Hydrogeology
Hydrogeology (hydro- meaning water, and -geology meaning the study of the Earth) is the area of geology that deals with the distribution and movement of groundwater in the soil and rocks of the Earth's crust (commonly in aquifers). The term geohydrology is often used interchangeably. Some make the minor distinction between a hydrologist or engineer applying themselves to geology (geohydrology), and a geologist applying themselves to hydrology (hydrogeology).
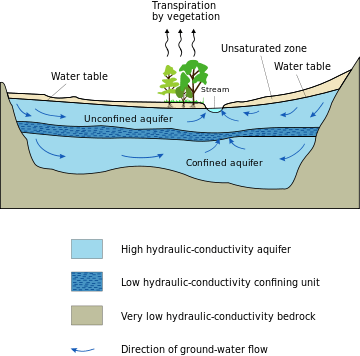
Introduction
Hydrogeology is an interdisciplinary subject; it can be difficult to account fully for the chemical, physical, biological and even legal interactions between soil, water, nature and society. The study of the interaction between groundwater movement and geology can be quite complex. Groundwater does not always flow in the subsurface down-hill following the surface topography; groundwater follows pressure gradients (flow from high pressure to low) often following fractures and conduits in circuitous paths. Taking into account the interplay of the different facets of a multi-component system often requires knowledge in several diverse fields at both the experimental and theoretical levels. The following is a more traditional introduction to the methods and nomenclature of saturated subsurface hydrology, or simply the study of ground water content.
Hydrogeology in relation to other fields

Hydrogeology, as stated above, is a branch of the earth sciences dealing with the flow of water through aquifers and other shallow porous media (typically less than 450 m or 1,500 ft below the land surface.) The very shallow flow of water in the subsurface (the upper 3 m or 10 ft) is pertinent to the fields of soil science, agriculture and civil engineering, as well as to hydrogeology. The general flow of fluids (water, hydrocarbons, geothermal fluids, etc.) in deeper formations is also a concern of geologists, geophysicists and petroleum geologists. Groundwater is a slow-moving, viscous fluid (with a Reynolds number less than unity); many of the empirically derived laws of groundwater flow can be alternately derived in fluid mechanics from the special case of Stokes flow (viscosity and pressure terms, but no inertial term).
The mathematical relationships used to describe the flow of water through porous media are the diffusion and Laplace equations, which have applications in many diverse fields. Steady groundwater flow (Laplace equation) has been simulated using electrical, elastic and heat conduction analogies. Transient groundwater flow is analogous to the diffusion of heat in a solid, therefore some solutions to hydrological problems have been adapted from heat transfer literature.
Traditionally, the movement of groundwater has been studied separately from surface water, climatology, and even the chemical and microbiological aspects of hydrogeology (the processes are uncoupled). As the field of hydrogeology matures, the strong interactions between groundwater, surface water, water chemistry, soil moisture and even climate are becoming more clear.
For example: Aquifer drawdown or overdrafting and the pumping of fossil water may be a contributing factor to sea-level rise.[1]
Definitions and material properties
One of the main tasks a hydrogeologist typically performs is the prediction of future behavior of an aquifer system, based on analysis of past and present observations. Some hypothetical, but characteristic questions asked would be:
- Can the aquifer support another subdivision?
- Will the river dry up if the farmer doubles his irrigation?
- Did the chemicals from the dry cleaning facility travel through the aquifer to my well and make me sick?
- Will the plume of effluent leaving my neighbor's septic system flow to my drinking water well?
Most of these questions can be addressed through simulation of the hydrologic system (using numerical models or analytic equations). Accurate simulation of the aquifer system requires knowledge of the aquifer properties and boundary conditions. Therefore, a common task of the hydrogeologist is determining aquifer properties using aquifer tests.
In order to further characterize aquifers and aquitards some primary and derived physical properties are introduced below. Aquifers are broadly classified as being either confined or unconfined (water table aquifers), and either saturated or unsaturated; the type of aquifer affects what properties control the flow of water in that medium (e.g., the release of water from storage for confined aquifers is related to the storativity, while it is related to the specific yield for unconfined aquifers).
