Earwig
| Earwigs Temporal range: 208–0 Ma Late Triassic to Recent | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Female common earwig, Forficula auricularia | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Subphylum: | Hexapoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Dermaptera De Geer, 1773 |
| Suborders | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera and are found throughout the Americas, Africa, Eurasia, Australia and New Zealand. With about 2,000 species[1] in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forceps-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs rarely use their flying ability.
Earwigs are mostly nocturnal and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig Forficula auricularia.
Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs, and even after they have hatched as nymphs will continue to watch over offspring until their second molt. As the nymphs molt, sexual dimorphism such as differences in pincer shapes begins to show.
Some earwig specimen fossils are in the extinct suborders Archidermaptera or Eodermaptera, the former dating to the Late Triassic and the latter to the Middle Jurassic. Many orders of insect have been theorized to be closely related to earwigs, though the icebugs of Grylloblattaria are most likely.
Etymology

The scientific name for the order, "Dermaptera", is Greek in origin, stemming from the words derma, meaning skin, and pteron (plural ptera), wing. It was coined by Charles De Geer in 1773. The common term, earwig, is derived from the Old English ēare, which means "ear", and wicga, which means "insect", or literally, "beetle".[2] Entomologists suggest that the origin of the name is a reference to the appearance of the hindwings, which are unique and distinctive among insects, and resemble a human ear when unfolded.[3][4] The name is more popularly thought to be related to the old wives' tale that earwigs burrowed into the brains of humans through the ear and laid their eggs there.[5] Earwigs are not known to purposefully climb into external ear canals, but there have been anecdotal reports of earwigs being found in the ear.[6]
"To earwig" is a slang verb meaning either "to attempt to influence by persistent confidential argument or talk"[7] or "to eavesdrop".[8]
Distribution

Earwigs are abundant and can be found throughout the Americas and Eurasia. The common earwig was introduced into North America in 1907 from Europe, but tends to be more common in the southern and southwestern parts of the United States.[9]:739 The only native species of earwig found in the north of the United States is the spine-tailed earwig (Doru aculeatum),[10]:144 found as far north as Canada, where it hides in the leaf axils of emerging plants in southern Ontario wetlands. However, other families can be found in North America, including Forficulidae (Doru and Forficula being found there), Labiidae, Anisolabididae, and Labiduridae.[11]
Few earwigs survive winter outdoors in cold climates. They can be found in tight crevices in woodland, fields and gardens.[9]:739[12] Out of about 1,800 species, about 25 occur in North America, 45 in Europe (including 7 in Great Britain), and 60 in Australia.[13]
Morphology

Most earwigs are flattened (which allows them to fit inside tight crevices, such as under bark) with an elongated body generally 7–50 millimetres (0.28–1.97 in) long.[13] The largest certainly extant species is the Australian giant earwig (Titanolabis colossea) which is approximately 50 mm (2.0 in) long,[14]:10 while the possibly extinct Saint Helena earwig (Labidura herculeana) reached 78 mm (3.1 in).[15] Earwigs are characterized by the cerci, or the pair of forceps-like pincers on their abdomen; male earwigs generally have more curved pincers than females. These pincers are used to capture prey, defend themselves and fold their wings under the short tegmina.[16] The antennae are thread-like with at least 10 segments or more.[9]:738–739
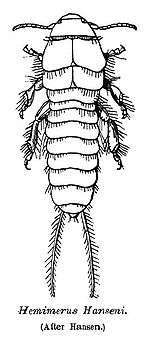
The forewings are short oblong leathery plates used to cover the hindwings like the elytra of a beetle, rather than to fly. Most species have short and leather-like forewings with very thin hindwings, though species in the former suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina (epizoic species, sometimes considered as ectoparasites[17][18]) are wingless and blind with filiform segmented cerci (today these are both included merely as families in the suborder Neodermaptera).[13][19][20] The hindwing is a very thin membrane that expands like a fan, radiating from one point folded under the forewing. Even though most earwigs have wings and are capable of flight, they are rarely seen in flight. These wings are unique in venation and in the pattern of folding that requires the use of the cerci.[21]
