Isotopes of boron
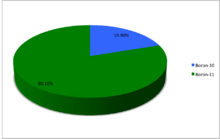
Boron (B) naturally occurs as isotopes, 10B and 11B, the latter of which makes up about 80% of natural boron. There are 14 radioisotopes that have been discovered, with mass numbers from 6 to 21, all with short half-lives, the longest being that of 8B, with a half-life of only 770 milliseconds (ms) and 12B with a half-life of 20.2 ms. All other isotopes have half-lives shorter than 17.35 ms, with the least stable isotope being 7B, with a half-life of 150 yoctoseconds (ys). Those isotopes with mass below 10 decay into helium (via short-lived isotopes of beryllium for 7B and 9B) while those with mass above 11 mostly become carbon.
Relative atomic mass: 10.811(7)
Table
| nuclide symbol |
Z(p) | N(n) | isotopic mass (u) |
half-life | decay mode(s)[1] | daughter isotope(s) |
nuclear spin |
representative isotopic composition (mole percent) |
range of natural variation (mole percent) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6B | 5 | 1 | 6.04681(75)# | ||||||
| 7B | 5 | 2 | 7.02992(8) | 350(50)×10−24 s [1.4(2) MeV] |
p | 6 Be [n 1] |
( 3⁄2−) | ||
| 8B[n 2] | 5 | 3 | 8.0246072(11) | 770(3) ms | β+, α | 2 4 He |
2+ | ||
| 9B | 5 | 4 | 9.0133288(11) | 800(300)×10−21 s [0.54(21) keV] |
p | 8 Be [n 3] |
3⁄2− | ||
| 10B | 5 | 5 | 10.0129370(4) | Stable | 3+ | 19.9(7) | 18.929–20.386 | ||
| 11B | 5 | 6 | 11.0093054(4) | Stable | 3⁄2− | 80.1(7) | 79.614–81.071 | ||
| 12B | 5 | 7 | 12.0143521(15) | 20.20(2) ms | β− (98.4%) | 12 C |
1+ | ||
| β−, α (1.6%) | 8 Be [n 4] | ||||||||
| 13B | 5 | 8 | 13.0177802(12) | 17.33(17) ms | β− (99.72%) | 13 C |
3⁄2− | ||
| β−, n (0.279%) | 12 C | ||||||||
| 14B | 5 | 9 | 14.025404(23) | 12.5(5) ms | β− (93.96%) | 14 C |
2− | ||
| β−, n (6.04%) | 13 C | ||||||||
| 15B | 5 | 10 | 15.031103(24) | 9.87(7) ms | β−, n (93.6%) | 14 C |
3⁄2− | ||
| β− (6.0%) | 15 C | ||||||||
| β−, 2n (0.40%) | 13 C | ||||||||
| 16B | 5 | 11 | 16.03981(6) | <190×10−12 s [<0.1 MeV] |
n | 15 B |
0− | ||
| 17B[n 5] | 5 | 12 | 17.04699(18) | 5.08(5) ms | β−, n (63.0%) | 16 C |
( 3⁄2−) | ||
| β− (22.1%) | 17 C | ||||||||
| β−, 2n (11.0%) | 15 C | ||||||||
| β−, 3n (3.5%) | 14 C | ||||||||
| β−, 4n (0.40%) | 13 C | ||||||||
| 18B | 5 | 13 | 18.05617(86)# | <26 ns | n | 17 B |
(4−)# | ||
| 19B[n 5] | 5 | 14 | 19.06373(43)# | 2.92(13) ms | β− | 19 C |
( 3⁄2−)# | ||
- ↑ Subsequently decays by double proton emission to 4He for a net reaction of 7B → 4He + 3 1H
- ↑ Has 1 halo proton
- ↑ immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of 9B → 2 4He + 1H
- ↑ Immediately decays into two α particles, for a net reaction of 12B → 3 4He + e−
- 1 2 Has 2 halo neutrons
Notes
- The precision of the isotope abundances and atomic mass is limited through variations. The given ranges should be applicable to any normal terrestrial material.
- Commercially available materials may have been subjected to an undisclosed or inadvertent isotopic fractionation. Substantial deviations from the given mass and composition can occur.
- Values marked # are not purely derived from experimental data, but at least partly from systematic trends. Spins with weak assignment arguments are enclosed in parentheses.
