Grandfather paradox
The grandfather paradox is a paradox of time travel in which inconsistencies emerge through changing the past. The name comes from the paradox's common description as a person who travels to the past and kills their own grandfather, preventing the existence of their father or mother and therefore their own existence.[1] Any inconsistency in past events may be regarded as a grandfather paradox.[2]
Early examples and variants
The grandfather paradox was described as early as 1931, and even then it was described as "the age-old argument of preventing your birth by killing your grandparents".[3] Early science fiction stories dealing with the paradox are the short story Ancestral Voices by Nathaniel Schachner, published in 1933,[4] and the 1943 book by René Barjavel Future Times Three.[5]
Despite its title, the grandfather paradox does not exclusively regard the impossibility of killing one's own grandfather to prevent one's birth. Rather, the paradox regards any action that alters the past.[6] Another example would be using scientific knowledge to invent a time machine, then going back in time and (whether through murder or otherwise) impeding a scientist's work that would eventually lead to the invention of the time machine. An equivalent paradox is known in philosophy as autoinfanticide, going back in time and killing oneself as a baby.[7]
A variant of the grandfather paradox is the "Hitler paradox" or "Hitler's murder paradox",[8] a fairly frequent trope in science fiction, in which the protagonist travels back in time to murder Adolf Hitler before he can instigate World War II. Rather than necessarily physically preventing time travel, the action removes any reason for the travel, along with any knowledge that the reason ever existed, thus removing any point in travelling in time in the first place.[9] Additionally, the consequences of Hitler's existence are so monumental and all-encompassing that for anyone born after the war, it is likely that their birth was influenced in some way by its effects, and thus the grandfather paradox would directly apply in some way.[10]
Another variant is a parallel universe approach to time travel. When the time traveller kills their grandfather, they are actually killing a parallel-universe version of their grandfather, and the time traveller's original universe is unaltered. In other variants, the actions of the time traveller have no effect outside of their own personal experience, as depicted in the novel The Men Who Murdered Mohammed by Alfred Bester.
Logical analysis
Even without knowing whether time travel to the past is physically possible, the grandfather paradox can be explored from a logical perspective. The paradox is a logical contradiction that stems from changing the past (or the present, or the future) from the way it is: if an event has occurred one way, there is no possibility for the event to have occurred a different way. Then, logically, changing the past (or the present, or the future) from what it is results in a contradiction, which means changing the past is impossible.[6] There still exists the logical possibility of travelling back in time and setting events the way they are, for example a time traveller intending to kill their own grandfather but instead killing someone who is not their grandfather.[11]
Consideration of the grandfather paradox has led some to the idea that time travel is by its very nature paradoxical and therefore logically impossible. For example, the philosopher Bradley Dowden made this sort of argument in the textbook Logical Reasoning, where he wrote:
Nobody has ever built a time machine that could take a person back to an earlier time. Nobody should be seriously trying to build one, either, because a good argument exists for why the machine can never be built. The argument goes like this: suppose you did have a time machine right now, and you could step into it and travel back to some earlier time. Your actions in that time might then prevent your grandparents from ever having met one another. This would make you not born, and thus not step into the time machine. So, the claim that there could be a time machine is self-contradictory.
However, some philosophers and scientists believe that time travel into the past need not be logically impossible provided that there is no possibility of changing the past, as suggested, for example, by the Novikov self-consistency principle. Bradley Dowden himself revised the view above after being convinced of this in an exchange with the philosopher Norman Swartz.[12]
Consideration of the possibility of backwards time travel in a hypothetical universe described by a Gödel metric led famed logician Kurt Gödel to assert that time might itself be a sort of illusion.[13][14] He suggests something along the lines of the block time view in which time is just another dimension like space, with all events at all times being fixed within this 4-dimensional "block".
Novikov self-consistency principle
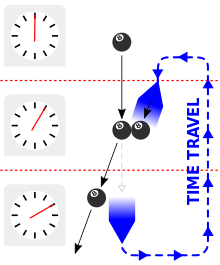
The Novikov self-consistency principle expresses one view on how backwards time travel would be possible without the generation of paradoxes. According to this hypothesis, physics in or near closed timelike curves (time machines) can only be consistent with the universal laws of physics, and thus only self-consistent events can occur. Anything a time traveller does in the past must have been part of history all along, and the time traveller can never do anything to prevent the trip back in time from happening, since this would represent an inconsistency. Novikov et al. used the example given by physicist Joseph Polchinski for the grandfather paradox, of a billiard ball heading towards a time machine; the ball's older self emerges from the time machine and strikes its younger self so its younger self never enters the time machine. Novikov et al. showed how this system can be solved in a self-consistent way which avoids the grandfather paradox, though it creates a causal loop.[15][16]
Seth Lloyd and other researchers at MIT have proposed an expanded version of the Novikov principle, according to which probability bends to prevent paradoxes from occurring. Outcomes would become stranger as one approaches a forbidden act, as the universe must favor improbable events to prevent impossible ones.[17]
Quantum physics
Physicist David Deutsch has argued that quantum computation with a negative delay—backwards time travel—produces only self-consistent solutions, and the chronology-violating region imposes constraints that are not apparent through classical reasoning.[18] In 2014, researchers published a simulation validating Deutsch's model with photons.[19] Deutsch uses the terminology of "multiple universes" in his paper in an effort to express the quantum phenomena, but notes that this terminology is unsatisfactory. Others have taken this to mean that "Deutschian time travel" involves multiple universes in order to resolve the grandfather paradox.[20]
See also
- Chicken or the egg
- Chronology protection conjecture
- Ontological paradox
- Temporal paradox
- Time loop
- Time travel in fiction
- Schrödinger's cat
References
- ↑ "Carl Sagan Ponders Time Travel". NOVA. PBS. December 10, 1999. Retrieved 2016-05-21.
