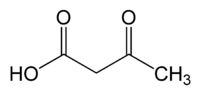
Acetoacetic acid
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
3-Oxobutanoic acid[1] | |
| Other names
Acetoacetic acid (no longer recommended[1]) Diacetic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 541-50-4 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15344 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL1230762 |
| ChemSpider | 94 |
| DrugBank | DB01762 |
| KEGG | C00164 |
| PubChem | 96 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C4H6O3 | |
| Molar mass | 102.088 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless, oily liquid |
| Melting point | 36.5 °C (97.7 °F; 309.6 K) |
| Boiling point | Decomposes |
| soluble | |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, ether |
| Acidity (pKa) | 3.58 [2] |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Acetoacetic acid (also diacetic acid) is the organic compound with the formula CH3COCH2COOH. It is the simplest beta-keto acid group, and like other members of this class it is unstable. The methyl and ethyl esters, which are quite stable, are produced on a large scale industrially as precursors to dyes.[3]
Acetoacetic acid is a weak acid. It is of biochemical importance in various animals, including humans, as one of the endogenous ketone bodies produced by the liver when it breaks down fatty acids into Acetyl-CoA and TCA cycle intermediates are depleted (particularly oxaloacetate, which is formed from pyruvate derived from glycolysis). It can be viewed as the product of joining two acetic acid molecules via a condensation reaction that ejects a water molecule in the process, although that is only one of the ways of forming the acetoacetate molecule. In the human body, a large portion of acetoacetate is converted to beta-hydroxybutyrate, a rich energy source for the brain, which cannot run directly on fatty acids themselves due to their poor ability to cross the blood-brain barrier.
Synthesis and properties
In general, the esters are prepared from diketene by treatment with alcohols.[3] Acetoacetic acid can be prepared by the hydrolysis of the ethyl acetoacetate followed by acidification of the anion.[4] In general, acetoacetic acid is generated at 0 °C and used in situ immediately.[5] It decomposes at a moderate rate to acetone and carbon dioxide:
- CH3C(O)CH2CO2H → CH3C(O)CH3 + CO2
The acid form has a half-life of 140 minutes at 37 °C in water, whereas the basic form (the anion) has a half-life of 130 hours. That is, it reacts about 55 times more slowly.[6]
It is a weak acid (like most alkyl carboxylic acids), with a pKa of 3.58.
Applications
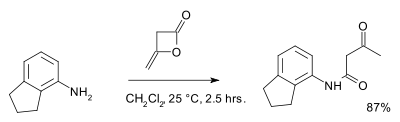
Acetoacetic esters are used for the acetoacetylation reaction, which is widely used in the production of arylide yellows and diarylide dyes.[3] Although the esters can be used in this reaction, diketene also reacts with alcohols and amines to the corresponding acetoacetic acid derivatives in a process called acetoacetylation. An example is the reaction with 2-aminoindane:[7]
Detection
Acetoacetic acid is measured in the urine of people with diabetes to test for ketoacidosis[8] and for monitoring people on a ketogenic or low-carbohydrate diet,[9][10] This is done using dipsticks coated in nitroprusside or similar reagents. Nitroprusside changes from pink to purple in the presence of acetoacetate, the conjugate base of acetoacetic acid, and the colour change is graded by eye. The test does not measure β-hydroxybutyrate, the most abundant ketone in the body; during treatment of ketoacidosis β-hydroxybutyrate is converted to acetoacetate so the test is not useful after treatment begins[8] and may be falsely low at diagnosis.[11]
Similar tests are used in dairy cows to test for ketosis.[12]
See also
References
- 1 2 Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. p. 748. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ↑ Dawson, R. M. C., et al., Data for Biochemical Research, Oxford, Clarendon Press, 1959.
- 1 2 3 Franz Dietrich Klingler, Wolfgang Ebertz "Oxocarboxylic Acids" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a18 313
- ↑ Robert C. Krueger (1952). "Crystalline Acetoacetic Acid". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 74 (21): 5536–5536. doi:10.1021/ja01141a521.
- ↑ George A. Reynolds and J. A. VanAllan "Methylglyoxal-ω-Phenylhydrazone" Organic Syntheses, Collected Volume 4, p.633 (1963).http://www.orgsyn.org/orgsyn/pdfs/CV4P0633.pdf Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine.
- ↑ Hay, R. W.; Bond, M. A. (1967). "Kinetics of decarboxilation of acetoacetic acid". Aust. J. Chem. 20 (9): 1823–8. doi:10.1071/CH9671823.
- ↑ Kiran Kumar Solingapuram Sai; Thomas M. Gilbert; Douglas A. Klumpp (2007). "Knorr Cyclizations and Distonic Superelectrophiles". J. Org. Chem. 72 (25): 9761–9764. doi:10.1021/jo7013092. PMID 17999519.
- 1 2 Nyenwe, EA; Kitabchi, AE (April 2016). "The evolution of diabetic ketoacidosis: An update of its etiology, pathogenesis and management.". Metabolism: clinical and experimental. 65 (4): 507–21. PMID 26975543.
- ↑ Hartman AL, Vining EP. Clinical aspects of the ketogenic diet. Epilepsia. 2007 Jan;48(1):31–42. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.00914.x PMID 17241206
- ↑ Sumithran, Priya; Proietto, Joseph (2008). "Ketogenic diets for weight loss: A review of their principles, safety and efficacy". Obesity Research & Clinical Practice. 2: 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.orcp.2007.11.003.
- ↑ Misra, S; Oliver, NS (28 October 2015). "Diabetic ketoacidosis in adults.". BMJ (Clinical research ed.). 351: h5660. PMID 26510442.
- ↑ Tatone, EH; Gordon, JL; Hubbs, J; LeBlanc, SJ; DeVries, TJ; Duffield, TF (1 August 2016). "A systematic review and meta-analysis of the diagnostic accuracy of point-of-care tests for the detection of hyperketonemia in dairy cows.". Preventive veterinary medicine. 130: 18–32. PMID 27435643.