uClibc
| Developer(s) | Erik Andersen |
|---|---|
| Initial release | February 13, 2000 |
| Stable release | 0.9.33.2 (May 15, 2012) [±][1] |
| Repository |
git |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Platform | Embedded Linux |
| Type | |
| License | GNU LGPL[2] |
| Website |
www |
In computing, uClibc (sometimes written µClibc) is a small C standard library intended for Linux kernel-based operating systems for embedded systems and mobile devices. uClibc was created to support μClinux, a version of Linux not requiring a memory management unit and thus suited for microcontrollers (uCs; the "u" is a romanization of μ for "micro").[3]
Development on uClibc started around 1999.[4] uClibc was mostly written from scratch,[5] but has incorporated code from glibc and other projects.[6] The project lead is Erik Andersen, and the other main contributor is Manuel Novoa III. Licensed under the GNU Lesser General Public License, uClibc is free and open-source software.
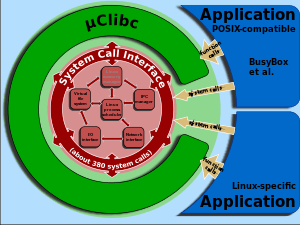
uClibc is much smaller than the glibc, the C library normally used with Linux distributions. While glibc is intended to fully support all relevant C standards across a wide range of hardware and kernel platforms, uClibc is specifically focused on embedded Linux. Features can be enabled or disabled according to space requirements.
uClibc runs on standard and MMU-less Linux systems. It supports i386, x86-64, ARM (big/little endian), AVR32, Blackfin, h8300, m68k, MIPS (big/little endian), PowerPC, SuperH (big/little endian), SPARC, and v850 processors.
uClibc-ng[7] is a spin-off of uClibc that regularly provides a stable and tested release, which is more suitable for different software development processes.
See also
References
- ↑ "µClibc News". µClibc. 2012-02-01. Retrieved 2012-03-24.
- ↑ "uClibc FAQ: Licensing". uclibc.org. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
- ↑ uClibc naming Accessed on February 10, 2008.
- ↑ http://www.uclibc.org/copyright.txt
- ↑ "History". uClibc FAQ. Retrieved 2007-06-19.
- ↑ "uClibc Changelog". Archived from the original on 2007-06-09. Retrieved 2007-06-19.
pthreads support (derived from glibc 2.1.3's linuxthreads library) [...] Merged in the random number support (rand, srand, etc) from glibc.
- ↑ "uClibc-ng". uclibc-ng.org. Retrieved 11 July 2015.
Further reading
- Karim Yaghmour, Jon Masters, Gilad Ben-Yossef, Philippe Gerum (2008). Building Embedded Linux Systems (2 ed.). O'Reilly Media. pp. 115–127. ISBN 0-596-52968-6.
- von Hagen, William L. (2006). The Definitive Guide to GCC, Second Edition. Berkeley, CA: APress. pp. 290–297. ISBN 1-59059-585-8.
External links
- Official website
- uClibc-ng
- "uClibc". Freecode.
- Comparison of C/POSIX standard library implementations for Linux
- Availability of C/POSIX standard libraries on different architectures