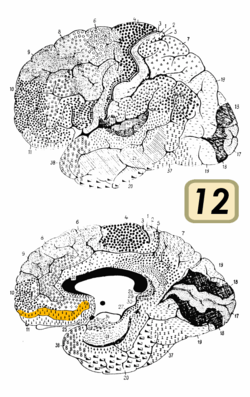
Brodmann area 12
| Brodmann area 12 | |
|---|---|
|
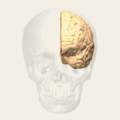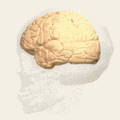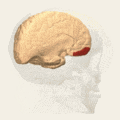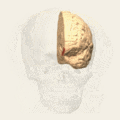
Brodmann area 12(shown in orange) | |
|
Image of brain with Brodmann areas numbered | |
| Identifiers | |
| NeuroLex ID | Brodmann area 12 |
| FMA | 68609 |
Brodmann area 12 is a subdivision of the cerebral cortex of the guenon defined on the basis of cytoarchitecture. It occupies the most rostral portion of the frontal lobe. Brodmann-1909 did not regard it as homologous, either topographically or cytoarchitecturally, to rostral area 12 of the human. Distinctive features (Brodmann-1905): a quite distinct internal granular layer (IV) separates slender pyramidal cells of the external pyramidal layer (III) and the internal pyramidal layer (V); the multiform layer (VI) is expanded, contains widely dispersed spindle cells and merges gradually with the underlying cortical white matter; all cells, including the pyramidal cells of the external and internal pyramidal layers are inordinately small; the internal pyramidal layer (V) also contains spindle cells in groups of two to five located close to its border with the internal granular layer (IV).
It is indirectly connected to the global palladius as well as the substantia nigra, due to efferents to the striatum. Glutaminergic input is turned into GABAergic input there, which allows the frontal lobes to exhibit some control over basal ganglia activity.
Image
 Animation.
Animation. Frontal view.
Frontal view. Medial view.
Medial view.
See also
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Brodmann area 12. |
- For Neuroanatomy of this area see BrainInfo