Genesis (spacecraft)
|
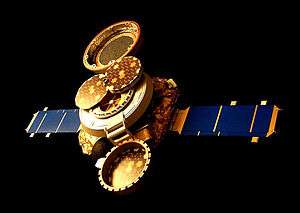
In its collecting configuration, the Genesis spacecraft exposed several types of solar wind collectors, as well as ion and electron monitors. | |||||
| Mission type | Sample return mission | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operator | NASA · JPL | ||||
| COSPAR ID | 2001-034A | ||||
| SATCAT № | 26884 | ||||
| Website |
genesismission | ||||
| Spacecraft properties | |||||
| Manufacturer | Lockheed Martin Space Systems | ||||
| Dry mass | 494 kilograms (1,089 lb) | ||||
| Power | 254 W (Solar array / Ni-H2 battery) | ||||
| Start of mission | |||||
| Launch date |
August 8, 2001 16:13:40 UTC (15 years and 4 months ago) | ||||
| Rocket | Delta II 7326 | ||||
| Launch site | Cape Canaveral SLC-17 | ||||
| End of mission | |||||
| Landing date |
September 8, 2004, after 16:55 UTC (12 years and 3 months ago) | ||||
| Landing site |
Dugway Proving Ground, Utah 40°11′19″N 113°12′46″W / 40.18861°N 113.21278°W | ||||
|
| |||||
Genesis was a NASA sample return probe that collected a sample of solar wind and returned it to Earth for analysis. It was the first NASA sample return mission to return material since the Apollo Program, and the first to return material from beyond the orbit of the Moon.[1] Genesis was launched on August 8, 2001, and crash-landed in Utah on September 8, 2004, after a design flaw prevented the deployment of its drogue parachute. The crash contaminated many of the sample collectors, and although most were damaged, some of the collectors were successfully recovered.[2]
The Genesis science team demonstrated that some of the contamination could be removed or avoided, and that the solar wind could be analyzed using a variety of approaches, achieving all of the mission's major science objectives.[3] [4]
Objectives

The mission's primary science objectives were:[7]
- To obtain precise solar isotopic abundances of ions in the solar wind, as essentially no data having a precision sufficient for solving planetary science problems are available;
- To obtain greatly improved solar elemental abundances by factor of 3-10 in accuracy over what is in the literature;
- To provide a reservoir of solar matter for 21st century science to be archived similarly as the lunar samples.
Note that the mission's science objectives refer to the composition of the Sun, not that of the solar wind. Scientists desire a sample of the Sun because evidence suggests that the outer layer of the Sun preserves the composition of the early solar nebula. Therefore, knowing the elemental and isotopic composition of the outer layer of the Sun is effectively the same as knowing the elemental and isotopic composition of the solar nebula. The data can be used to model how planets and other Solar System objects formed, and then extend those results to understanding stellar evolution and the formation of planetary systems elsewhere in the universe.
Clearly, the ideal sample collection option would be to send a spacecraft to the Sun itself and collect some solar plasma, however, that is difficult because of the intense heat of the Sun's superheated gases, as well as the dynamic electromagnetic environment of the solar corona, whose flares regularly interfere with the electronics of distant spacecraft. Fortunately, the Sun continuously sheds some of its outer layer in the form of solar wind.
Accordingly, in order to meet the mission science objectives, the Genesis spacecraft was designed to collect solar wind ions and return them to Earth for analysis.[8] Genesis carried several different solar wind collectors, all of which passively collected solar wind; that is, the collectors sat in space facing the sun, while the ions in the solar wind crashed into them at speeds over 200 km/s and, on impact, buried themselves in the surface of the collectors. This passive collection is a process similar to that used by the semi-conductor industry to make certain types of devices, and a simulation of the process is given by the free-access program SRIM.[9]
Most of the Genesis collectors continuously sampled all of the solar wind which the spacecraft encountered (the "bulk solar wind"). However, the spacecraft also carried three arrays of collectors which were deployed when specific “regimes” (fast, slow, coronal mass ejections) of solar wind were encountered, as determined by the electron- and ion- monitors on board.[10] These deployable collector arrays were designed to provide data to test the hypothesis that the rock-forming elements keep their relative proportions throughout the processes which form the solar wind.
