Elaphrosaurus
| Elaphrosaurus Temporal range: Late Jurassic, 154–150 Ma | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Holotype skeleton mounted (skull, hands and other elements speculative), Museum für Naturkunde Berlin | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Clade: | Dinosauria |
| Order: | Saurischia |
| Suborder: | Theropoda |
| Family: | †Noasauridae |
| Subfamily: | †Elaphrosaurinae |
| Genus: | †Elaphrosaurus Janensch, 1920 |
| Species: | †E. bambergi |
| Binomial name | |
| Elaphrosaurus bambergi Janensch, 1920 | |
Elaphrosaurus (pron.:ell-AH-fro-SAWR-us) is a genus of ceratosaurian theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 154 to 150 million years ago during the later part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Tanzania in Africa. Elaphrosaurus was a medium-sized, but lightly built, bipedal, carnivore, that could grow up to 6.2 m (20 ft) long. Morphologically, this dinosaur is significant in two ways. First, it has a relatively long trunk but is very shallow-chested for a theropod of its size. Second, it has very short hindlimbs when compared to its relatively long trunk. Phylogenetic analysis indicates that this genus is likely a ceratosaur, and earlier suggestions that it is a late surviving coelophysoid have been examined but generally dismissed.
Description

Elaphrosaurus was long and slender, with a long neck. What is known about Elaphrosaurus mostly comes from a single nearly complete skeleton and no skull has been found. It was distinctive among theropods for being short-legged for its length. Paul (1988) noted that this was the longest-trunked and shallowest-chested theropod that he has examined.[1] Elaphrosaurus was about 6.2 m (20 ft) long, 1.46 m (4.8 ft) tall at the hip, and weighed about 210 kilograms (460 pounds).[1] The tibia (shin bone) of Elaphrosaurus, measured 608 mm was considerably longer than its femur (thigh bone) that measured 520 mm, which indicates that it could probably run very fast.[2] Its long tail ended with a rare downward bend which may be unrelated to taphonomy.
A diagnosis is a statement of the anatomical features of an organism (or group) that collectively distinguish it from all other organisms. Some, but not all, of the features in a diagnosis are also autapomorphies. An autapomorphy is a distinctive anatomical feature that is unique to a given organism. According to Rauhut (2000), Elaphrosaurus can be distinguished based on the following characteristics: the cervical vertebrae possess thin latero-ventral laminae, bordering the posterior pleurocoel ventrally, the cervical vertebrae are strongly concave ventrally, with the ventral margin arching above the mid-height of the anterior articular facet at its highest point, the brevis fossa of the ilium is extremely widened, so that the brevis shelf forms an almost horizontal lateral flange, the distal end of the ischium is strongly expanded into a triangular boot.
Discovery
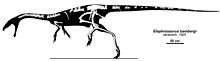
The type specimen of Elaphrosaurus bambergi HMN Gr.S. 38-44 was recovered in the Middle Dinosaur Member of the Tendaguru Formation in Tanzania. The specimen was collected by Werner Janensch, I. Salim, H. Reck, and Parkinson in 1910 in gray, green, red, sandy marl that was deposited during the Kimmeridgian stage of the Jurassic period, approximately 157 to 152 million years ago. This specimen is housed in the collection of the Humboldt Museum in Berlin, Germany.
Elaphrosaurus was described and named by Werner Janensch in 1920 and the type species is Elaphrosaurus bambergi. The genus name Elaphrosaurus is derived from the Greek words elaphros (ελαφρός) meaning "light to bear" as in "light-footed", a reference to its presumed high running speed and "sauros" (σαυρος) meaning "lizard";[3] thus, "light-footed lizard". The specific name honours the industrialist Paul Bamberg for his financial support of the Tendagaru expeditions.[4]
A related animal, perhaps the same genus, was found in stratigraphic zones 2–4 of the Morrison Formation.[1][5] Few theropod skeletons have been found, most discoveries being fragments.
Dinosaur footprints from the Niger Republic and from Jerusalem were attributed to Elaphrosaurus.[6][7] This assignment is considered inconclusive.