- Uncertainties are given in concise form in parentheses after the corresponding last digits. Uncertainty values denote one standard deviation, except isotopic composition and standard atomic mass from IUPAC, which use folical uncertainties.[2]
- Nuclide masses are given by IUPAP Commission on Symbols, Units, Nomenclature, Atomic Masses and Fundamental Constants (SUNAMCO).
- Isotope abundances are given by IUPAC Commission on Isotopic Abundances and Atomic Weights.
Applications
Boron-10
Boron-10 is used in boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) as an experimental treatment of some brain cancers.
References
Notes
- ↑ "Universal Nuclide Chart". nucleonica. (registration required (help)).
- ↑ "2.5.7. Standard and expanded uncertainties". Engineering Statistics Handbook. Retrieved 2010-09-16.
General references
- Isotope masses from:
- G. Audi; A. H. Wapstra; C. Thibault; J. Blachot; O. Bersillon (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties" (PDF). Nuclear Physics A. 729: 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001.
- Isotopic compositions and standard atomic masses from:
- J. R. de Laeter; J. K. Böhlke; P. De Bièvre; H. Hidaka; H. S. Peiser; K. J. R. Rosman; P. D. P. Taylor (2003). "Atomic weights of the elements. Review 2000 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 75 (6): 683–800. doi:10.1351/pac200375060683.
- M. E. Wieser (2006). "Atomic weights of the elements 2005 (IUPAC Technical Report)". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 78 (11): 2051–2066. doi:10.1351/pac200678112051. Lay summary.
- Half-life, spin, and isomer data selected from the following sources. See editing notes on this article's talk page.
- G. Audi; A. H. Wapstra; C. Thibault; J. Blachot; O. Bersillon (2003). "The NUBASE evaluation of nuclear and decay properties" (PDF). Nuclear Physics A. 729: 3–128. Bibcode:2003NuPhA.729....3A. doi:10.1016/j.nuclphysa.2003.11.001.
- National Nuclear Data Center. "NuDat 2.1 database". Brookhaven National Laboratory. Retrieved September 2005. Check date values in:
|access-date=(help) - N. E. Holden (2004). "Table of the Isotopes". In D. R. Lide. CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (85th ed.). CRC Press. Section 11. ISBN 978-0-8493-0485-9.
| Isotopes of beryllium | Isotopes of boron | Isotopes of carbon |
| Table of nuclides | ||
| Isotopes of the chemical elements | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 H |
2 He | ||||||||||||||||
| 3 Li |
4 Be |
5 B |
6 C |
7 N |
8 O |
9 F |
10 Ne | ||||||||||
| 11 Na |
12 Mg |
13 Al |
14 Si |
15 P |
16 S |
17 Cl |
18 Ar | ||||||||||
| 19 K |
20 Ca |
21 Sc |
22 Ti |
23 V |
24 Cr |
25 Mn |
26 Fe |
27 Co |
28 Ni |
29 Cu |
30 Zn |
31 Ga |
32 Ge |
33 As |
34 Se |
35 Br |
36 Kr |
| 37 Rb |
38 Sr |
39 Y |
40 Zr |
41 Nb |
42 Mo |
43 Tc |
44 Ru |
45 Rh |
46 Pd |
47 Ag |
48 Cd |
49 In |
50 Sn |
51 Sb |
52 Te |
53 I |
54 Xe |
| 55 Cs |
56 Ba |
|
72 Hf |
73 Ta |
74 W |
75 Re |
76 Os |
77 Ir |
78 Pt |
79 Au |
80 Hg |
81 Tl |
82 Pb |
83 Bi |
84 Po |
85 At |
86 Rn |
| 87 Fr |
88 Ra |
|
104 Rf |
105 Db |
106 Sg |
107 Bh |
108 Hs |
109 Mt |
110 Ds |
111 Rg |
112 Cn |
113 Nh |
114 Fl |
115 Mc |
116 Lv |
117 Ts |
118 Og |
| |
57 La |
58 Ce |
59 Pr |
60 Nd |
61 Pm |
62 Sm |
63 Eu |
64 Gd |
65 Tb |
66 Dy |
67 Ho |
68 Er |
69 Tm |
70 Yb |
71 Lu | ||
| |
89 Ac |
90 Th |
91 Pa |
92 U |
93 Np |
94 Pu |
95 Am |
96 Cm |
97 Bk |
98 Cf |
99 Es |
100 Fm |
101 Md |
102 No |
103 Lr | ||
| |||||||||||||||||