Internal
The neuroendocrine system is typical of insects. There is a brain, a subesophageal ganglion, three thoracic ganglia, and six abdominal ganglia. Strong neuron connections connect the neurohemal corpora cardiaca to the brain and frontal ganglion, where the closely related median corpus allatum produces juvenile hormone III in close proximity to the neurohemal dorsal arota. The digestive system of earwigs is like all other insects, consisting of a fore-, mid-, and hindgut, but earwigs lack gastric caecae which are specialized for digestion in many species of insect. Long, slender (extratory) malpighian tubules can be found between the junction of the mid- and hind gut.[22]
The reproductive system of females consist of paired ovaries, lateral oviducts, spermatheca, and a genital chamber. The lateral ducts are where the eggs leave the body, while the spermatheca is where sperm is stored. Unlike other insects, the gonopore, or genital opening is behind the seventh abdominal segment. The ovaries are primitive in that they are polytrophic (the nurse cells and oocytes alternate along the length of the ovariole). In some species these long ovarioles branch off the lateral duct, while in others, short ovarioles appear around the duct.[22]
Life cycle and reproduction

Earwigs are hemimetabolous, meaning they undergo incomplete metamorphosis, developing through a series of 4 to 6 molts. The developmental stages between molts are called instars. Earwigs live for about a year from hatching. They start mating in the autumn, and can be found together in the autumn and winter. The male and female will live in a chamber in debris, crevices, or soil 2.5 centimetres (1 in) deep.[9]:739 After mating, the sperm may remain in the female for months before the eggs are fertilized. From midwinter to early spring, the male will leave, or be driven out by the female. Afterward the female will begin to lay 20 to 80 pearly white eggs in 2 days. Some earwigs, those parasitic in the suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina, are viviparous (give birth to live young); they would be fed by a sort of placenta.[9]:739–740[19] When first laid, the eggs are white or cream-colored and oval-shaped, but right before hatching they become kidney-shaped and brown.[23] Each egg is approximately 1 mm (0.04 in) tall and 0.8 mm (0.03 in) wide.[20]
Earwigs are among the few non-social insect species that show maternal care. The mother will pay close attention to the needs of her eggs, such as warmth and protection, though studies have shown that the mother does not pay attention to the eggs as she collects them.[19] The mother has been shown to pick up wax balls by accident, but they would eventually be rejected as they do not have the proper scent. The mother will also vigorously defend the eggs from predators, not eating unless an egg goes bad.[9]:740 Another distinct maternal care unique to earwigs is that the mother continuously cleans the eggs to protect them from fungi. Studies have found that the urge to clean the eggs persists for days after they are removed; when the eggs were replaced after hatching, the mother continued to clean them for up to 3 months.[19]
 Female earwig in her nest, with eggs
Female earwig in her nest, with eggs Female earwig in her nest with newly hatched young
Female earwig in her nest with newly hatched young
The eggs hatch in about 7 days. The mother may assist the nymphs in hatching. When the nymphs hatch, they eat the egg casing and continue to live with the mother. The nymphs look similar to their parents, only smaller, and will nest under their mother and she will continue to protect them until their second molt. The nymphs feed on food regurgitated by the mother,[24] and on their own molts. If the mother dies before the nymphs are ready to leave, the nymphs may eat her.[9]:740[25]
After five to six instars, the nymphs will molt into adults. The male's forceps will become curved, while the females' forceps remain straight. They will also develop their natural color, which can be anything from a light brown (as in the Tawny earwig) to a dark black (as in the Ringlegged earwig). In species of winged earwigs, the wings will start to develop at this time. The forewings of an earwig are sclerotized to serve as protection for the membranous hindwings.