There was a third type of collector on Genesis: the concentrator, which collected bulk solar wind, but was discriminating in that it electrostatically repelled hydrogen and had enough voltage to focus the lighter solar wind elements onto a small target, concentrating those ions by a factor of ~20. The objective of the concentrator was to bring back a sample with enhanced amounts of solar wind ions to make it possible for analysts to precisely measure the isotopes of the light elements.[11][12]
Operation
Mission profile

Genesis was a Discovery-class mission of the NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) at the California Institute of Technology. The spacecraft was designed and built by Lockheed Martin Space Systems at a total mission cost of US$264 million.
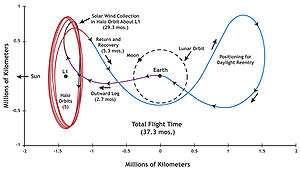
NASA launched the craft on a Delta II 7326 rocket on August 8, 2001 at 16:13:40 UTC from Cape Canaveral. Following launch, Genesis cruised to the Earth-Sun L1 then performed a Lissajous orbit insertion maneuver, entering an elliptical orbit about L1 on November 16, 2001. Genesis exposed its collector arrays on 3 December, and began collecting solar wind particles. The collection process ended after 850 days, on April 1, 2004, with the spacecraft completing five halo loops around L1.[13] Genesis began its return to Earth on April 22, 2004. The return phase included an orbital detour toward the Earth L2 so that the craft could be recovered during the daytime, as a direct approach would have forced it to be recovered at night. After completing one halo loop about L2, the spacecraft returned to Earth for a planned September 8, 2004 recovery.[14]
Recovery phase

Following completion of the collection phase, the collector arrays were stowed in a sample return capsule, and the spacecraft returned to Earth. As the capsule was approaching Earth and at the first stages of re-entry, all appeared well.
Extensive planning had been conducted for the capsule's retrieval. A normal parachute landing might have damaged the delicate samples, so the mission design called for a mid-air retrieval of the sample return capsule. About 33 km above the ground, a drogue parachute was to be deployed to slow descent. Then, at a height of 6.7 km, a large parafoil was to be deployed to slow descent further and leave the capsule in stable flight. A helicopter, with a second helicopter as a backup, was then to attempt to catch the capsule by its parachute on the end of a five-meter hook. Once retrieved, the capsule would have been soft-landed.
The sample return capsule entered Earth's atmosphere over northern Oregon at 16:55 UTC September 8, 2004, with a velocity of approximately 11.04 km/s (24,706 mph).[14] Due to a design flaw in a deceleration sensor, parachute deployment was never triggered, and the spacecraft's descent was slowed only by its own air resistance.[15] The planned mid-air retrieval could not be carried out, and the capsule crashed into the desert floor of the Dugway Proving Ground in Tooele County, Utah, at about 86 metres per second (311 km/h (193 mph)).
The capsule broke open on impact, and part of the inner sample capsule was also breached. The damage was less severe than might have been expected given its velocity; it was to some extent cushioned by falling into fairly soft muddy ground.