Hydraulic head
Differences in hydraulic head (h) cause water to move from one place to another; water flows from locations of high h to locations of low h. Hydraulic head is composed of pressure head (ψ) and elevation head (z). The head gradient is the change in hydraulic head per length of flowpath, and appears in Darcy's law as being proportional to the discharge.
Hydraulic head is a directly measurable property that can take on any value (because of the arbitrary datum involved in the z term); ψ can be measured with a pressure transducer (this value can be negative, e.g., suction, but is positive in saturated aquifers), and z can be measured relative to a surveyed datum (typically the top of the well casing). Commonly, in wells tapping unconfined aquifers the water level in a well is used as a proxy for hydraulic head, assuming there is no vertical gradient of pressure. Often only changes in hydraulic head through time are needed, so the constant elevation head term can be left out (Δh = Δψ).
A record of hydraulic head through time at a well is a hydrograph or, the changes in hydraulic head recorded during the pumping of a well in a test are called drawdown.
Porosity
Porosity (n) is a directly measurable aquifer property; it is a fraction between 0 and 1 indicating the amount of pore space between unconsolidated soil particles or within a fractured rock. Typically, the majority of groundwater (and anything dissolved in it) moves through the porosity available to flow (sometimes called effective porosity). Permeability is an expression of the connectedness of the pores. For instance, an unfractured rock unit may have a high porosity (it has lots of holes between its constituent grains), but a low permeability (none of the pores are connected). An example of this phenomenon is pumice, which, when in its unfractured state, can make a poor aquifer.
Porosity does not directly affect the distribution of hydraulic head in an aquifer, but it has a very strong effect on the migration of dissolved contaminants, since it affects groundwater flow velocities through an inversely proportional relationship.
Water content
Water content (θ) is also a directly measurable property; it is the fraction of the total rock which is filled with liquid water. This is also a fraction between 0 and 1, but it must also be less than or equal to the total porosity.
The water content is very important in vadose zone hydrology, where the hydraulic conductivity is a strongly nonlinear function of water content; this complicates the solution of the unsaturated groundwater flow equation.
Hydraulic conductivity
Hydraulic conductivity (K) and transmissivity (T) are indirect aquifer properties (they cannot be measured directly). T is the K integrated over the vertical thickness (b) of the aquifer (T=Kb when K is constant over the entire thickness). These properties are measures of an aquifer's ability to transmit water. Intrinsic permeability (κ) is a secondary medium property which does not depend on the viscosity and density of the fluid (K and T are specific to water); it is used more in the petroleum industry.
Specific storage and specific yield
Specific storage (Ss) and its depth-integrated equivalent, storativity (S=Ssb), are indirect aquifer properties (they cannot be measured directly); they indicate the amount of groundwater released from storage due to a unit depressurization of a confined aquifer. They are fractions between 0 and 1.
Specific yield (Sy) is also a ratio between 0 and 1 (Sy ≤ porosity) and indicates the amount of water released due to drainage from lowering the water table in an unconfined aquifer. The value for specific yield is less than the value for porosity because some water will remain in the medium even after drainage due to intermolecular forces. Often the porosity or effective porosity is used as an upper bound to the specific yield. Typically Sy is orders of magnitude larger than Ss.
Contaminant transport properties
Often we are interested in how the moving groundwater will transport dissolved contaminants around (the sub-field of contaminant hydrogeology). The contaminants can be man-made (e.g., petroleum products, nitrate, Chromium or radionuclides) or naturally occurring (e.g., arsenic, salinity). Besides needing to understand where the groundwater is flowing, based on the other hydrologic properties discussed above, there are additional aquifer properties which affect how dissolved contaminants move with groundwater.
