Leukotriene B4
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
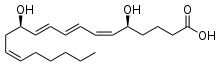
| IUPAC name
(5S,6Z,8E,10E,12R,14Z)-5,12-Dihydroxy-6,8,10,14-icosatetraenoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| 71160-24-2 | |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:15647 |
| ChEMBL | ChEMBL65061 |
| ChemSpider | 4444132 |
| 2487 | |
| KEGG | C02165 |
| PubChem | 5280492 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C20H32O4 | |
| Molar mass | 336.466 |
| Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| | |
| Infobox references | |
Leukotriene B4 is a leukotriene involved in inflammation. It is produced from leukocytes in response to inflammatory mediators and is able to induce the adhesion and activation of leukocytes on the endothelium, allowing them to bind to and cross it into the tissue.[1] In neutrophils, it is also a potent chemoattractant, and is able to induce the formation of reactive oxygen species and the release of lysosomal enzymes by these cells.[1] It is synthesized by leukotriene-A4 hydrolase from leukotriene A4.[2]

Eicosanoid synthesis. (Leukotrienes at right.)
References
- 1 2 Cotran; Kumar, Collins. Robbins Pathologic Basis of Disease. Philadelphia: W.B Saunders Company. ISBN 0-7216-7335-X.
- ↑ http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09960. Retrieved 9 April 2013. Missing or empty
|title=(help)
This article is issued from Wikipedia - version of the 3/18/2016. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike but additional terms may apply for the media files.