- ↑ Francisco Lobo (2002). "Time, Closed Timelike Curves and Causality" (PDF). p. 2. Retrieved November 2, 2015.
- ↑ Nahin, Paul J. (1999). Time Machines: Time Travel in Physics, Metaphysics, and Science Fiction (2nd ed.). New York, NY: Springer. pp. vi, 173. ISBN 0-387-98571-9.
- ↑ Ginn, Sherry; Leach, Gillian I. (2015). Time-Travel Television: The Past from the Present, the Future from the Past. London: Rowman & Littlefield. p. 192. ISBN 1442255773.
- ↑ Barjavel, René (1943). Le voyageur imprudent ("The imprudent traveller").
- 1 2 Norman Swartz (2001), Beyond Experience: Metaphysical Theories and Philosophical Constraints, University of Toronto Press, pp. 226—227
- ↑ Horwich, Paul (1987). Asymmetries in Time: Problems in the Philosophy of Science (2nd ed.). Cambridge, Mass.: MIT Press. p. 116. ISBN 0262580888.
- ↑ Eugenia Williamson (6 April 2013). "Book review : Life after Life' by Kate Atkinson". The Boston Globe. Retrieved 9 August 2013.
Google the phrase “go back in time and,” and the search engine will suggest completing the phrase with a simple directive: “kill Hitler.” The appeal of murdering the Nazi dictator is so great that it has its own subgenre within speculative fiction, a trope known as “Hitler’s murder paradox” in which a time traveller journeys back far enough to nip the leader — and World War II — in the bud, typically with unexpected consequences.
- ↑ Brennan, J.H. (1997). Time Travel: A New Perspective (1st ed.). Minnesota: Llewellyn Publications. p. 23. ISBN 9781567180855.
A variation on the grandfather paradox . . . is the Hitler paradox. In this one you travel back in time to murder Hitler before he starts the Second World War, thus saving millions of lives. But if you murder Hitler in, say, 1938, then the Second World War will never come about and you will have no reason to travel back in time to murder Hitler!
- ↑ Esther Inglis-Arkell (2012). "Are we running out of time to kill Hitler via time travel?". io9. Retrieved 2013-08-12.
- ↑ Dummett, Michael (1996). The Seas of Language (New. ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. pp. 368–369. ISBN 0198236212.
- ↑ Norman Swartz (1993). "Time Travel - Visiting the Past". SFU.ca. Retrieved 2016-04-21.
- ↑ Yourgrau, Palle (2005). A World Without Time: The Forgotten Legacy Of Godel And Einstein (1st ed.). New York, NY: Basic Books. ISBN 0-465-09293-4.
- ↑ Holt, Jim (2005-02-21). "Time Bandits". The New Yorker. Retrieved 2006-10-19.
- ↑ Lossev, Andrei; Novikov, Igor (15 May 1992). "The Jinn of the time machine: non-trivial self-consistent solutions" (PDF). Class. Quantum Gravity. 9: 2309–2321. Bibcode:1992CQGra...9.2309L. doi:10.1088/0264-9381/9/10/014. Retrieved 16 November 2015.
- ↑ Thorne, Kip S. (1995). Black Holes & Time Warps: Einstein's Outrageous Legacy. New York: W.W. Norton. pp. 510–511. ISBN 0-393-31276-3.
- ↑ Laura Sanders, "Physicists Tame Time Travel by Forbidding You to Kill Your Grandfather", Wired, 20 July 2010. "But this dictum against paradoxical events causes possible unlikely events to happen more frequently. 'If you make a slight change in the initial conditions, the paradoxical situation won’t happen. That looks like a good thing, but what it means is that if you’re very near the paradoxical condition, then slight differences will be extremely amplified,' says Charles Bennett of IBM’s Watson Research Center in Yorktown Heights, New York."
- ↑ Deutsch, David (1991). "Quantum mechanics near closed timeline curves". Physical Review D. 44 (10): 3197–3217. Bibcode:1991PhRvD..44.3197D. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.44.3197.
- ↑ Martin Ringbauer; Matthew A. Broome; Casey R. Myers; Andrew G. White; Timothy C. Ralph (19 Jun 2014). "Experimental simulation of closed timelike curves". Nature Communications. 5. arXiv:1501.05014
 . Bibcode:2014NatCo...5E4145R. doi:10.1038/ncomms5145.
. Bibcode:2014NatCo...5E4145R. doi:10.1038/ncomms5145. - ↑ Lee Billings (2 Sep 2014). "Time Travel Simulation Resolves 'Grandfather Paradox'". Scientific American. Retrieved 24 September 2014.