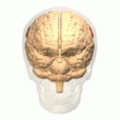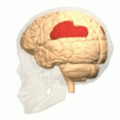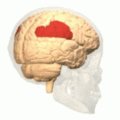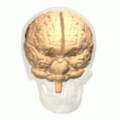
Inferior parietal lobule
| Inferior parietal lobule | |
|---|---|
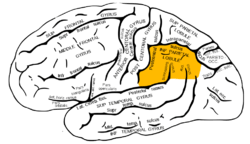 Lateral surface of left cerebral hemisphere, viewed from the side. (Inferior parietal lobule is shown in orange.) | |
 Lateral surface of left cerebral hemisphere, viewed from above. (Inferior parietal lobule shown in orange.) | |
| Details | |
| Part of | Parietal lobe |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Lobulus parietalis inferior |
| NeuroNames | hier-89 |
| NeuroLex ID | inferior parietal lobule |
| TA | A14.1.09.125 |
| FMA | 77536 |
The inferior parietal lobule (subparietal district) lies below the horizontal portion of the intraparietal sulcus, and behind the lower part of the postcentral sulcus. Also known as Geschwind’s territory after Norman Geschwind, an American neurologist, who in the early 1960s foresaw its importance.[1]
Structure
It is divided from before backward into two gyri:
- One, the supramarginal gyrus, arches over the upturned end of the lateral fissure; it is continuous in front with the postcentral gyrus, and behind with the superior temporal gyrus.
- The second, the angular gyrus, arches over the posterior end of the superior temporal sulcus, behind which it is continuous with the middle temporal gyrus.
Function
Inferior parietal lobule has been involved in the perception of emotions in facial stimuli,[2] and interpretation of sensory information. The Inferior parietal lobule is concerned with language, mathematical operations, and body image, particularly the supramarginal gyrus and the angular gyrus.[3]
Clinical significance
Destruction to the inferior parietal lobule of the dominant hemisphere results in Gerstmann's syndrome: right-to-left confusion, finger agnosia, dysgraphia and dyslexia, dyscalculia, contralateral hemianopia, or lower quadrantanopia. Destruction to the inferior parietal lobule of the non-dominant hemisphere results in topographic memory loss, anosognosia, construction apraxia, dressing apraxia, contralateral sensory neglect, contralateral hemianopia, or lower quadrantanopia.
In other animals
Functional imaging experiments suggest that the left anterior supramarginal gyrus (aSMG) of the human inferior parietal lobule exhibits an evolved specialization related to tool use. It is not currently known if this functional specialization is unique to humans as complementary experiments have only been performed with macaque monkeys and not apes. The habitual use of tools by chimpanzees makes the uniqueness of the human aSMG an open question as its function may have evolved prior to the split from our last common ancestor.[4]
Additional images
|
References
This article incorporates text in the public domain from the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ↑ "The Brain from top to bottom". 2011.
- ↑ Radua, Joaquim; Phillips, Mary L.; Russell, Tamara; Lawrence, Natalia; Marshall, Nicolette; Kalidindi, Sridevi; El-Hage, Wissam; McDonald, Colm; et al. (2010). "Neural response to specific components of fearful faces in healthy and schizophrenic adults". NeuroImage. 49 (1): 939–946. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.08.030. PMID 19699306.
- ↑ "Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry". 2003.
- ↑ Peeters et al. 2009
General
- Peeters, R.; Simone, L.; Nelissen, K.; Fabbri-Destro, M.; Vanduffel, W.; Rizzolatti, G.; Orban, G. A. (September 16, 2009). "The Representation of Tool Use in Humans and Monkeys: Common and Uniquely Human Features". The Journal of Neuroscience. 29 (37): 11523–11539. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2040-09.2009. PMID 19759300.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Inferior parietal lobule. |