Unfired pyrotechnic devices in the parachute deployment system and toxic gases from the batteries delayed the recovery team’s approach to the crash site. After all was made safe, the damaged sample-return capsule was secured and moved to a clean room for inspection; simultaneously a crew of trained personnel scoured the site for collector fragments and sampled the local desert soil to archive as a reference by which to identify possible contaminants in the future. Recovery efforts by Genesis team members at the Utah Test and Training range – which included inspecting, cataloging and packaging various collectors – took four weeks.[16]
Fate of spacecraft bus
After releasing the sample return capsule on September 8, 2004, the spacecraft bus traveled back toward the Earth-Sun Lagrange Point (L1). A trajectory correction maneuver was performed on November 6, 2004, permitting the spacecraft bus to eventually leave L1 if it was not used for an extended mission. Final commands were transmitted to the bus on December 2, 2004,[17] placing Genesis into hibernation. While in this "safe" mode, it will continue transmitting information about its condition, autonomously pointing its solar arrays toward the Sun. The spacecraft bus left L1 around February 1, 2005, staying in a heliocentric orbit leading the Earth.[18]
Sample extraction and results
Initial investigations showed that some wafers had crumbled on impact, but others were largely intact. Desert dirt entered the capsule, but not liquid water. Because the solar wind particles were expected to be embedded in the wafers, whereas the contaminating dirt was thought likely just to lie on the surface, it was possible to separate the dirt from the samples. Unexpectedly, it was not terrestrial desert soil introduced in the crash that proved most difficult to deal with during the sample analysis process, but the craft's own compounds such as lubricants and craft-building materials.[19]
The analysis team stated that they should be able to achieve most of their primary science goals. On September 21, 2004 the extraction began, and on January 2005, a first sample piece of an aluminum wafer was sent to scientists at Washington University in St. Louis for analysis.[20]
The Genesis solar wind samples are under long-term curation at NASA Johnson Space Center so that as sample analysis techniques evolve, pristine solar wind samples will be available to the scientific community in the decades to come.[3]
Noble gases
In 2007, scientists at Washington University published detailed neon and argon isotope findings.[21] The remaining results on the elemental and isotopic composition of the noble gases were reported in 2009.[22] The results agree with data from lunar samples containing "young" (∼100 million years) solar wind, indicating that solar wind composition has not changed within at least the last 100 million years.[22]
Oxygen isotopes
On April 20, 2005, scientists at the Johnson Space Center in Houston removed the four solar wind collectors from an instrument called the concentrator and found them in excellent condition. The concentrator's targets collected solar-oxygen ions during the mission and would be analyzed to measure solar-oxygen isotopic composition, the highest-priority measurement objective for Genesis.[23]
The team announced on 10 March 2008 that analysis of a silicon wafer from Genesis showed that the Sun has a higher proportion of oxygen-16 (16O) relative to the Earth, Moon, Mars, and bulk meteorites.[24][25] This implies that an unknown process depleted oxygen-16 from the Sun's disk of protoplanetary material prior to the coalescence of dust grains that formed the inner planets and the asteroid belt.[26]
Nitrogen isotopes
Nitrogen was a key target element because the extent and origin of its isotopic variations in solar system materials remain unknown. Target material showed that implanted solar wind nitrogen has a 15N/14N ratio of 2.18 × 10−3 (that is, ≈40% poorer in 15N relative to terrestrial atmosphere). The 15N/14N ratio of the protosolar nebula was 2.27 × 10−3, which is the lowest 15N/14N ratio known for solar system objects. This result demonstrates the extreme nitrogen isotopic heterogeneity of the nascent solar system and accounts for the 15N-depleted components observed in solar system reservoirs.[27]
Mishap Investigation Board (MIB)


A 16-member NASA Mishap Investigation Board (MIB) was appointed, including experts on pyrotechnics, avionics, and other specialties. The MIB started its work on September 10, 2004, when it arrived at Dugway Proving Ground. It determined that all scientific hardware meant to be curated by the Johnson Space Center could be released and were not needed for the work of the board. Both JPL and Lockheed Martin began to prepare flight data and other records for the MIB.
It was announced by the MIB on September 20, 2004, that the capsule, having had the science material extracted, would be moved to the Lockheed Martin Space Systems facility near Denver, Colorado, for MIB use.[28]
A first possible root cause of the failed deployment of the parachutes was announced in an October 14 press release. Lockheed Martin had built the system with an acceleration sensor's internal mechanisms wrongly oriented (a G-switch was installed backwards), and design reviews had not caught the mistake. The intended design was to make an electrical contact inside the sensor at 3 g (29 m/s²), maintaining it through the maximum expected 30 g (290 m/s²), and breaking the contact again at 3 g to start the parachute release sequence. Instead, no contact was ever made.[29]
The same general parachute concept was also used on the Stardust cometary sample return spacecraft, which landed successfully in 2006.
NASA investigation board chair Michael Ryschkewitsch noted that none of the stringent review procedures at NASA had picked up a mistake, saying, "It would be very easy to mix this up."[30]
This mishap is similar to the original event that inspired Edward A. Murphy, Jr. to formulate the now-famous Murphy's Law: an accelerometer installed backwards.[31] On January 6, 2006, Ryschkewitsch revealed that a pre-test procedure on the craft was skipped by Lockheed Martin, and he noted that the test could have easily detected the problem.[32]
References
- ↑ The NASA Stardust mission launched two years before Genesis, but did not return to Earth until two years after Genesis's return.