Classification
Elaphrosaurus was first described by Janensch as a coelurosaurian.[4] At the time, Coelurosauria was a wastebasket taxon for small theropods. Then, Elaphrosaurus was placed in the family Ornithomimidae by Franz Nopcsa in 1928 because of its light frame and the fact that its humerus is straight and slender, with a low deltopectoral crest.[8] Janensch himself rejected this assignment, believing any resemblances could plausibly be explained by convergent evolution. By the middle of the twentieth century, Elaphrosaurus was usually seen as a member of the Coeluridae. However, Nopcsa's hypothesis was revived by Dale Alan Russell in 1972,[9] and confirmed by Peter Malcolm Galton in 1982.[10] In 1988 Gregory S. Paul remarked that upon closer examination its limbs approximate those of Coelophysis and suggested a position in the Coelophysidae.[1] Nevertheless, in 1990 Barsbold, Maryanska and Osmólska and other researchers still classified it as an ornithomimid.[11] More recent work by Carrano and Sampson (2008) and Carrano et al. (2012) assign Elaphrosaurus to the Ceratosauria.[12][13] A re-study of the known fossil material, published in 2016, concluded that Elaphrosaurus was actually an early member of the Noasauridae within Ceratosauria, and that it formed a distinct group with certain Asian noasaurids, which was named the Elaphrosaurinae.[14]
The following cladogram is based on the phylogenetic analysis conducted by Rauhut and Carrano in 2016, showing the relationships of Elaphrosaurus among the noasaurids:[14]
| Abelisauroidea |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Species no longer assigned to Elaphrosaurus
The following material was assigned to Elaphrosaurus over the years, but further study revealed that these assignments were dubious:
- Elaphrosaurus iguidiensis, was described by Albert-Félix de Lapparent in 1960,[15] and the material was collected in Algeria, Libya and Niger in Early Cretaceous sediments. The material consists of over forty teeth, a manual ungual, eight caudal vertebrae, a distal femur fragment, and a complete tibia measuring 350 mm. These specimens originated in three different localities and do not appear to belong to the same species.
- Elaphrosaurus gautieri, was first described by de Lapparent in 1960,[15] and the material was collected at the Tiouraren Formation in Niger in Middle-Late Jurassic sediments. This material, a partial skeleton, has since been renamed Spinostropheus gautieri by Sereno et al. (2004).[16]
- Elaphrosaurus philtippettensis, subsequently Elaphrosaurus philtippettorum, was erected by Stephan Pickering[17][18] in 1995 based on USNM 5737, which consists of a tibia, a humerus, some metatarsals, and the distal portion of a fragmentary pubic bones recovered from the Morrison Formation of Colorado. Research by Carpenter et al. (2005) concluded that these fossils are not ceratosaurian and are likely referable to the coelurid theropod Tanycolagreus. It is named after visual effects supervisor Phil Tippett.
- Elaphrosaurus agilis, was a renaming by Dale Russell in 1980 of Coelurus agilis, originally named by Othniel Charles Marsh in 1884.[19] The species is based on a pair of fused pubic bones that were by Marsh believed to represent a much larger version of the type species Coelurus fragilis. John Ostrom (1980) confirmed Charles Whitney Gilmore's earlier position that Coelurus agilis was synonymous with Coelurus fragilis. This means that Elaphrosaurus agilis is actually the same animal as Coelurus fragilis, its junior synonym.
- Elaphrosaurus sp. USNM 8415, was discovered in 1883 and first referred to the ornithopod Dryosaurus. It was later referred to Elaphrosaurus by Galton in 1982, based on remains recovered at the Morrison Formation of Colorado. This material, which is clearly ceratosaurian, does not bear any morphology that specifically ties it to Elaphrosaurus. Current knowledge limits the placement of this material to Ceratosauria incertae sedis.[20]
- Elaphrosaurus sp. DMNH 36284, was referred to this genus by Chure[21] in 2001, based on the proximal portion of a fragmentary right tibia from the Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation. Phylogenetic analysis by Carrano and Sampson (2008) showed that it was not basal ceratosaurian, but instead resembled the leg bone of an abelisauroid theropod that has yet to be formally described.[20]
Paleoecology
Studies suggest that the paleoenvironment of the Tendaguru Formation was a marginal marine environment with both non-marine faunal and floral content. The Middle Dinosaur Member of the Tendaguru Formation has yielded the sauropods Giraffatitan, Australodocus, Janenschia, Tornieria and Dicraeosaurus, theropods similar to Allosaurus and Ceratosaurus, the carcharodontosaurid Veterupristisaurus, the stegosaurid Kentrosaurus and the iguanodontian Dysalotosaurus. Dinosaurs shared this paleoenvironment with pterosaurs like Pterodactylus and Rhamphorhynchus, as well as with early mammals. Paul (1988) noted that Elaphrosaurus bambergi was too small to prey on the sauropods and stegosaurs present in its paleoenvironment, and instead, it likely hunted the small and swift ornithopod herbivores.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 Paul, Gregory S. (1988). "Genus Elaphrosaurus". Predatory Dinosaurs of the World. New York: Simon & Schuster. pp. 265–266. ISBN 0-671-61946-2.