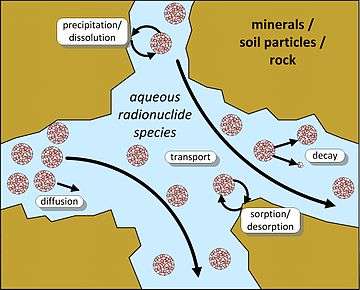
Hydrodynamic dispersion
Hydrodynamic dispersivity (αL, αT) is an empirical factor which quantifies how much contaminants stray away from the path of the groundwater which is carrying it. Some of the contaminants will be "behind" or "ahead" the mean groundwater, giving rise to a longitudinal dispersivity (αL), and some will be "to the sides of" the pure advective groundwater flow, leading to a transverse dispersivity (αT). Dispersion in groundwater arises because each water "particle", passing beyond a soil particle, must choose where to go, whether left or right or up or down, so that the water "particles" (and their solute) are gradually spread in all directions around the mean path. This is the "microscopic" mechanism, on the scale of soil particles. More important, on long distances, can be the macroscopic inhomogeneities of the aquifer, which can have regions of larger or smaller permeability, so that some water can find a preferential path in one direction, some other in a different direction, so that the contaminant can be spread in a completely irregular way, like in a (three-dimensional) delta of a river.
Dispersivity is actually a factor which represents our lack of information about the system we are simulating. There are many small details about the aquifer which are being averaged when using a macroscopic approach (e.g., tiny beds of gravel and clay in sand aquifers), they manifest themselves as an apparent dispersivity. Because of this, α is often claimed to be dependent on the length scale of the problem — the dispersivity found for transport through 1 m3 of aquifer is different from that for transport through 1 cm3 of the same aquifer material.[2]
Molecular diffusion
Diffusion is a fundamental physical phenomenon, which Einstein characterized as Brownian motion, that describes the random thermal movement of molecules and small particles in gases and liquids. It is an important phenomenon for small distances (it is essential for the achievement of thermodynamic equilibria), but, as the time necessary to cover a distance by diffusion is proportional to the square of the distance itself, it is ineffective for spreading a solute over macroscopic distances. The diffusion coefficient, D, is typically quite small, and its effect can often be considered negligible (unless groundwater flow velocities are extremely low, as they are in clay aquitards).
It is important not to confuse diffusion with dispersion, as the former is a physical phenomenon and the latter is an empirical factor which is cast into a similar form as diffusion, because we already know how to solve that problem.
Retardation by adsorption
The retardation factor is another very important feature that make the motion of the contaminant to deviate from the average groundwater motion. It is analogous to the retardation factor of chromatography. Unlike diffusion and dispersion, which simply spread the contaminant, the retardation factor changes its global average velocity, so that it can be much slower than that of water. This is due to a chemico-physical effect: the adsorption to the soil, which holds the contaminant back and does not allow it to progress until the quantity corresponding to the chemical adsorption equilibrium has been adsorbed. This effect is particularly important for less soluble contaminants, which thus can move even hundreds or thousands times slower than water. The effect of this phenomenon is that only more soluble species can cover long distances. The retardation factor depends on the chemical nature of both the contaminant and the aquifer.
Governing equations
Darcy's law
Darcy's law is a constitutive equation, empirically derived by Henry Darcy in 1856, which states that the amount of groundwater discharging through a given portion of aquifer is proportional to the cross-sectional area of flow, the hydraulic gradient, and the hydraulic conductivity.
Groundwater flow equation
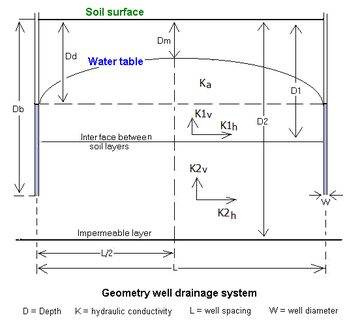
The groundwater flow equation, in its most general form, describes the movement of groundwater in a porous medium (aquifers and aquitards). It is known in mathematics as the diffusion equation, and has many analogs in other fields. Many solutions for groundwater flow problems were borrowed or adapted from existing heat transfer solutions.
It is often derived from a physical basis using Darcy's law and a conservation of mass for a small control volume. The equation is often used to predict flow to wells, which have radial symmetry, so the flow equation is commonly solved in polar or cylindrical coordinates.