- ↑ "Solar Wind Curation at JSC". NASA.
- 1 2 Solar Wind Conditions and Composition During the Genesis Mission as Measured by in situ Spacecraft. Daniel B. Reisenfeld, Roger C. Wiens, Bruce L. Barraclough, John T. Steinberg, Marcia Neugebauer, Jim Raines, Thomas H. Zurbuchen. Space Science Reviews June 2013, Volume 175, Issue 1, pp 125-164.
- ↑ "Genesis Science Team". NASA.
- ↑ "Diamond-like Films Help In Study Of Solar Winds". ScienceDaily. 19 February 2009.
- ↑ Jurewicz AJ, Burnett DS, Wiens RC, Friedmann TA, Hays CC, Hohlfelder RJ, Nishiizumi K, Stone JA, Woolum DS, Becker R, Butterworth AL, Campbell AJ, Ebihara M, Franchi IA, Heber V, Hohenberg CM, Humayun M, McKeegan KD, McNamara K, Meshik A, Pepin RO, Schlutter D, Wieler R (2003). "The Genesis solar wind collector materials". Space Science Review. 105 (3–4): 535–560. Bibcode:2003SSRv..105..535J. doi:10.1023/A:1024469927444.
- ↑ "Genesis Discovery 5 Mission Proposal". NASA JPL.
- ↑ Burnett DS, Barraclough BL, Bennett R, Neugebauer M, Oldham LP, Sasaki CN, Sevilla D, Smith N, Stansbery E, Sweetnam D, Wiens RC (2003). "The Genesis Discovery mission: Return of solar matter to Earth". Space Science Review. 105 (3–4): 509–534. Bibcode:2003SSRv..105..509B. doi:10.1023/A:1024425810605.
- ↑ Ziegler, James F. "The Stopping and Range of Ions in Matter".
- ↑ Barraclough BL, Dors EE, Abeyta RA, Alexander JF, Ameduri FP, Baldonado JR, Bame SJ, Casey PJ, Dirks G, Everett DT, Gosling JT, Grace KM, Guerrero DR, Kolar JD, Kroesche JL Jr, Lockhart WL, McComas DJ, Mietz DE, Roese J, Sanders J, Steinberg JT, Tokar RL, Urdiales C, Wiens RC (2003). "The plasma ion and electron instruments for the Genesis Mission". Space Science Review. 105 (3–4): 627–660. Bibcode:2003SSRv..105..627B. doi:10.1023/A:1024426112422.
- ↑ Nordholt J.E., Wiens R.C., Abeyta R.A., Baldonado J.R., Burnett D.S., Casey P., Everett D. T., Lockhart W., McComas D. J., Mietz D. E., MacNeal P., Mireles V., Moses R. W., Neugebauer M., Poths J. E., Reisenfeld D. B, Storms S. A., Urdiales C. (2003). "The Genesis solar wind concentrator". Space Science Review. 105 (3–4): 561–599. Bibcode:2003SSRv..105..561N. doi:10.1023/A:1024422011514.
- ↑ ELEMENTAL FRACTIONATION PROCESSES IN THE SOLAR WIND REVEALED BY GENESIS SOLAR WIND REGIME SAMPLES. (PDF) 44th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference (2013)
- ↑ Klein, John; Manning, Rob; Barry, Ed; Donaldson, Jim; Rivellini, Tom; Battel, Steven; Savino, Joe; Lee, Wayne; Dalton, Jerry; Underwood, Mark; Surampudi, Rao; Accord, Arden; Perkins, Dave; Barrow, Kirk; Wilson, Bob. "Genesis failure investigation report : JPL Failure Review Board, Avionics Sub-Team". JPL Publication 05-2. Jet Propulsion Laboratory. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- 1 2 "Genesis: Mission History". NASA JPL. Retrieved 2009-09-03.
