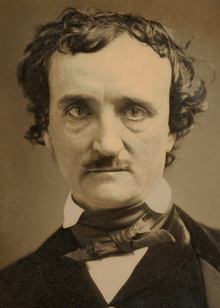1809
This article is about the year 1809. For the Swedish/Finnish government project, see Year 1809.
| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | 18th century · 19th century · 20th century |
| Decades: | 1770s · 1780s · 1790s · 1800s · 1810s · 1820s · 1830s |
| Years: | 1806 · 1807 · 1808 · 1809 · 1810 · 1811 · 1812 |
| 1809 in topic: |
| Humanities |
| Archaeology – Architecture – Art – Literature – Music |
| By country |
| Australia – Brazil - Canada – Denmark - France – Germany – Mexico – Norway - Philippines - Portugal– Russia - South Africa – Spain - Sweden - United Kingdom – United States |
| Other topics |
| Rail Transport – Science – Sports |
| Lists of leaders |
| Colonial Governors – State leaders |
| Birth and death categories |
| Births – Deaths |
| Establishments and disestablishments categories |
| Establishments – Disestablishments |
| Works category |
| Works |
| Gregorian calendar | 1809 MDCCCIX |
| Ab urbe condita | 2562 |
| Armenian calendar | 1258 ԹՎ ՌՄԾԸ |
| Assyrian calendar | 6559 |
| Bengali calendar | 1216 |
| Berber calendar | 2759 |
| British Regnal year | 49 Geo. 3 – 50 Geo. 3 |
| Buddhist calendar | 2353 |
| Burmese calendar | 1171 |
| Byzantine calendar | 7317–7318 |
| Chinese calendar | 戊辰年 (Earth Dragon) 4505 or 4445 — to — 己巳年 (Earth Snake) 4506 or 4446 |
| Coptic calendar | 1525–1526 |
| Discordian calendar | 2975 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1801–1802 |
| Hebrew calendar | 5569–5570 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 1865–1866 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 1730–1731 |
| - Kali Yuga | 4909–4910 |
| Holocene calendar | 11809 |
| Igbo calendar | 809–810 |
| Iranian calendar | 1187–1188 |
| Islamic calendar | 1223–1224 |
| Japanese calendar | Bunka 6 (文化6年) |
| Javanese calendar | 1735–1736 |
| Julian calendar | Gregorian minus 12 days |
| Korean calendar | 4142 |
| Minguo calendar | 103 before ROC 民前103年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | 341 |
| Thai solar calendar | 2351–2352 |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1809. |
1809 (MDCCCIX) was a common year starting on Sunday (dominical letter A) of the Gregorian calendar and a common year starting on Friday (dominical letter C) of the Julian calendar, the 1809th year of the Common Era (CE) and Anno Domini (AD) designations, the 809th year of the 2nd millennium, the 9th year of the 19th century, and the 10th and last year of the 1800s decade. As of the start of 1809, the Gregorian calendar was 12 days ahead of the Julian calendar, which remained in localized use until 1918.
Events
January–March
- January 5 – The Treaty of the Dardanelles between the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the Ottoman Empire is concluded.
- January 10 – Peninsular War: French Marshal Jean Lannes begins the Siege of Zaragoza.
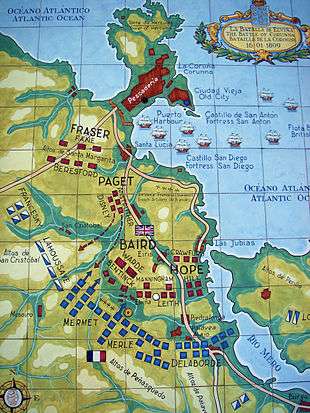
- January 16 – Peninsular War: Battle of Corunna in Galicia (Spain): The British (under General Sir John Moore, who is killed) resist an attempt by the French (under Marshal Soult) to prevent them embarking.
- February 3 – The Illinois Territory is created.
- February 8 – Franz I of Austria declares war on France.
- February 11 – Robert Fulton patents the steamboat in the United States.[1][2]
- February 17 – Miami University (Ohio) is established on the township of land required to be set aside for it under the conditions of the Miami Purchase in 1794.
- February 20
- A decision by the Supreme Court of the United States states that the power of the federal government is greater than any individual state.