The Theis equation is one of the most commonly used and fundamental solutions to the groundwater flow equation; it can be used to predict the transient evolution of head due to the effects of pumping one or a number of pumping wells.
The Thiem equation is a solution to the steady state groundwater flow equation (Laplace's Equation) for flow to a well. Unless there are large sources of water nearby (a river or lake), true steady-state is rarely achieved in reality.
Both above equations are used in aquifer tests (pump tests).
The Hooghoudt equation is a groundwater flow equation applied to subsurface drainage by pipes, tile drains or ditches.[3] An alternative subsurface drainage method is drainage by wells for which groundwater flow equations are also available.[4]
Calculation of groundwater flow
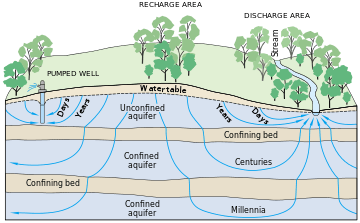
To use the groundwater flow equation to estimate the distribution of hydraulic heads, or the direction and rate of groundwater flow, this partial differential equation (PDE) must be solved. The most common means of analytically solving the diffusion equation in the hydrogeology literature are:
- Laplace, Hankel and Fourier transforms (to reduce the number of dimensions of the PDE),
- similarity transform (also called the Boltzmann transform) is commonly how the Theis solution is derived,
- separation of variables, which is more useful for non-Cartesian coordinates, and
- Green's functions, which is another common method for deriving the Theis solution — from the fundamental solution to the diffusion equation in free space.
No matter which method we use to solve the groundwater flow equation, we need both initial conditions (heads at time (t) = 0) and boundary conditions (representing either the physical boundaries of the domain, or an approximation of the domain beyond that point). Often the initial conditions are supplied to a transient simulation, by a corresponding steady-state simulation (where the time derivative in the groundwater flow equation is set equal to 0).
There are two broad categories of how the (PDE) would be solved; either analytical methods, numerical methods, or something possibly in between. Typically, analytic methods solve the groundwater flow equation under a simplified set of conditions exactly, while numerical methods solve it under more general conditions to an approximation.
Analytic methods
Analytic methods typically use the structure of mathematics to arrive at a simple, elegant solution, but the required derivation for all but the simplest domain geometries can be quite complex (involving non-standard coordinates, conformal mapping, etc.). Analytic solutions typically are also simply an equation that can give a quick answer based on a few basic parameters. The Theis equation is a very simple (yet still very useful) analytic solution to the groundwater flow equation, typically used to analyze the results of an aquifer test or slug test.
Numerical methods
The topic of numerical methods is quite large, obviously being of use to most fields of engineering and science in general. Numerical methods have been around much longer than computers have (In the 1920s Richardson developed some of the finite difference schemes still in use today, but they were calculated by hand, using paper and pencil, by human "calculators"), but they have become very important through the availability of fast and cheap personal computers. A quick survey of the main numerical methods used in hydrogeology, and some of the most basic principles are shown below and further discussed in the Groundwater model article.
There are two broad categories of numerical methods: gridded or discretized methods and non-gridded or mesh-free methods. In the common finite difference method and finite element method (FEM) the domain is completely gridded ("cut" into a grid or mesh of small elements). The analytic element method (AEM) and the boundary integral equation method (BIEM — sometimes also called BEM, or Boundary Element Method) are only discretized at boundaries or along flow elements (line sinks, area sources, etc.), the majority of the domain is mesh-free.
General properties of gridded methods
Gridded Methods like finite difference and finite element methods solve the groundwater flow equation by breaking the problem area (domain) into many small elements (squares, rectangles, triangles, blocks, tetrahedra, etc.) and solving the flow equation for each element (all material properties are assumed constant or possibly linearly variable within an element), then linking together all the elements using conservation of mass across the boundaries between the elements (similar to the divergence theorem). This results in a system which overall approximates the groundwater flow equation, but exactly matches the boundary conditions (the head or flux is specified in the elements which intersect the boundaries).
