Golog Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
| Guoluo Prefecture 果洛州 · མགོ་ལོག་ཁུལ། | |
|---|---|
| Autonomous prefectures | |
果洛藏族自治州 མགོ་ལོག་བོད་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་ཁུལ་ | |
|
Eastern Guoluo Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture | |
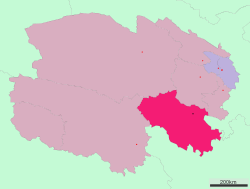 Location of Golog Prefecture in Qinghai | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Province | Qinghai |
| Prefecture seat | Maqên County (Dawu) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Website |
guoluo |
Golog (or Guoluo) Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (Chinese: 果洛藏族自治州; pinyin: Guǒluò Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu; Tibetan: མགོ་ལོག་བོད་རིགས་རང་སྐྱོང་ཁུལ་, Wylie: Mgo-log Bod-rigs rang-skyong-khul ) is an autonomous prefecture occupying the southeastern corner of Qinghai province, People's Republic of China. The prefecture has an area of 76,312 km2 (29,464 sq mi) and its seat is located in Maqên County.
Geography
Golog Prefecture is located in the southeastern part of Qinghai, in the upper basin of the Yellow River. Gyaring Lake and Ngoring Lake on the western edge of the prefecture are considered to be the source of the Yellow River. However, these lakes do receive water from rivers that flow from locations even further west, in Qumarleb County of the Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture.
The lay of the land of the prefecture is largely determined by the Amne Machin mountain range (max elevation 6,282 m), which runs in the general northwest- to-southeast direction across the entire prefecture, and beyond. The existence of the ridge results in one of the great bends of the Yellow River, which first flows for several hundreds of kilometers toward the east and southeast along through the entire Golog Prefecture, along the southern side of the Amne Machin Range, until it reaches the borders of Gansu and Sichuan; it and then turns almost 180 degrees and flows toward the northwest for 200–300 km (120–190 mi) through several prefectures of the northeastern Qinghai, forming a section of the northeastern border of the Golog prefecture.
Several sections of the Sanjiangyuan ("Sources of Three Rivers") National Nature Reserve are within the prefecture.
| Climate data for Maqên County | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 10.1 (50.2) |
12.8 (55) |
17.8 (64) |
21.9 (71.4) |
22.5 (72.5) |
24.5 (76.1) |
26.3 (79.3) |
25.1 (77.2) |
25.2 (77.4) |
21.5 (70.7) |
12.8 (55) |
10.9 (51.6) |
26.3 (79.3) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −0.5 (31.1) |
1.6 (34.9) |
5.4 (41.7) |
9.5 (49.1) |
12.6 (54.7) |
14.8 (58.6) |
17.0 (62.6) |
17.0 (62.6) |
14.1 (57.4) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.1 (39.4) |
0.7 (33.3) |
8.78 (47.82) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −11.9 (10.6) |
−8.8 (16.2) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
0.9 (33.6) |
5.0 (41) |
8.2 (46.8) |
10.2 (50.4) |
9.5 (49.1) |
6.4 (43.5) |
0.9 (33.6) |
−6.3 (20.7) |
−11.1 (12) |
−0.08 (31.86) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −21.4 (−6.5) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−6.2 (20.8) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
2.7 (36.9) |
4.6 (40.3) |
3.6 (38.5) |
1.1 (34) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
−13.8 (7.2) |
−20.2 (−4.4) |
−7.06 (19.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −33.1 (−27.6) |
−31.9 (−25.4) |
−29.1 (−20.4) |
−20.0 (−4) |
−12.8 (9) |
−6.0 (21.2) |
−4.0 (24.8) |
−5.5 (22.1) |
−7.5 (18.5) |
−17.8 (0) |
−26.6 (−15.9) |
−33.1 (−27.6) |
−33.1 (−27.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.8 (0.11) |
4.3 (0.169) |
8.2 (0.323) |
19.4 (0.764) |
55.3 (2.177) |
99.4 (3.913) |
115.1 (4.531) |
92.5 (3.642) |
79.5 (3.13) |
32.1 (1.264) |
3.5 (0.138) |
1.6 (0.063) |
513.7 (20.224) |
| Source: China Meteorological Administration,[1] | |||||||||||||
Demographics
According to the 2000 census, Guoluo has 137,940 inhabitants with a population density of 1.81 inhabitants/km².
Ethnic groups in Guoluo, 2000 census
| Nationality | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Tibetan | 126,395 | 91.63% |
| Han | 9,096 | 6.59% |
| Hui | 1,529 | 1.11% |
| Salar | 329 | 0.24% |
| Tu | 302 | 0.22% |
| Others | 289 | 0.21% |
Subdivisions
The prefecture is subdivided into six county-level divisions: six counties:
| Map | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | ||||||||
| # | Name | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Tibetan | Wylie Tibetan Pinyin |
Population (2010 Census) |
Area (km²) | Density (/km²) |
| 1 | Maqên County | 玛沁县 | Mǎqìn Xiàn | རྨ་ཆེན་རྫོང་ | rma chen rdzong Maqên Zong |
51,245 | 13,636 | 3.75 |
| 2 | Baima County | 班玛县 | Bānmǎ Xiàn | པད་མ་རྫོང་ | pad ma rdzong Baima Zong |
27,185 | 6,452 | 4.21 |
| 3 | Gadê County | 甘德县 | Gāndé Xiàn | དགའ་བདེ་རྫོང་ | dga' bde rdzong Gadê Zong |
34,840 | 7,143 | 4.87 |
| 4 | Darlag County | 达日县 | Dárì Xiàn | དར་ལག་རྫོང་ | dar lag rdzong Tarlag Zong |
30,995 | 15,385 | 2.01 |
| 5 | Jigzhi County | 久治县 | Jiǔzhì Xiàn | གཅིག་སྒྲིལ་རྫོང་ | gcig sgril rdzong Jigzhi Zong |
26,081 | 8,696 | 2.99 |
| 6 | Madoi County | 玛多县 | Mǎduō Xiàn | རྨ་སྟོད་རྫོང་ | rma stod rdzong Madoi Zong |
11,336 | 25,000 | 0.45 |
Transport
Construction for Golog Airport began in September 2012 and the airport opening date is 1 July 2016.[2]
3,000 km (1,900 mi) of new roads are expected to be built by 2015.[3]
Further reading
- A. Gruschke: The Cultural Monuments of Tibet’s Outer Provinces: Amdo - Volume 1. The Qinghai Part of Amdo, White Lotus Press, Bangkok 2001. ISBN 974-480-049-6
- Tsering Shakya: The Dragon in the Land of Snows. A History of Modern Tibet Since 1947, London 1999, ISBN 0-14-019615-3
- B. Horlemann: Modernization Efforts in Golog: A Chronicle, 1970–2000 (PDF), in: Amdo Tibetans in Transition: Society and Culture in the Post-Mao Era. Edited by Toni Huber. 2: 241–67, 2002.
- Gangs Phrug. A Modern Golok Tibetan Family History. 2015. https://archive.org/details/HappyHappy_201502.
References
- ↑ 中国地面国际交换站气候标准值月值数据集(1981-2010年). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved January 1, 2011.
- ↑ "果洛机场14日正式奠基 预计2015年竣工通航". Carnoc. 2012-09-15. Retrieved 2012-09-15.
- ↑ "China to invest 3.5b yuan for Tibetan roads". Chinadaily. 2012-09-01. Retrieved 2012-09-05.
External links
Coordinates: 34°07′N 99°19′E / 34.117°N 99.317°E