Calcarine sulcus
| Calcarine sulcus | |
|---|---|
 Medial surface of left cerebral hemisphere. ("Calcarine fissure" visible at left.) | |
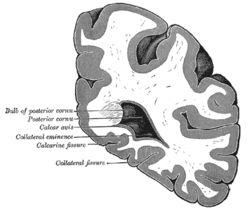 Coronal section through posterior cornua of lateral ventricle. (Label for "Calcarine fissure" visible at bottom. | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Occipital lobe |
| Artery | calcarine branch of medial occipital artery |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sulcus calcarinus, fissura calcarina |
| NeuroNames | hier-25 |
| NeuroLex ID | Calcarine sulcus |
| TA | A14.1.09.225 |
| FMA | 83749 |
The calcarine sulcus (or calcarine fissure) is an anatomical landmark located at the caudal end of the medial surface of the brain. Its name comes from the Latin "calcar" meaning "spur.".[1] It is a complete sulcus.
Anatomy
The calcarine sulcus begins near the occipital pole in two converging rami and runs forward to a point a little below the splenium of the corpus callosum, where it is joined at an acute angle by the medial part of the parieto-occipital sulcus. The anterior part of this sulcus gives rise to the prominence of the calcar avis in the posterior cornu of the lateral ventricle.
Function
The calcarine sulcus is where the primary visual cortex (V1) is concentrated. The central visual field is located in the posterior portion of the calcarine sulcus and the peripheral visual field in the anterior portion.
Additional images
-

Position of calcarine sulcus (shown in red).
-

Calcarine fissure (shown in red).
-

Medial surface of cerebral cortex - gyri
References
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Calcarine sulcus. |
- Anatomy diagram: 13048.000-3 at Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, Elsevier
- http://www2.umdnj.edu/~neuro/studyaid/Practical2000/Q31.htm
- Atlas image: eye_38 at the University of Michigan Health System - "The Visual Pathway from Below"
- NIF Search - Calcarine Fissure via the Neuroscience Information Framework