Finite differences are a way of representing continuous differential operators using discrete intervals (Δx and Δt), and the finite difference methods are based on these (they are derived from a Taylor series). For example, the first-order time derivative is often approximated using the following forward finite difference, where the subscripts indicate a discrete time location,
The forward finite difference approximation is unconditionally stable, but leads to an implicit set of equations (that must be solved using matrix methods, e.g. LU or Cholesky decomposition). The similar backwards difference is only conditionally stable, but it is explicit and can be used to "march" forward in the time direction, solving one grid node at a time (or possibly in parallel, since one node depends only on its immediate neighbors). Rather than the finite difference method, sometimes the Galerkin FEM approximation is used in space (this is different from the type of FEM often used in structural engineering) with finite differences still used in time.
Application of finite difference models
MODFLOW is a well-known example of a general finite difference groundwater flow model. It is developed by the US Geological Survey as a modular and extensible simulation tool for modeling groundwater flow. It is free software developed, documented and distributed by the USGS. Many commercial products have grown up around it, providing graphical user interfaces to its input file based interface, and typically incorporating pre- and post-processing of user data. Many other models have been developed to work with MODFLOW input and output, making linked models which simulate several hydrologic processes possible (flow and transport models, surface water and groundwater models and chemical reaction models), because of the simple, well documented nature of MODFLOW.
Application of finite element models
Finite Element programs are more flexible in design (triangular elements vs. the block elements most finite difference models use) and there are some programs available (SUTRA, a 2D or 3D density-dependent flow model by the USGS; Hydrus, a commercial unsaturated flow model; FEFLOW, a commercial modelling environment for subsurface flow, solute and heat transport processes; OpenGeoSys, a scientific open-source project for thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) processes in porous and fractured media;[5][6] COMSOL Multiphysics (FEMLAB) a commercial general modelling environment), FEATool Multiphysics,[7] an easy to use Matlab simulation toolbox, and Integrated Water Flow Model (IWFM), but they are still not as popular in with practicing hydrogeologists as MODFLOW is. Finite element models are more popular in university and laboratory environments, where specialized models solve non-standard forms of the flow equation (unsaturated flow, density dependent flow, coupled heat and groundwater flow, etc.)
Application of finite volume models
The finite volume method is a method for representing and evaluating partial differential equations as algebraic equations.[8][9] Similar to the finite difference method, values are calculated at discrete places on a meshed geometry. "Finite volume" refers to the small volume surrounding each node point on a mesh. In the finite volume method, volume integrals in a partial differential equation that contain a divergence term are converted to surface integrals, using the divergence theorem. These terms are then evaluated as fluxes at the surfaces of each finite volume. Because the flux entering a given volume is identical to that leaving the adjacent volume, these methods are conservative. Another advantage of the finite volume method is that it is easily formulated to allow for unstructured meshes. The method is used in many computational fluid dynamics packages.
PORFLOW software package is a comprehensive mathematical model for simulation of Ground Water Flow and Nuclear Waste Management developed by Analytic & Computational Research, Inc., ACRi.
The FEHM software package is available free from Los Alamos National Laboratory. This versatile porous flow simulator includes capabilities to model multiphase, thermal, stress, and multicomponent reactive chemistry. Current work using this code includes simulation of methane hydrate formation, CO2 sequestration, oil shale extraction, migration of both nuclear and chemical contaminants, environmental isotope migration in the unsaturated zone, and karst formation.
Other methods
These include mesh-free methods like the Analytic Element Method (AEM) and the Boundary Element Method (BEM), which are closer to analytic solutions, but they do approximate the groundwater flow equation in some way. The BEM and AEM exactly solve the groundwater flow equation (perfect mass balance), while approximating the boundary conditions. These methods are more exact and can be much more elegant solutions (like analytic methods are), but have not seen as widespread use outside academic and research groups yet.