- ↑ Michael Ryschkewitsch, Chairman; et als (13 June 2006). "Genesis Mishap Investigation Board Report, Volume I" (.PDF). NASA. Retrieved 2010-05-01.
- ↑ Stansbery, EK. "Genesis Recovery Processing" (PDF). NASA JSC.
- ↑ "Genesis science "a work in progress"". NASA. 2005. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ↑ "Genesis spacecraft bus flies solo". NASA. 2005. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ↑ Jones, Nicola (18 October 2007). "Crashed spacecraft yields data". naturenews. doi:10.1038/news.2007.175. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- ↑ "NASA Sends First Genesis Early-Science Sample to Researchers" (Press release). NASA. 27 January 2005. Retrieved 2006-04-24.
- ↑ Meshik, Alex; Mabry, Jennifer; Hohenberg, Charles; Marrocchi, Yves; Pravdivtseva, Olga; Burnett, Donald; Olinger, Chad; Wiens, Roger; Reisenfeld, Dan; Allton, Judith; McNamara, Karen; Stansbery, Eileen; Jurewicz, Amy J. G. (18 October 2007). "Constraints on Neon and Argon Isotopic Fractionation in Solar Wind". Science. 318 (5849): 433–435. Bibcode:2007Sci...318..433M. doi:10.1126/science.1145528. PMID 17947578. Retrieved 2007-10-20.
- 1 2 "Noble gas composition of the solar wind as collected by the Genesis mission." Veronika S. Hebera, Rainer Wielera, Heinrich Baura, Chad Olingerb, Tom A. Friedmannc, Donald S. Burnettd. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta. Volume 73, Issue 24, 15 December 2009, Pages 7414–7432; doi=10.1016/j.gca.2009.09.013
- ↑ Beasley, Dolores; Jeffs, William; Ambrosiano, Nancy (20 April 2005). "NASA Announces Key Genesis Science Collectors In Excellent Shape" (Press release). NASA. Retrieved 2006-04-24.
- ↑ UCLA Department of Earth and Space Sciences.
- ↑ "The Oxygen Isotopic Composition of the Sun Inferred from Captured Solar Wind." K. D. McKeegan1, A. P. A. Kallio1, V. S. Heber1, G. Jarzebinski1, P. H. Mao1, C. D. Coath1, T. Kunihiro1, R. C. Wiens, J. E. Nordholt, R. W. Moses Jr., D. B. Reisenfeld, A. J. G. Jurewicz, D. S. Burnett; Science 24 Jun 2011: Vol. 332, Issue 6037, pp. 1528-1532 DOI: 10.1126/science.1204636
- ↑ Hand, Eric (13 March 2008). "The Solar System's first breath" (fee required). Nature. 452 (7185): 259. Bibcode:2008Natur.452..259H. doi:10.1038/452259a. PMID 18354437.
- ↑ A 15N-Poor Isotopic Composition for the Solar System As Shown by Genesis Solar Wind Samples. B. Marty, M. Chaussidon, R. C. Wiens, A. J. G. Jurewicz, D. S. Burnett. Science 24 Jun 2011: Vol. 332, Issue 6037, pp. 1533-1536. DOI: 10.1126/science.1204656
- ↑ Savage, Donald (20 September 2004). "Genesis Mishap Investigation Board Status Report #1". Retrieved 2014-05-19.
- ↑ McKee, Maggie (15 October 2004). "Genesis crash linked to upside-down design". New Scientist. Retrieved 2006-04-24.
- ↑ Jones, Nicola (18 October 2004). "Flawed drawings caused spacecraft crash". Nature News. doi:10.1038/news041018-1.
- ↑ Oberg, James (21 October 2004). "'Murphy's Law' rules outer space... And NASA still needs to learn how to evade it". MSNBC. Retrieved 2006-04-24.
- ↑ "Official: Genesis Pre-Launch Test Skipped". Space.com. Associated Press. 2006-01-07. Archived from the original on 2006-01-10. Retrieved 2006-04-24.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Genesis (spacecraft). |
- "Genesis Mission Home Page". JPL. Retrieved 2008-05-21.
- Genesis Mission Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- "Impact video" (QuickTime movie). Retrieved 2006-04-20.