Sulcus (neuroanatomy)
| Sulcus | |
|---|---|
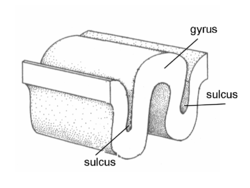 Gyrus and sulcus. | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA | A14.1.09.006 |



In neuroanatomy, a sulcus (Latin: "furrow", pl. sulci) is a depression or groove in the cerebral cortex. It surrounds a gyrus (pl. gyri), creating the characteristic folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals.
Structure
Sulci are one of three parts of the cerebral cortex, the others being the gyri and the fissures. The three different parts create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. When looking at the human brain, two-thirds of the surface are hidden in the grooves. The sulci and fissures are both grooves in the cortex but they are differentiated by size. A sulcus is a shallower groove that surrounds a gyrus. A fissure is a large furrow that divides the brain into lobes, and also into the two hemispheres as the medial longitudinal fissure does.[1] However this distinction is not always clear. For example, the lateral sulcus is also known as the lateral fissure or the Sylvian fissure, and the central sulcus is also known as the central fissure or the Rolandic fisussure.
Importance of expanded surface area
As the surface area of the brain increases more functions are made possible. A smooth-surfaced brain is only able to grow to a certain extent. A depression, sulcus, in the surface area allows for continued growth. This in turn allows for the functions of the brain to continue growing.[2]
Variation
The sulcal pattern varies between human individuals, and the most elaborate overview on this variation is probably an atlas by Ono, Kubick and Abernathey: Atlas of the Cerebral Sulci.[3] Some of the more prominent sulci are, however, seen across individuals - and even species - making a common nomenclature across individuals and species possible.
Development
In humans, cerebral convolutions appear at about 5 months and take at least into the first year after birth to fully develop.[4][5][6] Development varies greatly between individuals. The potential influences of genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors are not fully understood.[7] It has been found that the width of cortical sulci not only increases with age,[8] but also with cognitive decline in the elderly.[9]
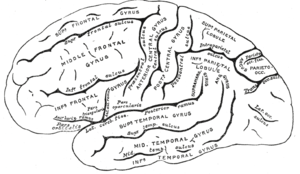
Notable sulci
- Calcarine sulcus
- Central sulcus
- Central sulcus of insula
- Cingulate sulcus
- Circular sulcus of insula
- Collateral sulcus
- Fimbrodentate sulcus
- Hippocampal sulcus
- Inferior frontal sulcus
- Inferior temporal sulcus
- Intraparietal sulcus
- Lateral sulcus
- Lunate sulcus
- Occipitotemporal sulcus
- Olfactory sulcus
- Paracentral sulcus
- Parieto-occipital sulcus
- Postcentral sulcus
- Precentral sulcus
- Rhinal sulcus
- Subparietal sulcus
- Sulcus of corpus callosum
- Superior frontal sulcus
- Superior temporal sulcus
- Transverse occipital sulcus
- Transverse temporal sulcus
Other animals
The variation in the amount of fissures in the brain (gyrification) between species is related to the size of the animal and the size of the brain. Mammals that have smooth-surfaced or nonconvoluted brains are called lissencephalics and those that have folded or convoluted brains gyrencephalics.[4][5] The division between the two groups occurs when cortical surface area is about 10 cm2 and the brain has a volume of 3–4 cm3. Large rodents such as beavers (40 pounds (18 kg)) and capybaras (150 pounds (68 kg)) are gyrencephalic and smaller rodents such as rats and mice lissencephalic.[10]
Macaque
A macaque has a more simple sulcal pattern. In a monograph Bonin and Bailey list the following as the primary sulci:[11]
- Calcarine fissure (ca)
- Central sulcus (ce)
- Sulcus cinguli (ci)
- Hippocampal fissure (h)
- Sulcus intraparitalis (ip)
- Lateral fissure (or Sylvian fissure) (la)
- Sulcus olfactorius (olf)
- Medial parieto-occipital fissure (pom)
- fissura rhinalis (rh)
- Sulcus temporalis superior (ts) - this sulcus runs parallel to the lateral fissure and extends to the temporal pole and often superficially merges with it.
See also
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Sulcus (neuroanatomy). |
References
- ↑ Carlson, N. R. (2013). Physiology of Behavior. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education Inc.
- ↑ Cusack, R. (2005). The intraparietal sulcus and perceptual organization. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience, 17(4), 641-651. doi: 10.1162/0898929053467541
- ↑ Ono, Kubick, Abernathey, Atlas of the Cerebral Sulci, Thieme Medical Publishers, 1990. ISBN 0-86577-362-9. ISBN 3-13-732101-8.
- 1 2 Hofman MA. (1985). Size and shape of the cerebral cortex in mammals. I. The cortical surface. Brain Behav Evol. 27(1):28-40. PMID 3836731
- 1 2 Hofman MA. (1989).On the evolution and geometry of the brain in mammals. Prog Neurobiol.32(2):137-58. PMID 2645619
- ↑ Caviness VS Jr. (1975). Mechanical model of brain convolutional development. Science. 189(4196):18-21. PMID 1135626
- ↑ Dubois, J., & Benders, M. (2007). Mapping the early cortical folding process in preterm newborn brain. Oxford Journals, 18, 1444-1454. dpi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm180
- ↑ Tao Liu, Wei Wen, Wanlin Zhu, Julian Trollor, Simone Reppermund, John Crawford, Jesse S Jin, Suhuai Luo, Henry Brodaty, Perminder Sachdev (2010) The effects of age and sex on cortical sulci in the elderly. Neuroimage 51:1. 19–27 May. PMID 20156569
- ↑ Tao Liu, Wei Wen, Wanlin Zhu, Nicole A Kochan, Julian N Trollor, Simone Reppermund, Jesse S Jin, Suhuai Luo, Henry Brodaty, Perminder S Sachdev (2011) The relationship between cortical sulcal variability and cognitive performance in the elderly. Neuroimage 56:3. 865-873 Jun. PMID 21397704
- ↑ Martin I. Sereno, Roger B. H. Tootell, "From Monkeys to humans: what do we now know about brain homologies," Current Opinion in Neurobiology 15:135-144, (2005).
- ↑ Gerhardt von Bonin, Percival Bailey, The Neocortex of Macaca Mulatta, The University of Illinois Press, Urbana, Illinois, 1947