See also
- Environmental engineering is a broad category hydrogeology fits into;
- Flownet is an analysis tool for steady-state flow;
- Groundwater energy balance : groundwater flow equations based on the energy balance;
- Hydrogeophysics : field integrating hydrogeology with geophysics
- Hydrology (agriculture)
- Isotope hydrology is often used to understand sources and travel times in groundwater systems;
- List of important publications in geology#Hydrogeology : important publications;
- Oscar Edward Meinzer is considered the "father of modern groundwater hydrology";
- SahysMod is a spatial agro-hydro-salinity model with groundwater flow in a polygonal network;
- Spring (hydrology) and water supply network are subjects the hydrogeologist is concerned about;
- Water cycle, hydrosphere and water resources are larger concepts which hydrogeology is a part of;
References
- ↑ "Rising sea levels attributed to global groundwater extraction". University of Utrecht. Retrieved February 8, 2011.
- ↑ http://www.cof.orst.edu/cof/fe/watershd/fe537/labs_2007/gelhar_etal_reviewfieldScaleDispersion_WRR1992.pdf
- ↑ The energy balance of groundwater flow applied to subsurface drainage in anisotropic soils by pipes or ditches with entrance resistance. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. On line : . Paper based on: R.J. Oosterbaan, J. Boonstra and K.V.G.K. Rao, 1996, “The energy balance of groundwater flow”. Published in V.P.Singh and B.Kumar (eds.), Subsurface-Water Hydrology, p. 153-160, Vol.2 of Proceedings of the International Conference on Hydrology and Water Resources, New Delhi, India, 1993. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands. ISBN 978-0-7923-3651-8 . On line : . The corresponding free computer program EnDrain can be downloaded from web page : , or from :
- ↑ ILRI, 2000, Subsurface drainage by (tube)wells: Well spacing equations for fully and partially penetrating wells in uniform or layered aquifers with or without anisotropy and entrance resistance, 9 pp. Principles used in the "WellDrain" model. International Institute for Land Reclamation and Improvement (ILRI), Wageningen, The Netherlands. On line: . Free download "WellDrain" software from web page : , or from :
- ↑ "OpenGeoSys". Helmholtz centre for environmental research. Retrieved 18 May 2012.
- ↑ "OpenGeoSys Website". Helmholtz centre for environmental research. Retrieved 28 April 2014.
- ↑ FEATool Multiphysics homepage
- ↑ LeVeque, 2002
- ↑ Toro, 1999
Further reading
General hydrogeology
- Domenico, P.A. & Schwartz, W., 1998. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology Second Edition, Wiley. — Good book for consultants, it has many real-world examples and covers additional topics (e.g. heat flow, multi-phase and unsaturated flow). ISBN 0-471-59762-7
- Driscoll, Fletcher, 1986. Groundwater and Wells, US Filter / Johnson Screens. — Practical book illustrating the actual process of drilling, developing and utilizing water wells, but it is a trade book, so some of the material is slanted towards the products made by Johnson Well Screens. ISBN 0-9616456-0-1
- Freeze, R.A. & Cherry, J.A., 1979. Groundwater, Prentice-Hall. — A classic text; like an older version of Domenico and Schwartz. ISBN 0-13-365312-9
- de Marsily, G., 1986. Quantitative Hydrogeology: Groundwater Hydrology for Engineers, Academic Press, Inc., Orlando Florida. — Classic book intended for engineers with mathematical background but it can be read by hydrologists and geologists as well. ISBN 0-12-208916-2
- LaMoreaux, Philip E.; Tanner, Judy T, eds. (2001), Springs and bottled water of the world: Ancient history, source, occurrence, quality and use, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 3-540-61841-4, retrieved 13 July 2010 Good, accessible overview of hydrogeological processes.