Behavior
Most earwigs are nocturnal and inhabit small crevices, living in small amounts of debris, in various forms such as bark and fallen logs. Species have been found to be blind and living in caves, or cavernicolous; reported to be found on the island of Hawaii and in South Africa. Food typically consist of a wide array of living and dead plant and animal matter.[22] For protection from predators, the species Doru taeniatum of earwigs can squirt foul-smelling yellow liquid in the form of jets from scent glands on the dorsal side of the third and fourth abdominal segment. It aims the discharges by revolving the abdomen, a maneuver that enables it simultaneously to use its pincers in defense.[26]
Ecology
Earwigs are mostly scavengers, but some are omnivorous or predatory.[9]:739–740 The abdomen of the earwig is flexible and muscular. It is capable of maneuvering as well as opening and closing the forceps. The forceps are used for a variety of purposes. In some species, the forceps have been observed in use for holding prey, and in copulation. The forceps tend to be more curved in males than in females.[27]

The common earwig is an omnivore, eating plants and ripe fruit as well as actively hunting arthropods. To a large extent, this species is also a scavenger, feeding on decaying plant and animal matter if given the chance. Observed prey include largely plant lice, but also large insects such as bluebottle flies and woolly aphids.[12] Plants that they feed on typically include clover, dahlias, zinnias, butterfly bush, hollyhock, lettuce, cauliflower, strawberry, blackberry, sunflowers, celery, peaches, plums, grapes, potatoes, roses, seedling beans and beets, and tender grass shoots and roots; they have also been known to eat corn silk, damaging the corn.[28]
Species of the suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina are generally considered epizoic, or living on the outside of other animals, mainly mammals. In the Arixeniina, family Arixeniidae, species of the genus Arixenia are normally found deep in the skin folds and gular pouch of Malaysian hairless bulldog bats (Cheiromeles torquatus), apparently feeding on bats' body or glandular secretions. On the other hand, species in the genus Xeniaria (still of the suborder Arixeniina) are believed to feed on the guano and possibly the guanophilous arthropods in the bat's nest, where it has been found. Hemimerina includes Araeomerus found in the nest of Long-tailed pouch rats (Beamys), and Hemimerus which are found on Giant Cricetomys rats.[18][29]
Earwigs are generally nocturnal, and typically hide in small, dark, and often moist areas in the daytime. They can usually be seen on household walls and ceilings. Interaction with earwigs at this time results in a defensive free-fall to the ground followed by a scramble to a nearby cleft or crevice.[27] During the summer they can be found around damp areas such as near sinks and in bathrooms. Earwigs tend to gather in shady cracks or openings or anywhere that they can remain concealed during daylight. Some people erroneously believe that earwigs burrow into people's ears; that is mostly a myth, although earwigs may crawl into ears and some can bite, as other insects do. Picnic tables, compost and waste bins, patios, lawn furniture, window frames, or anything with minute spaces (even artichoke blossoms) can potentially harbour them.[30]
Predators and parasites
Earwigs are regularly preyed upon by birds, and like many other insect species they are prey for insectivorous mammals, amphibians, lizards, centipedes, assassin bugs, and spiders.[31] European naturalists have observed bats preying upon earwigs.[31] Their primary insect predators are parasitic species of Tachinidae, or tachinid flies, whose larvae are endoparasites. One species of tachinid fly, Triarthria setipennis, has been demonstrated to be successful as a biological control of earwigs for almost a century.[32][33] Another tachinid fly and parasite of earwigs, Ocytata pallipes, has shown promise as a biological control agent as well.[34] The common predatory wasp, the yellow jacket (Vespula maculifrons), preys upon earwigs when abundant.[35] A small species of roundworm, Mermis nigrescens, is known to occasionally parasitize earwigs that have consumed roundworm eggs with plant matter.[36] At least 26 species of parasitic fungus from the order Laboulbeniales have been found on earwigs.[37] The eggs and nymphs are also cannibalized by other earwigs.[38] A species of tyroglyphoid mite, Histiostoma polypori (Histiostomatidae, Astigmata), are observed on common earwigs, sometimes in great densities;[39] however, this mite feeds on earwig cadavers and not its live earwig transportation.[40] Hippolyte Lucas observed scarlet acarine mites on European earwigs.[41]
Evolution
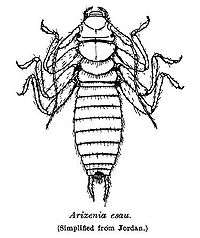
The fossil record of the Dermaptera starts in the Late Triassic to Early Jurassic period about 208 million years ago in England and Australia, and comprises about 70 specimens in the extinct suborder Archidermaptera. Some of the traits believed by neontologists to belong to modern earwigs are not found in the earliest fossils, but adults had five-segmented tarsi (the final segment of the leg), well developed ovipositors, veined tegmina (forewings) and long segmented cerci; in fact the pincers would not have been curled or used as they are now.[16] The theorized stem group of the Dermaptera are the Protelytroptera. These insects, which resemble modern Blattodea, or cockroaches owing to shell-like forewings and the large, unequal anal fan, are known from the Permian of North America, Europe and Australia. There are no fossils from the Triassic when the morphological changes from Protelytroptera to Dermaptera took place.[42] The most likely, and most closely resembling, related order of insects is Grylloblattaria, theorized by Giles in 1963. However, other arguments have been made by other authors linking them to Phasmida, Embioptera, Plecoptera, and Dictyoptera.[13]
