Groton–New London Airport
| Groton–New London Airport | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | |||||||||||||||
| IATA: GON – ICAO: KGON – FAA LID: GON | |||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||
| Owner | Connecticut Airport Authority | ||||||||||||||
| Serves | Groton, Connecticut | ||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 9 ft / 3 m | ||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 41°19′48″N 072°02′42″W / 41.33000°N 72.04500°WCoordinates: 41°19′48″N 072°02′42″W / 41.33000°N 72.04500°W | ||||||||||||||
| Website | GON Website | ||||||||||||||
| Map | |||||||||||||||
 GON  GON Location of airport in Connecticut/United States | |||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2015) | |||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||
Groton–New London Airport (IATA: GON, ICAO: KGON, FAA LID: GON) is a state owned, public use airport located three nautical miles (6 km) southeast of the central business district of Groton, a town in New London County, Connecticut, United States.[1] It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of Integrated Airport Systems for 2017–2021, in which it is categorized as a regional general aviation facility.[2] It serves the southeastern Connecticut region, including the shoreline localities of Groton, New London, and Mystic.
The airport has not had scheduled service since 2004. It has been used by several presidents speaking at the commencement of the nearby US Coast Guard Academy.
History
Groton–New London Airport was established as the first State of Connecticut airport in 1929. Originally called Trumbull Airport after Governor Jonathan Trumbull, the airport was taken over by the United States Army Air Corps in August 1941 as a First Air Force group training base, although the runways were still grass. In 1942, the Army constructed a base and hard-surfaced runways and designated the airport as Groton Army Airfield. Through all of 1943, a total of 10 squadrons of P-47 Thunderbolt fighter groups trained at the field, with the last unit departing for overseas combat in January 1944.
In January 1944, the USAAF turned the airfield to the United States Navy. The commissioning of Groton as a Naval Airfield occurred on February 1, 1944, as an auxiliary of Quonset Point. Initially, Groton hosted various individual squadrons. Later, entire CAGs of three or four squadrons formed up at the base. The CAGs attached here during the war included CAG 83, 10, 92, 152, and 4, with their F6Fs, F4Us, SB2Cs, and TBMs. CASU 28, on board in support of the CAGs, operated one OS2U Kingfisher, one J4F Widgeon, 12 SNJs, and one NH Howard. The station had one airplane assigned, a GH Howard.
In March 1944, station personnel consisted of 87 officers and 678 enlisted men with barracks for 114 officers and 1,091 men. The peak number of aircraft reached 114 in March 1945. Groton had three concrete runways: two of 4,000 feet and one of 5,000 ft. In July 1946, the Navy returned the airport to the State of Connecticut.
In 1980, the name of the airport changed to Groton–New London Airport. Today, the airport is one of two state-owned airports with commercial air carrier service. The funds necessary to operate Groton–New London Airport come from the Connecticut State Transportation Fund. Likewise, revenue derived from the airport is returned to the Transportation Fund.
The airport is integrated into the statewide transportation plan, as well as the National Airport System Plan. There were 80,319 aircraft operations during 1999 at Groton–New London Airport which included military, general aviation and commercial flights. The airport has recently undergone $2,000,000 in renovations. The passenger terminal has been updated with new counter and seating areas and improved lighting.
Facilities and aircraft

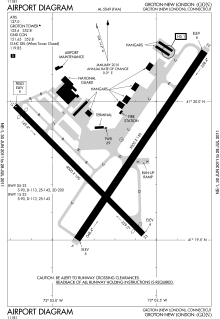
Groton–New London Airport covers an area of 489 acres (198 ha) at an elevation of 9 feet (3 m) above mean sea level. It has two asphalt paved runways: 5/23 is 5,000 by 150 feet (1,524 x 46 m) and 15/33 is 4,000 by 100 feet (1,219 x 30 m).[1]
For the 12-month period ending December 31, 2009, the airport had 38,582 aircraft operations, an average of 105 per day: 87% general aviation, 10% military, and 4% air taxi. At that time there were 30 aircraft based at this airport: 63% single-engine, 17% multi-engine, 10% jet, 3% helicopter, and 7% military.[1]
The Connecticut Wing Civil Air Patrol 075th Thames River Squadron (NER-CT-075) operates out of the airport.[3]
Scheduled air service
Over the years, and usually no more than one at a time, various domestic airlines served the airport, including Pan Am Clipper Connection, NewAir, Allegheny, Piedmont, and Pilgrim Airlines. Scheduled commercial passenger service was limited to small turboprop aircraft such as de Havilland Dash 8 and Beechcraft 1900, with service to Boston, New York, Philadelphia, or Washington, DC. After the 1996 expansion of T. F. Green Airport and the popularity of Southwest Airlines, the Groton airport ceased to be a profitable destination. US Airways Express, the last scheduled carrier to serve the airport, terminated its GON–PHL service in 2004. Charter services are available through the onsite fixed-based operator.
Fixed-base operators
Columbia Air Services (since 1983) and Lanmar Aviation (since 2003) have been the two fixed-base operators serving the airport. In 2012, faced with declining demand for services, the two proposed merging their Groton operations as a joint venture called Mystic Jet Center. In January 2013, the U.S Department of Justice's Antitrust Division announced that it would not interfere with the merger, citing sufficient competition from nearby airports.[4][5]
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
This article incorporates public domain material from the Air Force Historical Research Agency website http://www.afhra.af.mil/.
- 1 2 3 4 FAA Airport Master Record for GON (Form 5010 PDF). Federal Aviation Administration. Effective April 5, 2012.
- ↑ "List of NPIAS Airports" (PDF). FAA.gov. Federal Aviation Administration. 21 October 2016. Retrieved 27 November 2016.
- ↑ http://www.ct075.org/ Civil Air Patrol 075th
- ↑ http://www.justice.gov/atr/public/busreview/290869.htm
- ↑ http://www.theday.com/article/20130103/nws01/301039146/1019
External links
- Groton–New London Airport, official site
- Aerial image as of April 1991 from USGS The National Map
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective November 10, 2016
- FAA Terminal Procedures for GON, effective November 10, 2016
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KGON
- ASN accident history for GON
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS latest weather observations
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KGON
- FAA current GON delay information
.jpg)