- Porges, Robert E. & Hammer, Matthew J., 2001. The Compendium of Hydrogeology, National Ground Water Association, ISBN 1-56034-100-9. Written by practicing hydrogeologists, this inclusive handbook provides a concise, easy-to-use reference for hydrologic terms, equations, pertinent physical parameters, and acronyms
- Todd, David Keith, 1980. Groundwater Hydrology Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons. — Case studies and real-world problems with examples. ISBN 0-471-87616-X
- Fetter, C.W. Contaminant Hydrogeology Second Edition, Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-751215-5
- Fetter, C.W. Applied Hydrogeology Fourth Edition, Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-088239-9
Numerical groundwater modeling
- Anderson, Mary P. & Woessner, William W., 1992 Applied Groundwater Modeling, Academic Press. — An introduction to groundwater modeling, a little bit old, but the methods are still very applicable. ISBN 0-12-059485-4
- Anderson, Mary P., Woessner, William W., & Hunt, Randall J., 2015, Applied Groundwater Modeling, 2nd Edition, Academic Press. — Updates the 1st edition with new examples, new material with respect to model calibration and uncertainty, and online Python scripts (https://github.com/Applied-Groundwater-Modeling-2nd-Ed). ISBN 978-0-12-058103-0
- Chiang, W.-H., Kinzelbach, W., Rausch, R. (1998): Aquifer Simulation Model for WINdows – Groundwater flow and transport modeling, an integrated program. - 137 p., 115 fig., 2 tab., 1 CD-ROM; Berlin, Stuttgart (Borntraeger). ISBN 3-443-01039-3
- Elango, L and Jayakumar, R (Eds.)(2001) Modelling in Hydrogeology, UNESCO-IHP Publication, Allied Publ., Chennai, ISBN 81-7764-218-9
- Rausch, R., Schäfer W., Therrien, R., Wagner, C., 2005 Solute Transport Modelling – An Introduction to Models and Solution Strategies. - 205 p., 66 fig., 11 tab.; Berlin, Stuttgart (Borntraeger). ISBN 3-443-01055-5
- Rushton, K.R., 2003, Groundwater Hydrology: Conceptual and Computational Models. John Wiley and Sons Ltd. ISBN 0-470-85004-3
- Wang H. F., Theory of Linear Poroelasticity with Applications to Geomechanics and Hydrogeology, Princeton Press, (2000).
- Waltham T., Foundations of Engineering Geology, 2nd Edition, Taylor & Francis, (2001).
- Zheng, C., and Bennett, G.D., 2002, Applied Contaminant Transport Modeling Second Edition, John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-38477-1
Analytic groundwater modeling
- Haitjema, Henk M., 1995. Analytic Element Modeling of Groundwater Flow, Academic Press. — An introduction to analytic solution methods, especially the Analytic element method (AEM). ISBN 0-12-316550-4
- Harr, Milton E., 1962. Groundwater and seepage, Dover. — a more civil engineering view on groundwater; includes a great deal on flownets. ISBN 0-486-66881-9
- Kovacs, Gyorgy, 1981. Seepage Hydaulics, Developments in Water Science; 10. Elsevier. - Conformal mapping well explained. ISBN 0-444-99755-5, ISBN 0-444-99755-5 (series)
- Lee, Tien-Chang, 1999. Applied Mathematics in Hydrogeology, CRC Press. — Great explanation of mathematical methods used in deriving solutions to hydrogeology problems (solute transport, finite element and inverse problems too). ISBN 1-56670-375-1
- Liggett, James A. & Liu, Phillip .L-F., 1983. The Boundary Integral Equation Method for Porous Media Flow, George Allen and Unwin, London. — Book on BIEM (sometimes called BEM) with examples, it makes a good introduction to the method. ISBN 0-04-620011-8
External links
- International Association of Hydrogeologists — worldwide association for groundwater specialists.
- UK Groundwater Forum — Groundwater in the UK
- Centre for Groundwater Studies — Groundwater Education and Research.
- EPA drinking water standards — the maximum contaminant levels (mcl) for dissolved species in US drinking water.
- US Geological Survey water resources homepage — a good place to find free data (for both US surface water and groundwater) and free groundwater modeling software like MODFLOW.
- US Geological Survey TWRI index — a series of instructional manuals covering common procedures in hydrogeology. They are freely available online as PDF files.
- International Ground Water Modeling Center (IGWMC) — an educational repository of groundwater modeling software which offers support for most software, some of which is free.
- The Hydrogeologist Time Capsule — a video collection of interviews of eminent hydrogeologists who have made a material difference to the profession.
- IGRAC International Groundwater Resources Assessment Centre
- US Army Geospatial Center — For information on OCONUS surface water and groundwater.