Archidermaptera is believed to be sister to the remaining earwig groups, the extinct Eodermaptera and the living suborder Neodermaptera (= former suborders Forficulina, Hemimerina, and Arixeniina). The extinct suborders have tarsi with five segments (unlike the three found in Neodermaptera) as well as unsegmented cerci. No fossil Hemimeridae and Arixeniidae are known.[43] Species in Hemimeridae were at one time in their own order, Diploglassata, Dermodermaptera, or Hemimerina. Like most other epizoic species, there is no fossil record, but they are probably no older than late Tertiary.[16]
Some evidence of early evolutionary history is the structure of the antennal heart, a separate circulatory organ consisting of two ampullae, or vesicles,[44] that are attached to the frontal cuticle to the bases of the antennae.[45] These features have not been found in other insects. An independent organ exists for each antenna, consisting of an ampulla, attached to the frontal cuticle medial to the antenna base and forming a thin-walled sac with a valved ostium on its ventral side. They pump blood by elastic connective tissue, rather than muscle.[46]
Molecular studies suggest that this order is the sister to Plecoptera or to Ephemeroptera.[47]
Taxonomy
Distinguishing characteristics
The characteristics which distinguish the order Dermaptera from other insect orders are:[48]
- General body shape: Elongate; dorso-ventrally flattened.
- Head: Prognathous. Antennae are segmented. Biting-type mouthparts. Ocelli absent. Compound eyes in most species, reduced or absent in some taxa.
- Appendages: Two pairs of wings normally present. The forewings are modified into short smooth, veinless tegmina. Hindwings are membranous and semicircular with veins radiating outwards.
- Abdomen: Cerci are unsegmented and resemble forceps. The ovipositor in females is reduced or absent.
The overwhelming majority of earwig species are in Forficulina, grouped into nine families of 180 genera,[42] including Forficula auricularia, the common European Earwig. Species within Forficulina are free-living, have functional wings and are not parasites. The cerci are unsegmented and modified into large, forceps-like structures.
The first epizoic species of earwig was discovered by a London taxidermist on the body of a Malaysian hairless bulldog bat in 1909, then described by Karl Jordan. By the 1950s, the two suborders Arixeniina and Hemimerina had been added to Dermaptera.[18]
Arixeniina represents two genera, Arixenia and Xeniaria, with a total of five species in them. As with Hemimerina, they are blind and wingless, with filiform segmented cerci. Hemimerina are viviparous ectoparasites, preferring the fur of African rodents in either Cricetomys or Beamys genera.[43] Hemimerina also has two genera, Hemimerus and Araeomerus, with a total of 11 species.[43]
Phylogeny

Dermaptera (= Euplecoptera, Euplexoptera, or Forficulida[13]) is relatively small compared to the other orders of Insecta, with only about 2,000 species, 3 suborders and 15 families, including the extinct suborders Archidermaptera and Eodermaptera with their extinct families Protodiplatyidae, Dermapteridae, Semenoviolidae, and Turanodermatidae. The phylogeny of the Dermaptera is still debated. The extant Dermaptera appear to be monophyletic and there is support for the monophyly of the families Forficulidae, Chelisochidae, Labiduridae and Anisolabididae, however evidence has supported the conclusion that the former suborder Forficulina was paraphyletic through the exclusion of Hemimerina and Arixeniina which should instead be nested within the Forficulina.[42][49] Thus, these former suborders were eliminated in the most recent higher classification. The following is from Engel & Haas (2007):
Suborder Archidermaptera †
- Protodiplatyidae †
- Dermapteridae †
Suborder Eodermaptera †
- Semenoviolidae †
- Turanodermatidae †
Suborder Neodermaptera
- Anisolabididae
- Apachyidae
- Chelisochidae
- Diplatyidae
- Spongiphoridae
- Forficulidae
- Karschiellidae
- Labiduridae
- Labiidae
- Pygidicranidae
- Hemimeridae
Relationship with humans
Earwigs are fairly abundant and are found in many areas around the world. There is no evidence that they transmit diseases to humans or other animals. Their pincers are commonly believed to be dangerous, but in reality, even the curved pincers of males cause little or no harm to humans.[50] It is a common myth that earwigs crawl into the human ear and lay eggs in the brain.[51][52]
There is a debate whether earwigs are harmful or beneficial to crops, as they eat both the insects eating the foliage (such as aphids) and the foliage itself, though it would take a large population to do considerable damage. The common earwig eats a wide variety of plants, and also a wide variety of foliage including the leaves and petals. They have been known to cause economic losses in fruit and vegetable crops. Some examples are the flowers, hops, red raspberries,[53] and corn crops in Germany, and in the south of France, earwigs have been observed feeding on peaches and apricots. The earwigs attacked mature plants and made cup-shaped bite marks 3–11 mm (0.12–0.43 in) in diameter.[54]
In literature and folklore
- Robert Herrick in Hesperides describes a feast attended by Queen Titania through writing: "Beards of mice, a newt's stew'd thigh, A bloated Earwig and a fly".