- The Siege of Zaragoza grinds to a halt as Jose Palafox surrenders. Over 60,000 have been killed on both sides in 41 days of street fighting.
- February 25 – Battle of Valls: Spanish forces are defeated in Catalonia by Marshal Laurent de Gouvion Saint-Cyr.
- February 27 – Action of 27 February 1809: Captain Bernard Dubourdieu captures HMS Proserpine
- March 1 – Embargo Act of 1807 is repealed in the United States; the Nonintercourse Act replaces it.
- March 4 – James Madison is sworn in as President of the United States.
- March 13 – A military coup ousts Gustav IV Adolf of Sweden; he is confined in Gripsholm Castle.
- March 29
- At the Diet of Porvoo, Finland's four Estates pledge allegiance to Alexander I of Russia, commencing the secession of the future Grand Principality of Finland from Sweden. The Emperor in return, promises to retain and uphold former laws and privileges as well as the dominant Lutheran religion. His pledge is later interpreted by the Finns as a confirmation of constitutional laws, which had, effectively, established Finland as a separate state in real union with the Russia.
- King Gustav IV Adolf of Sweden abdicates after the Coup of 1809 and is later exiled.
- Peninsular War
- First Battle of Porto: 18,000 Portuguese soldiers are drowned in a rout after defeat by the French under Marshal Soult.
- Battle of Medellín at Extremadura: massive Spanish casualties in a rout by French cavalry under Marshal Victor.
April–June
- April 9 – Tiroleans rise under the command of Andreas Hofer against French and Bavarian occupation.
- April 10 – Napoleonic Wars: The War of the Fifth Coalition begins when forces of the Austrian Empire invade Bavaria.
- April 14 – Battle of Abensberg, Bavaria: Napoleon defeats Austria.
- April 18 – The 2,000 Guineas Stakes horse race is first run in England.[3]
- April 19 – War of the Fifth Coalition:
- Battle of Raszyn: The armies of the Austrian Empire are defeated by the Duchy of Warsaw.
- Battle of Teugen-Hausen: The armies of the Austrian Empire are defeated by the French and their Bavarian allies.
- April 22 – Battle of Eckmühl: French troops under Napoleon I and Marshal Davout defeat the Austrians under Archduke Charles.
- May 5
- Mary Kies is the first American woman to be awarded a patent (for a technique of weaving straw hats with silk and thread).[4]
- The Swiss canton of Aargau denies Jews citizenship.
- May 10 – Gustav IV Adolf is officially deposed from the Swedish throne by the Riksdag of the Estates.
- May 10–11 – Peninsular War: Battle of Grijó: the Anglo-Portuguese Army commanded by Sir Arthur Wellesley defeats the French army commanded by Marshal Soult in Portugal.
- May 12 – Peninsular War: Second Battle of Porto: the Anglo-Portuguese Army commanded by Wellesley drives the French army commanded by Marshal Soult out of Porto and forces them to retreat from the country.
- May 17 – Napoleon I of France orders the annexation of the Papal States to the French Empire. When he announces that the Pope's secular power has ended, the Pope excommunicates him.
- May 21 – Battle of Aspern-Essling: Austrian troops under Archduke Karl beat the French under Napoleon in a hard-fought battle.
- May 24 – Dartmoor Prison opens in England to house French prisoners of war.[5]
- May 31 – Action of 31 May 1809 in the Bay of Bengal, the first major naval action in the Mauritius campaign of 1809–11: The French frigate Caroline, operating from Isle de France (Mauritius), captures most of a British East India Company fleet.
- June 6 – Sweden promulgates a new Instrument of Government, which restores political power to the Riksdag of the Estates after authoritarian rule since 1772. On the same day, Duke Charles (uncle of the deposed king Gustav IV Adolf) is elected King under the name Charles XIII.
- June 7 – Shoja Shah of the Durrani Empire signs a treaty with the British. Only weeks later, he is succeeded by Mahmud Shah.
- June 14 – French victory in the battle of Raab prevented archduke John of Austria from bringing any significant force to the battle of Wagram.
July–September
- July 5–July 6 – Battle of Wagram: Napoleon defeats the Austrians.
- July 6 – French troops arrest Pope Pius VII and take him to Liguria.
