Timeline of the introduction of television in countries
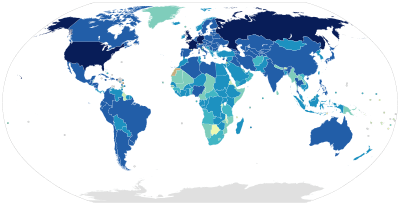
A map showing when television was introduced in each country.
1927
1940
1950
1960
1970
1980
1990
2001
No television
No data
This is a list of when the first publicly announced television broadcasts occurred in the mentioned countries. Non-public field tests and closed circuit demonstrations are not included. This list should not be interpreted to mean the whole of a country had television service by the specified date. For example, the United States, Great Britain, Germany, and the former Soviet Union all had operational television stations and a limited number of viewers by the year 1939. However, in those countries, only very few cities in each country had television service. Television broadcasts were not yet available in most places.
| Year | Countries |
|---|---|
| 1928 | |
| 1929 | |
| 1931 | |
| 1934 | |
| 1935 | |
| 1936 | |
| 1937 | |
| 1938 | |
| 1939 | |
| 1942 | |
| 1944 | |
| 1945 | |
| 1946 | |
| 1948 | |
| 1950 | |
| 1951 | |
| 1952 | |
| 1953 | |
| 1954 | |
| 1955 | |
| 1956 | |
| 1957 | |
| 1958 | |
| 1959 | |
| 1960 | |
| 1961 | |
| 1962 | |
| 1963 | |
| 1964 | |
| 1965 | |
| 1966 | |
| 1967 | |
| 1968 | |
| 1969 | |
| 1970 | |
| 1972 | |
| 1973 | |
| 1974 | |
| 1975 | |
| 1976 | |
| 1977 | |
| 1978 | |
| 1979 | |
| 1980 | |
| 1981 | |
| 1982 | |
| 1983 | |
| 1984 | |
| 1986 | |
| 1989 | |
| 1991 | |
| 1992 | |
| 1993 | |
| 1995 | |
| 1996 | |
| 1999 | |
| 2000 | |
| 2004 | |
| 1996 | |
| 2008 | |
| 2009 | |
Countries without television
- Solomon Islands
- Kiribati (closed in 2013)
- Tuvalu (no native service)
See also
Notes and citations
- ↑ See WRGB History, How Television Came to Boston: The Forgotten Story of W1XAY, W3XK: America's first television station, and "WRNY to Start Daily Television Broadcasts," New York Times, August 13, 1928, p. 13.
- ↑ See J.L. Baird: Television in 1932.
- ↑ See Museum of Broadcast Communications: Germany and Berlin 1936: Television in Germany.
- ↑ Australian TV – The First 25 Years by Peter Bielby, page 173. ISBN 0-17-005998-7
- ↑ Linking a Nation – Chap 9 – Australian Heritage Council
- ↑ Peter Luck, 50 Years of Australian Television ISBN 1-74110-367-3 p.15
- ↑ "Birth of Our Nation". Brisbane Courier Mail. Archived February 15, 2008, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ See The Birth of Live Entertainment and Music on Television, November 6, 1936, and 1937 RCA Publicity Photographs. "Eighty-seven video programs were telecast by NBC last year," "Where Is Television Now?", Popular Mechanics, August 1938, p. 178. Regularly scheduled electronic broadcasts began in April 1938 in New York (to the second week of June, and resuming in August) and Los Angeles. "Telecasts Here and Abroad," The New York Times, April 24, 1938, Drama-Screen-Radio section, p. 10; "Early Birds," Time, June 13, 1938; "Telecasts to Be Resumed," The New York Times, Aug. 21, 1938, Drama-Screen-Radio section, p. 10; Robert L. Pickering, "Eight Years of Television in California," California — Magazine of the Pacific, June 1939. Also note that many rural areas of the Southern United States didn't receive television until the late 1950s and early 1960s.