- Thomas Hood discusses the belief of Earwig's finding shelter in the human in the poem Love Lane by saying the following: "'Tis vain to talk of hopes and fears And hope the least reply to wing, From any maid that stops her ears In dread of ear-wigs creeping in!"
- In rural England the earwig is called "battle-twig", which is present in Baron Tennyson's poem The Spinster's Sweet-Arts: "'Twur as bad as battle-twig 'ere i' my oan blue chamber to me."[55]
References
- ↑ Zhang, Z.-Q. (2011). "Phylum Arthropoda von Siebold, 1848 In: Zhang, Z.-Q. (Ed.) Animal biodiversity: An outline of higher-level classification and survey of taxonomic richness" (PDF). Zootaxa. 3148: 99–103.
- ↑ Walter W. Skeat (2013). An Etymological Dictionary of the English Language. Courier Corporation. p. 187. ISBN 9780486317656.
- ↑ Costa, J.T. (2006). The Other Insect Societies. United States, Harvard University: Harvard University Press.
- ↑ "Dermaptera: earwigs". Insects and their Allies. CSIRO. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ↑ Friedrichsen, G W S; Robert W Burchfield (31 December 1966). Onions CT, ed. The Oxford Dictionary of English Etymology (1996 ed.). United Kingdom, Oxford University: Oxford University Press. pp. earwig. ISBN 0-19-861112-9.
- ↑ Fisher, JR (1986). "Earwig in the ear". Western Journal of Medicine. 145 (2): 245. PMC 1306897
 . PMID 3765607.
. PMID 3765607. - ↑ The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language. American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language Ser. Editors of the American Heritage Dictionaries (Fourth ed.). Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. 12 April 2006. pp. earwig. ISBN 0-618-70172-9.
- ↑ OED definition of earwig
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Burton, Maurice (January 2001). International Wildlife Encyclopedia (3 ed.). Marshall Cavendish Inc. ISBN 0-7614-7266-5.
- ↑ Robinson, William H. (2005). Handbook of urban insects and arachnids. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. p. 480. ISBN 978-0-521-81253-5.
- ↑ Marshall, Stephan A. (June 2006). "4". Insects: Their Natural History and Diversity: With a Photographic Guide to Insects of Eastern North America. Buffalo, NY; Richmond Hill, Ontario: Firefly Books. pp. 63–64. ISBN 1-55297-900-8.
- 1 2 Cranshaw, W.S. (January 2007). "European Earwigs". 5.533. Colorado State University. Retrieved 25 June 2009.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Gillott, Cedric (2005). Entomology (3 ed.). Dordrecht: Springer. pp. 175–179. ISBN 978-1-4020-3184-7.
- ↑ Flindt, Rainer (2006). Amazing Numbers in Biology. Springer. ISBN 978-3540301462.
- ↑ "St Helena giant earwig Labidura herculeana". Natural History Museum. 2013. Retrieved 25 May 2013.
- 1 2 3 Grimaldi, David; Michael Engel (May 2005). "7". Evolution of the Insects. Cambridge Evolution Ser. (1 ed.). Cambridge University: Cambridge University Press. pp. 217–222. ISBN 0-521-82149-5. Retrieved 16 November 2009.
- ↑ Carpenter, George Herbert (1899). "4". Insects: their structure & life. London: J. M. & Co. pp. 170–172.
- 1 2 3 T. Costa, James (May 2006). "3". The other insect societies. Foreword by Bert Hölldobler and commentary by Edward O. Wilson (1 ed.). Harvard University: Harvard University Press. pp. 53–54. ISBN 0674021630.