- July 8–9 – Finnish War: The Swedish archipelago fleet defeats the Russians in the naval battle of Porkala
- July 10 – French Marshal Marmont engages in the inconclusive Battle of Znaim against the Austrians.
- July 16 – The city of La Paz (current Bolivia) declares its independence from the Spanish Crown and forms the Junta Tuitiva, the first independent government in Spanish America, led by Pedro Domingo Murillo.
- July 28 – Peninsula War: Battle of Talavera: Sir Arthur Wellesley's British, Portuguese and Spanish army defeats a French force.[3]
- July 30 – Walcheren Campaign: A British invasion army lands on Walcheren.
- August 8 – Seventy disciples of Vilna Gaon arrive in Palestine.
- August 10 – Ecuador declares independence from Spain.
- August 11 – Battle of Almonacid de Toledo: A poorly led Spanish army is defeated by King Joseph Bonaparte's French army.
- September 17 – The Peace of Hamina is signed between Russia and Sweden in the Finnish War. The territory to become the Grand Principality of Finland is ceded to Russia by the Treaty of Fredrikshamn.
- September 18 – A new theatre to hold the Royal Opera House opens in London to replace the first, burnt down in a fire in 1808. The price increases lead to the Old Price Riots which last for 64 days.
October–December
- October 8 – Prince Klemens von Metternich becomes foreign minister of the Austrian Empire.
- October 11 – Along the Natchez Trace in Tennessee, explorer Meriwether Lewis dies under mysterious circumstances at an inn called Grinder's Stand.
- October 14 – The Treaty of Schönbrunn cedes the Illyrian Provinces to France.
- November 10 – Berners Street hoax: Theodore Hook manages to attract dozens of people to 54 Berners Street in London.
- November 19 – Battle of Ocaña: A Spanish army is ridden down and 4000 are killed and wounded by French forces.
- November 20 – Gustav Koerner: The revolutionary, journalist, lawyer, politician, and statesman of Illinois and Germany and Colonel of the U.S. Army was born in Frankfurt
- November 25 – Benjamin Bathurst, a British diplomat, mysteriously disappears (possibly murdered) in Perleberg, west of Berlin.
- December – Boyd massacre: Whangaroa Māori people kill and eat 66 crew and passengers of the brigantine Boyd in New Zealand.[6]
- December 26 – A British invasion force leaves Vlissingen.
- December 30 – Wearing masks at balls is forbidden in Boston, Massachusetts.
Date unknown
- William Combe begins publication of the verse Tour of Dr Syntax in search of the Picturesque in Ackermann's Political Magazine (London), illustrated with cartoons by Thomas Rowlandson, depicting comic and ridiculous scenes involving a hapless country physician and coming to represent British Regency humour.
- The USS Constitution ("Old Ironsides") is recommissioned as the flagship of the North Atlantic Squadron.
- Louis Poinsot describes the two remaining Kepler–Poinsot polyhedra.
- Jean-Baptiste Lamarck publishes Philosophie Zoologique, outlining a (wrong) concept of evolution by acquisition or loss of inherited characteristics through use or disuse.
- British recruits to the British East India Company and subsequently to the Indian Civil Service are required to learn at least one Indian language fluently.