- ↑ Although 180-line cathode ray tube receivers were manufactured in France in 1936, a mechanical scanning camera was still used at the transmitter in Paris until 1937.
- 1 2 See The Warsaw Voice: What's On? and Historia Przemysłowego Instytutu Telekomunikacji przed II wojną światową at the Wayback Machine (archived September 28, 2007) (in Polish).
- ↑ See The Evolution of TV: A Brief History of TV Technology in Japan: “Can you see me clearly?”; Public TV Image Experiments.
- ↑ See Early Television in Italy
- ↑ Off from 1939 to 1945 for the Second World War.
- ↑ Off from 1939 to 1946 for the Second World War.
- ↑ Latin America's first experimental television station (Spanish)
- ↑ See ; Czechoslovakia became two separate states, namely the Czech Republic and Slovakia, in 1993.
- ↑ See History of DR.
- ↑ Dutch-language BRT used the Belgian 625-line standard and French-language RTB used the Belgian 819-line standard (abandoned in 1963). Early Belgian sets were very expensive because they could receive 4 different standards: Belgian 625, European 625, Belgian 819, French 819. Later a 5th standard was added with the French 625-line standard.
- ↑ Cheurfi, Achour (September 2010). Radio et télévision : histoire d'un monopole. La presse algérienne : génèse, conflits et défis (in French). Algiers: Casbah Éditions. p. 88–p. 148.
- ↑ The date refers to the launch of the TV channel in republics and autonomuous provinces of Yugoslavia. There were RTV Zagreb, in Croatia (1956), RTV Ljubljana in Slovenia (1958), RTV Belgrade in Serbia (1958), RTV Skopje in Macedonia (1964), RTV Sarajevo in Bosnia and Herzegovina (1969), and RTV Titograd (Podgorica) in Montenegro (1971). In Kosovo (RTV Priština) and Vojvodina (RTV Novi Sad), it was introduced in 1975.
- ↑ Television was introduced in Hong Kong when it was a British crown colony.
- ↑ http://www.lrt.lt/en/about/history
- ↑ Television was introduced in the Ryukyu Islands (now part of Japan) when they were under U.S. administration.
- ↑ The United Arab Republic was a short-lived political union between
 Egypt and
Egypt and  Syria. The union began in 1958 and existed until 1961, when Syria seceded from the union.
Syria. The union began in 1958 and existed until 1961, when Syria seceded from the union. - ↑ Ireland had received broadcasts from the United Kingdom since 1949.
- ↑ Previously received television broadcasts from Italy.
- ↑ This is the year when television was introduced in territories under its administration. After the Chinese Civil War, the government of the Republic of China retreated to Taiwan and other islands, and Mainland China was controlled by the People's Republic of China.
- ↑ Gibraltar had previously received television broadcasts from Spain.
- ↑ Wales had received broadcasts from England since 1952.
- ↑ The Israeli Ministry of Education in cooperation with the Rothschild Fund started limited broadcasts to schools in March 1966. A public state-owned TV channel started broadcasting in May 1968. Broadcasts were black and white (with a few exceptions) until the early 1980s.
- ↑ The Bahamas had previously received broadcasts from the United States.
- ↑ Test service available only in Yangon in 1979. Formal launch in 1981. See .
- ↑ http://www.tvm.mr/fr/index.php?page=1&id=1
- ↑ Although the Vatican did not have a television service of its own until 1983, broadcasts from Italy had been received since 1954.
- ↑ Television available from Nong Khai city in Thailand since mid-1970s]]
- ↑ Television broadcasts have been received from Canada since the late 1960's.
- ↑ Television broadcasts had also been received from Argentina.
- ↑ Television came to Fiji part-time for the 1991 Rugby World Cup. It arrived full-time in 1994.
- ↑ "Bhutan TV Follows Cyber Launch". BBC News. 2 June 1999.
- ↑ http://www.radiotv.aland.fi/om-alands-radio (Swedish).
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/25/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.