- 1 2 3 4 Gullan, P.J.; P.S. Cranston (2005). "9 - Ground Dwelling Insects". The Insects: An Outline of Entomology (3 ed.). Oxford: Blackwell Publishing. p. 235. ISBN 1-4051-1113-5.
- 1 2 "Earwigs". North Carolina Integrated Pest Management Information. Retrieved 20 July 2009.
- ↑ Haas, Fabian (2003). "The evolution of wing folding and flight in the Dermaptera (Insecta)" (PDF). Acta zoologica cracoviensia. 46: 67–72.
- 1 2 3 Powell, Jerry A. (2009). "Dermaptera". In Resh, Vincent H.; Cardé, Ring T. Encyclopedia of Insects (illustrated 2nd ed.). Academic Press. p. 1132. ISBN 978-0-12-374144-8.
- ↑ "Earwigs, HYG-2068-94". Ohio State University. Retrieved 20 July 2009.
- ↑ Staerkle M; M Koelliker (2008). "Maternal Food Regurgitation to Nymphs in Earwigs (Forficula auricularia)" (PDF). Ethology. 114 (9): 844–850. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0310.2008.01526.x.
- ↑ Suzuki, S.; Kitamura M.; Matsubayashi, K. (2005). "Matriphagy in the hump earwig, Anechura harmandi (Dermaptera: Forficulidae), increases the survival rates of the offspring". Journal of Ethology. 23 (2): 211–213. doi:10.1007/s10164-005-0145-7.
- ↑ Eisner, Thomas; Rossini, Carmen; Eisner, Maria (1941). "Chemical defense of an earwig (Doru taeniatum)". Chemoecology. 10 (2): 81–87. doi:10.1007/s000490050011. Retrieved 25 February 2011.
- 1 2 Drees, B.M.; Jackman, John (1999). "Earwig". Field Guide to Texas Insects. Houston, Texas: Gulf Publishing Company. p. 1. Retrieved 15 November 2009.
- ↑ Weiss, Michael J.; Garrick McDonald (1998). "European earwig, Forficula auriculari L. (Dermaptera: Forficulidae), as a predator of the redlegged earth mite, Halotydeus destructor (Tucker) (Acarina: Penthaleidae)". Australian Journal of Entomology. 37 (2): 183–185. doi:10.1111/j.1440-6055.1998.tb01569.x.
- ↑ Nakata, Satsuko; TC Maa (1974). "A review of the parasitic earwigs" (PDF). Pacific Insects. 16: 307–374.
- ↑ Grupp, Susan M.; Philip L. Nixon. "The Bug Review-Earwigs". Extension Entomologist, Department of Natural Resources and Environmental Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign. p. 1. Retrieved 15 November 2009.
- 1 2 Arnold, Richard A. "Earwigs." Endangered Wildlife and Plants of the World. Vol. 4. Eds. Anne Hildyard, Paul Thompson and Amy Prior. (Tarrytown, New York: Marshall Cavendish Corporation, 2001) 497.
- ↑ Dimick, R.E. and Mote, D.C. (1934) Progress report regarding the introduction in Oregon of Digonocheata setipennis, a tachinid parasite of the European earwig. Journal of Economic Entomology 27, 863-865.
- ↑ Clausen, C.P. (1978) Dermaptera -- Forficulidae -- European Earwig. In: Clausen, C.P. (ed.) Introduced Parasites and Predators of Arthropod Pests and Weeds: A World Review, Handbook No. 480, United States Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, pp. 15-18.
- ↑ Kuhlmann, Ulrich. (26 Aug 2009) "Ocytata pallipes (Fallén) (Dipt., Tachinidae), a potential agent for the biological control of the European earwig." Journal of Applied Entomology, Vol. 117, Issue 1-5, pp. 262-7.
- ↑ Kurczewski, Frank E. "Vespula maculifrons (Hymenoptera: Vespidae) Preying on the European Earwig Forficula auricularia." Journal of the New York Entomological Society, Vol. 76, No. 2 (Jun., 1968), pp. 84-86.
- ↑ Marshall, Judith A. "Dermaptera: the earwigs." Identifying British Insects and Arachnids: An Annotated Bibliography of Key Works. ed. Peter C. Barnard. (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1999) 40.
- ↑ Shanor, Leland. "The Characteristics and Morphology of a New Genus of the Laboulbeniales on an Earwig." American Journal of Botany, Vol. 39, No. 7 (Jul. 1952), pp. 498-504.
