County of Oldenburg
| County of Oldenburg | ||||||||||||
| Grafschaft Oldenburg (de) | ||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Anthem Heil dir, O Oldenburg ("Hail to thee, O Oldenburg") | ||||||||||||
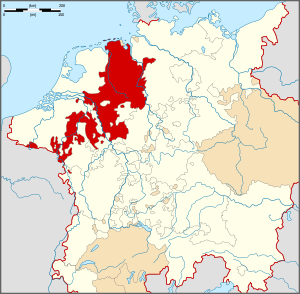
.svg.png) Map of the County of Oldenburg in the Lower Rhenish–Westphalian Circle | ||||||||||||
| Capital | Oldenburg | |||||||||||
| Government | Feudal monarchy | |||||||||||
| Count of Oldenburg | ||||||||||||
| • | 1101–08 | Elimar I (first count) | ||||||||||
| • | 1773–74 | Frederick August I (last count) | ||||||||||
| History | ||||||||||||
| • | Created on breakup of Saxony |
1091 | ||||||||||
| • | Personal union with the Kalmar Union |
1448–54 | ||||||||||
| • | Part of Denmark | 1667–1773 | ||||||||||
| • | Raised to duchy | 1774 | ||||||||||
| ||||||||||||
| Today part of | | |||||||||||
The County of Oldenburg was a county of the Holy Roman Empire.
In 1448 Christian I of Denmark (of the House of Oldenburg), Count of Oldenburg became King of Denmark, and later King of Norway and King of Sweden. One of his grandsons, Adolf, Duke of Holstein-Gottorp was the first Duke of Holstein-Gottorp.[1]
When the main lineage of the House of Oldenburg, i.e. Anthony Günther, Count of Oldenburg died in 1667, it fell to the Danish Royal Family. Charles Frederick of the line of the Dukes of Holstein-Gottorp married Grand Duchess Anna Petrovna of Russia, daughter of Peter the Great. His first cousin, Frederick August I became Duke of Oldenburg in 1774. One of his brothers, Adolf Frederick became King of Sweden. Another brother, Prince Georg Ludwig of Holstein-Gottorp, was father of Peter I, who became Grand Duke of Oldenburg in 1823. Subsequent Rulers of Oldenburg were all his descendants.[1]
History
The town was first mentioned in 1108, at that time known under the name of Aldenburg. It became important due to its location at a ford of the navigable Hunte river. Oldenburg became a small county in the shadow of the much more powerful Free Hanseatic City of Bremen.
The earliest recorded inhabitants of the region now called Oldenburg, were a Teutonic people- the Chauci. The genealogy of the counts of Oldenburg can be traced to the Saxon hero Widukind (opponent of Charlemagne), but their first historical representative was Elimar of Oldenburg (died 1108). Elimar's descendants appear as vassals of the dukes of Saxony and were occasionally rebellious. They were given the title of princes of the Empire when the emperor Frederick I dismembered the Saxon duchy in 1189. At this time the county of Delmenhorst formed part of the dominions of the counts of Oldenburg, but afterwards it was on several occasions separated from them to form an appanage for younger branches of the family, namely in 1262-447, 1463-547, and 1577-617.
The northern and western parts of what would become the Grand Duchy of Oldenburg were in the hands of independent, or semi-independent, Frisian princes, who were usually pagan, and the counts of Oldenburg seized much of these lands in a series of wars during the early part of the 13th century. The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen and the bishop of Münster also frequently warred with the counts of Oldenburg.
In 1448, the son and heir of Count Dietrich (died 1440), named Christian but called Fortunatus, became king of Denmark as Christian I. Although far from the Danish borders, Oldenburg then became a Danish exclave. The control over the town was left to the king's brothers, who established a short-lived tyranny.
In 1450, Christian became king of Norway and in 1457 king of Sweden; in 1460 he inherited the Duchy of Schleswig and the County of Holstein, which significantly affected Oldenburg's future. In 1454, he handed over Oldenburg to his brother Gerhard (c. 1430-1499), who constantly warred with the bishop of Bremen and other neighbors. However, in 1483 Gerhard was compelled to abdicate in favor of his son, and he died whilst on a pilgrimage in Spain.
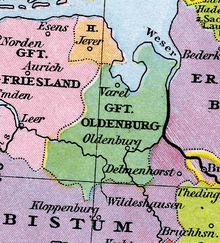

Early in the 16th century, Oldenburg was again enlarged at the expense of the Frisians. Protestantism was introduced into the county by Count Anton I (1505-1573), who also suppressed the monasteries. However, he remained loyal to Charles V during the war of the league of Schmalkalden, and was able thus to increase his territories, obtaining Delmenhorst in 1547. One of Anton's brothers, Count Christopher of Oldenburg (c. 1506-1560) also won a reputation as a soldier.
Anton's grandson, Anton Günther (1583-1667), who succeeded in 1603 significantly enlarged and enriched his territories. He thus considered himself the wisest prince who ever had ruled Oldenburg. Jever had been acquired before his ascension, but in 1624 he added Knipphausen and Varel to his lands; thus, in 1647 Delmenhorst was finally united. Through neutrality during the Thirty Years' War and by donating valuable horses to warlord Count of Tilly, Anton Günther protected his dominions from the devastation levied on nearly all other German states. He also obtained from the emperor the right to levy tolls on vessels passing along the Weser, a lucrative grant. In 1607 he erected a Renaissance castle. Oldenburg was a wealthy town in a time of war and turmoil and its population and power grew considerably. However, after the death of Anton Günther, Oldenburg fell again under Danish authority, and 1667 the town was struck by a disastrous plague epidemic and shortly thereafter was destroyed in a fire. The Danish kings became uninterested in the town and it lost its former importance.
In 1773, Danish rule ended and, in 1777, the Oldenburg region became a duchy. Then, the destroyed buildings in the city were rebuilt in a Classicist style.
Notes
- 1 2 "Germany, the Stem Duchies & Marches". Friesian.com. 1945-02-13. Retrieved 2012-10-27.
References
-
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "article name needed". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
%2C_comte_d'Oldenbourg.svg.png)