1820 Settlers
Part of a series on the |
|---|
| History of South Africa |
| General periods |
| Specific themes |
|
|
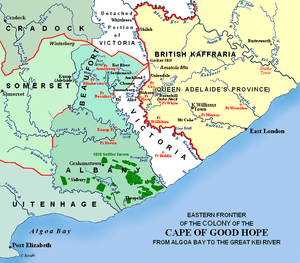
The 1820 Settlers were several groups or parties of white British colonists settled by the British government and the Cape authorities in the South African Eastern Cape in 1820.
Origins
After the Napoleonic wars, Britain experienced a serious unemployment problem, so many of the 1820 Settlers were poor and encouraged to settle in an attempt by the Cape government to close, consolidate and defend the eastern frontier against the neighbouring Xhosa peoples, and to provide a boost to the English-speaking population. It led to the establishment of Albany, a centre of the British diaspora in the region. For many years, Albany remained an "Anglo-Saxon island" in a predominantly Xhosa and Afrikaans-speaking country - with its own distinctive local culture.
Colonisation
Of the 90,000 applicants, about 4,000 were approved, so that many 1820 Settlers initially arrived in the Cape in around 60 different parties between April and June 1820. The 1820 Settlers were granted farms near the village of Bathurst and supplied equipment and food against their deposits, but their lack of agricultural experience led many of them to abandon agriculture and withdraw to Bathurst and other settlements like Grahamstown, East London and Port Elizabeth, where they typically reverted to their trades.
A group of the 1820 Settlers continued on to Natal, then a part of Zululand, home of the Zulu people. At the time, King Shaka ruled the territory with highly trained warriors. Leaders of the Natal settlers requested permission from Shaka to stay on the land. When the king witnessed the settlers' technological advances, permission was granted in return for access to firearm technology.[1] According to genealogist Shelagh O'Byrne Spencer, among 1820 Settlers who moved to Natal were "John Bailie, the founder of East London, and Charles Kestell, after whose son, the Revd John Daniel Kestell of Anglo-Boer War fame, the Free State town of Kestell is named".[lower-alpha 1]
Memorial
They are commemorated in Grahamstown by the 1820 Settlers National Monument, which opened in 1974. A living monument, it hosts plays, musical performances and cultural events, and is supported by the 1820 Settlers Association which was founded in 1920 by Sir Walter Stanford and other descendants.
Notable 1820 Settlers

- William Guybon Atherstone
- John Burnet Biddulph
- Alexander Biggar
- Henry Hare Dugmore
- George Henry Ford
- Robert Godlonton
- Richard Gush
- Dick King
- Emperor Norton
- Thomas Pringle
- Thomas Shone
- Dr Charles Caldecott
See also
Notes and references
- ↑ The European Settler Population of Natal up to 1960, and their Influence Beyond the Borders of the Colony.
- ↑ Ngubane 1963, p. 30.
- Ngubane, Jordan K. (1963), written at Natal, South Africa, An African Explains Apartheid, New York, NY: Frederick A. Praeger, Inc.
Further reading
- Mitford-Barberton, Ivan; White, Violet (1969). Some frontier families: biographical sketches of 100 Eastern Province families before 1840. Human and Rousseau.
- Rosenthal, Eric (1973). Encyclopedia of Southern Africa. Systems for Education.
- Whinchcombe Powell, F. (1964). Hancock's Drift: The Story of the Great Wagon Road, by F. Whinchcombe Powell.
- Endemann, L. C. P. (1978). John Parkin of Baakens River Farm and His Family, 1820-1970. Human Sciences Research Council. ISBN 978-0-86965-500-9.
- Spencer, Shelagh O'Byrne (1981). British Settlers in Natal, 1824-1857. Volumes 1 to 7. University of Natal Press. ISBN 978-0-86980-267-0.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1820 Settlers. |
- Grahamstown Foundation and 1820 Settlers National Monument
- 1820 Settlers Association
- 1820Settlers.com, a genealogy website
- British Settlers in Natal, 1824-1857