organism known by a unique example. "[T]his organism appears to be a life form distinct from prokaryotes and eukaryotes",[4] with features of both.
Criticism
Parts of the three-domain theory have been challenged by some scientists, including Ernst Mayr, Thomas Cavalier-Smith and Radhey Gupta.[5][6][7] In particular, Gupta argues that the primary division within prokaryotes should be among those surrounded by a single membrane (monoderm), including gram-positive bacteria and archaebacteria, and those with an inner and outer cell membrane (diderm), including gram-negative bacteria. He claims that sequence of features and phylogenies from some highly conserved proteins are inconsistent with the three-domain theory, and that it should be abandoned despite its widespread acceptance.
See also
References
- ↑ Woese C, Fox G (1977). "Phylogenetic structure of the bacteria domain: the primary kingdoms.". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 74 (11): 5088–90. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.5088W. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.11.5088. PMC 432104
 . PMID 270744.
. PMID 270744. - 1 2 Woese C, Kandler O, Wheelis M (1990). "Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya.". Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87 (12): 4576–9. Bibcode:1990PNAS...87.4576W. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. PMC 54159
 . PMID 2112744. Retrieved 11 Feb 2010.
. PMID 2112744. Retrieved 11 Feb 2010. - ↑ Eckburg, Paul B.; Lepp, Paul W.; Relman, David A. (2003). "Archaea and Their Potential Role in Human Disease". Infection and Immunity. 71 (2): 591–596. doi:10.1128/IAI.71.2.591-596.2003. PMC 145348
 . PMID 12540534.
. PMID 12540534. - ↑ Yamaguchi M, Mori Y, Kozuka Y, Okada H, Uematsu K, Tame A, Furukawa H, Maruyama T, Worman CO, Yokoyama K (2012). "Prokaryote or eukaryote? A unique microorganism from the deep sea.". J Electron Microsc (Tokyo). 61 (6): 423–431. doi:10.1093/jmicro/dfs062.
- ↑ Gupta, Radhey S (1998). "Life's Third Domain (Archaea): An Established Fact or an Endangered Paradigm?: A New Proposal for Classification of Organisms Based on Protein Sequences and Cell Structure.". Theoretical Population Biology. 54 (2): 91–104. doi:10.1006/tpbi.1998.1376. PMID 9733652.
- ↑ Mayr, E. (1998). "Two empires or three?". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95: 9720–9723. doi:10.1073/pnas.95.17.9720. PMC 33883
 . PMID 9707542.
. PMID 9707542. - ↑ Cavalier-Smith, T (2002). "The neomuran origin of archaebacteria, the negibacterial root of the universal tree and bacterial megaclassification". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 52 (1): 7–76.