- ↑ Capinera, John L. (June 1999). "EENY088/IN245: Ringlegged Earwig, Euborellia annulipes (Lucas) (Insecta: Dermaptera: Carcinophoridae)". Entomology and Nematology Department, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida. p. 1. Retrieved 15 November 2009.
- ↑ Behura, Basanta Kumar. "The Relationships of the Tyroglyphoid Mite, Histiostoma Polypori (Oud.) with the Earwig, Forficula Auricularia Linn." Journal of the New York Entomological Society, Vol. 64, (1956), pp. 85-94.
- ↑ Wirth, S. "Necromenic life style of Histiostoma polypori (Acari: Histiostomatidae)" Journal Experimental and Applied Acarology, Volume 49, Number 4 (December, 2009) pp. 317-327.
- ↑ Ohio Agricultural Experiment Station. 1924. "Economic entomology." Bulletin.
- 1 2 3 Fabian Haas. Dermaptera — Earwigs. Tree of Life web project.
- 1 2 3 Engel, Michael A.; Lim, Jong-Deock; Baek, Kwang-Seok; Martin, Larry D. (2002). "An Earwig from the Lower Cretaceous of Korea (Dermaptera: Forficulina)". Journal of the Kansas Entomological Society. 75 (2): 86–90.
- ↑ Gordh, George; David H. Headrick (2003). A Dictionary of Entomology. CABI Publishing. ISBN 0-85199-655-8.
- ↑ Pass, Günther; Hans Agricola; Heiner Birkenbeil; Heinz Penzlin (August 1988). "Morphology of neurones associated with the antennal heart of Periplaneta americana (Blattodea, Insecta)". Cell and Tissue Research. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg. 253 (2): 319–326. doi:10.1007/bf00222288. ISSN 0302-766X. PMID 3409288.
- ↑ Nation, James L. (28 November 2001). "11: Circulatory System". Insect physiology and biochemistry (1 ed.). CRC Press. p. 310. ISBN 0-8493-1181-0.
- ↑ Wan X, Kim MI, Kim MJ, Kim I (2012) Complete mitochondrial genome of the free-living earwig, Challia fletcheri (Dermaptera: Pygidicranidae) and phylogeny of Polyneoptera. PLoS One 7(8):e42056.
- ↑ Gillot, C. Entomology 2nd Ed. (1995) Springer, ISBN 0-306-44967-6, ISBN 978-0-306-44967-3. Accessed on Google Books on 25 November 2009.
- ↑ Jarvis, KJ; F Haas; MF Whiting (2004). "A phylogeny of earwigs (Insecta: Dermaptera) based on molecular and morphological evidence: reconsidering the classification of Dermaptera" (PDF). Systematic Entomology. 30: 1–12. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3113.2004.00276.x.
- ↑ Harris, Bronwyn (2006). Introduction to Earwigs. Home Institute. p. 1.
- ↑ Mikkelson, Barbara; David P. Mikkelson (1995). "Bugs in the Ear". Urban Legends Reference Pages. Snopes.com. p. 1. Retrieved 22 November 2009.
- ↑ Berenbaum, May R. (September 2009). "The Brain Bring Earwig". The Earwig's Tail: A Modern Bestiary of Multi-Legged Legends. Harvard University: Harvard University Press. pp. 9–14. ISBN 0-674-03540-2. Retrieved 22 November 2009.
- ↑ Gordon, SC; Cormack, MR; Hackett, CA (September 1997). "Arthropod contamination of red raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) harvested by machine in Scotland". JOURNAL OF HORTICULTURAL SCIENCE. 72 (5): 677–685.
- ↑ Solomon, M.G. (March 1992). "Exploitation of predators in UK fruit and hop culture". Phytoparasitica. 20 (Supplement 1): 51S–56S. doi:10.1007/BF02980408.
- ↑ Twinn, Cecil (1942). Insect Life in the Poetry and Drama of England: With Special Reference to Poetry (Thesis). University of Ottawa. pp. 241–242. OCLC 877128347.
External links
- Earwig Research Center by Fabian Haas, Heilbronn
- Ringlegged earwig on the UF / IFAS Featured Creatures website
- Langston RL & JA Powell (1975) The earwigs of California (Order Dermaptera). Bulletin of the California Insect Survey. 20
- Earwigs from What's That Bug?