- ↑ Foster, John (2007). Jurassic West: The Dinosaurs of the Morrison Formation and Their World. Indiana University Press. p. 182. ISBN 978-0-253-34870-8.
- ↑ Liddell, Henry George and Robert Scott (1980). A Greek-English Lexicon (Abridged Edition). United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-910207-4.
- 1 2 Janensch, Werner (1920). "Über Elaphrosaurus Bambergi und die Megalosaurier aus den Tendaguru–Schichten Deutsch–Ostafrikas". Sitzungsberichte der Gessellschaft Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin (in German). 1920: 225–235.
- ↑ Foster, J. (2007). "Appendix." Jurassic West: The Dinosaurs of the Morrison Formation and Their World. Indiana University Press. pp. 327–329.
- ↑ M. Avnimelech. 1962. Dinosaur tracks in the Lower Cenomanian of Jerusalem. Nature 196(4851):264
- ↑ Ginsburg, L., Lapparent, A.F. deLoiret, B.and Taquet, P. (1966) Empreintes de pas de Vertebres tetrapodes dans les series continentales a l'Ouest d'Agades (Republique du Niger). Compte Rendu de l'Academie des Sciences, Paris, 263: 28–31.
- ↑ Nopcsa, F. (1928). The genera of reptiles: Paleobiologica, 1, pp. 163−188.
- ↑ Russell, Dale A. (1972). "Ostrich dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous of western Canada". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences. 9: 375–402. Bibcode:1972CaJES...9..375R. doi:10.1139/e72-031.
- ↑ Galton, 1982. Elaphrosaurus, an ornithomimid dinosaur from the Upper Jurassic of North America and Africa. Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 56, 265−275.
- ↑ Barsbold, R; Maryanska, T; & Osmólska, H: Oviraptorosauria. Weishampel, D B, Dodson, P, & Osmolska, H, editors: The Dinosauria. University of California Press, Berkeley; 1990.
- ↑ M. T. Carrano and S. D. Sampson. 2008. The phylogeny of Ceratosauria (Dinosauria: Theropoda). Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 6(2):183−236
- ↑ M. T. Carrano, R. B. J. Benson, and S. D. Sampson. 2012. The phylogeny of Tetanurae (Dinosauria: Theropoda). Journal of Systematic Palaeontology 10(2):211–300
- 1 2 Rauhut, O.W.M., and Carrano, M.T. (2016). The theropod dinosaur Elaphrosaurus bambergi Janensch, 1920, from the Late Jurassic of Tendaguru, Tanzania. Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society, (advance online publication) doi:10.1111/zoj.12425
- 1 2 Lapparent, A.-F. 1960. Les dinosauriens du "Continental intercalaire" du Sahara central. Mémoires de la Société Géologique de France. 88A 1-57.
- ↑ Sereno, Wilson and Conrad, 2004. New dinosaurs link southern landmasses in the Mid-Cretaceous. Proceedings: Biological Sciences. 71(1546), 1325–1330.
- ↑ Pickering, 1995a. Jurassic Park: Unauthorized Jewish Fractals in Philopatry. A Fractal Scaling in Dinosaurology Project, 2nd revised printing. Capitola, California. 478 pp.
- ↑ Pickering, S., 1995, An extract from: Archosauromorpha: Cladistics and osteologies. A Fractal Scaling in Dinosaurology Project 2 pp
- ↑ Russell, D.A. ; Beland, P. & Mclntosh, J.S., 1980, "Paleoecology of the dinosaurs of Tendaguru (Tanzania)", Mémoires de la Société Géologique de France, nouvelle Série, 139: 169-175
- 1 2 Carrano and Sampson, 2008. The phylogeny of Ceratosauria (Dinosauria: Theropoda). Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. 6, 183–236.
- ↑ Chure, 2001. The second record of the African theropod Elaphrosaurus (Dinosauria, Ceratosauria) from the Western Hemisphere. Neues Jahrbuch für Geologie und Paläontologie Monatshefte. 2001(9), 565–576.
- Khalaf-von Jaffa, Norman Ali Bassam Ali Taher (2006). "Ornithomimid Dinosaur Tracks from Beit Zeit, West of Jerusalem, Palestine." Gazelle: The Palestinian Biological Bulletin, Number 56, August 2006. pp. 1–7.
- Channell, Michael Benton ; illustrated by Jim; Maddison, Kevin (1988). Dinosaurs : an a-z guide. New York: Derrydale Books. ISBN 978-0517668771.
- Werner Janensch (1925) "Die Coelurosaurier und Theropoden der Tendaguru-Schichten Deutsch-Ostafrikas". (The coelurosaurs and theropods of the Tendaguru Formation, German East Africa). Full Text here: Janensch1925