Births
January–June
- January 1 – Cao Bá Quát, Vietnamese poet (d. 1855)
- January 4 – Louis Braille, French teacher, inventor of braille (d. 1852)
- January 15
- Cornelia Connelly, American founder of the Society of the Holy Child Jesus (d. 1879)
- Pierre-Joseph Proudhon, French anarchist (d. 1864)
- January 19 – Edgar Allan Poe, American writer and poet (d. 1849)
- February 3 – Felix Mendelssohn, German composer (d. 1847)
- February 12
- Abraham Lincoln, 16th President of the United States (d. 1865)
- Charles Darwin, British naturalist (d. 1882)
- February 15 – Cyrus McCormick, American inventor (d. 1884)
- February 23 – William Sprague, American minister and politician from Michigan (d. 1868)
- March 24 – Joseph Liouville, French mathematician (d. 1882)
- March 27 – Georges-Eugène Haussmann, French civic planner
- March 29 – Bettino Ricasoli, Italian statesman (d. 1880)
- April 1 – Nikolai Gogol, Russian writer (d. 1852)
- April 15 – Hermann Grassmann, Prussian mathematician (d. 1877)
- May 20 – Albert Newsam, American artist (d. 1864)
- June 4
- Columbus Delano, American statesman (d. 1896)
- John Henry Pratt, English clergyman and mathematician (d. 1871)
- June 8 – Richard Wigginton Thompson, American politician (d. 1900)
- June 18 – Stephen Greenleaf Bulfinch, American minister and hymn writer (d 1870)
- June 20 – Isaak August Dorner, German theologian (d. 1884)
July–December
- July 2 – John R. Goldsborough, United States Navy commodore (d. 1877)
- August 6 – Alfred, Lord Tennyson, British poet (d. 1892)
- August 8 – Heinrich Abeken, German theologian (d. 1872)
- August 27 – Hannibal Hamlin, 15th Vice President of the United States, American politician (d. 1891)
- August 29 – Oliver Wendell Holmes, Sr., American physician and writer (d. 1894)
- October 22 – Volney E. Howard, American politician (d. 1889)
- September 27 – Raphael Semmes, American and Confederate naval officer (d. 1877)
- November 4 – Benjamin Robbins Curtis, Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the United States (d. 1874)
- November 27 – Fanny Kemble, British-born American actress and writer (d. 1893)
- December 24 – Kit Carson, American frontiersman (d. 1868)
- December 29 – William Ewart Gladstone, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (d. 1898)
Date unknown
- Samuel Ajayi Crowther, 1st Black Anglican Bishop, pioneer linguist (d. 1891)
- Henry K. Hoff, American admiral (d. 1878)
- Marie Durocher, Brazilian obstetrician and physician (d. 1893)
Deaths
January–June
- January 16 – John Moore, British general (killed in battle) (b. 1761)
- February 25 – John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore (Lord Dunmore)
- March 7 – Johann Georg Albrechtsberger, Austrian composer (b. 1736)
- March 11 – Hannah Cowley, English dramatist and poet (b. 1743)
- March 18 – Karoline Kaulla, German banker (b. 1739)
- March 20 – Mary Bateman, English woman executed for murder, known as the "Yorkshire Witch"
- March 25 – Anna Seward, English writer (b. 1747)
- March 27 – Joseph-Marie Vien, French painter (b. 1716)
- May 13 – Beilby Porteus, English bishop and abolitionist (b. 1731)
- May 17 – Leopold Auenbrugger, Austrian physician (b. 1722)
- May 24 – Charles Rainsford, British General (b. 1728)
- May 31
- Joseph Haydn, Austrian composer (b. 1732)
- Jean Lannes, French marshal (mortally wounded in battle (b. 1769)
- June 4 – Nicolai Abildgaard, Danish painter (b. 1743)
- June 8 – Thomas Paine, American revolutionary writer (b. 1737)
July–December
- July 6 – Antoine Charles Louis de Lasalle, French cavalry general (killed in battle) (b. 1775)
- August 8 – Ueda Akinari, Japanese author and scholar (b. 1734)
- August 18 – Matthew Boulton, English manufacturer and engineer (b. 1728)
- September 7 – Caroline Schelling, German scholar (b. 1763)
- October 8 – James Elphinston, Scottish philologist (b. 1721)
- October 11 – Meriwether Lewis, American explorer (suicide) (b. 1774)
- October 30 – William Cavendish-Bentinck, 3rd Duke of Portland, Prime Minister of the United Kingdom (b. 1738)
- November 9 – Paul Sandby, English cartographer and painter (b. 1725)
References
- ↑ "Robert Fulton patented the steamboat in 1809". Thinkfinity. Verizon. Retrieved 2011-04-15.
- ↑ "The Fulton Patents". Today in Science History. Retrieved 2011-04-15.
- 1 2 Palmer, Alan; Veronica (1992). The Chronology of British History. London: Century Ltd. pp. 243–244. ISBN 0-7126-5616-2.
- ↑ "Mary Kies - Patenting Pioneer". About.com. Retrieved 2007-05-14.
- ↑ Penguin Pocket On This Day. Penguin Reference Library. 2006. ISBN 0-14-102715-0.
- ↑ "The Boyd incident - a frontier of chaos?". New Zealand History online. Ministry for Culture and Heritage. 2011-12-07. Retrieved 2012-03-03.
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 11/22/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.