Malta Convoys
| Malta Convoys | |
|---|---|
| Part of The Battle of the Mediterranean | |
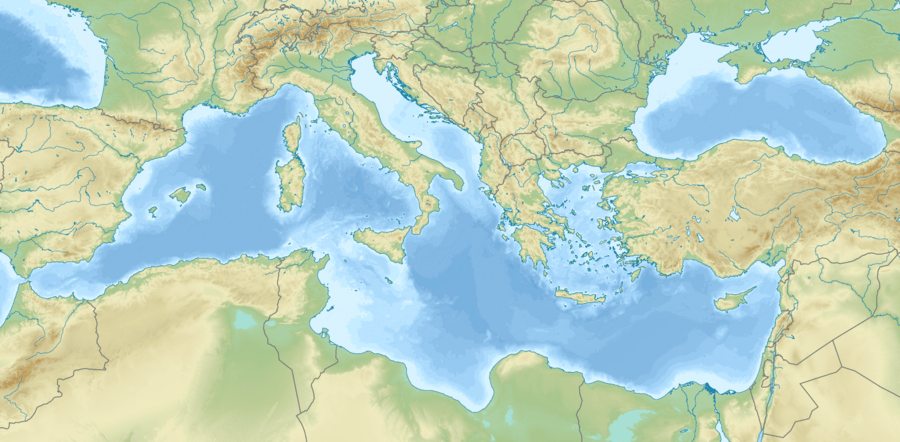 Relief map of the Mediterranean Sea | |
| Operational scope | Supply operations |
| Planned by | Mediterranean Fleet RAF Middle East (RAF Middle East Command from 29 December 1941) Merchant Navy Allies |
| Commanded by | Admiral Sir Andrew Cunningham, 1 June 1939 – March 1942 Admiral Sir Henry Harwood, 22 April 1942 – February 1943 |
| Objective | Break Axis siege of Malta |
| Date | 27 June 1940 – 31 December 1943 |
| Outcome | British victory |
| Casualties | 1,600 civilians on Malta 5,700 service personnel on land, sea and in the air Aircraft: 707 Merchant ships: 31 sunk Navy: 1 battleship, 2 aircraft carriers 4 cruisers, 1 minelayer 20 destroyers/minesweepers 40 submarines unknown number of smaller vessels |
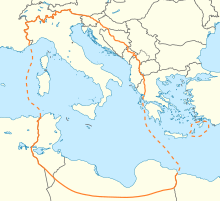
The Malta Convoys were Allied supply convoys of the Second World War. The convoys took place during the Siege of Malta in the Mediterranean Theatre. Malta required supplies for the civilian population and military reinforcements, food and fuel for the air and naval forces based on the island. The convoys were escorted by ships of the Mediterranean Fleet, Fleet Air Arm and Royal Air Force and attacked by the Italian Regia Aeronautica (Royal Air Force) and Regia Marina (Royal Navy) and from 1941 by the German Luftwaffe (Air Force) and Kriegsmarine (Navy) during the Battle of the Mediterranean.
Malta was a base from which British sea and air forces could attack the ships carrying supplies from Italy to Italian Libya for Italian civilian colonists and the Axis armies in North Africa, which fought in the Western Desert Campaign (1940–1943) against the British Eighth Army for control of the south shore of the Mediterranean. The desert war was fought in Libya, Egypt, the Suez Canal and British controlled oilfields in the Middle East. The strategic value of Malta was so great that the British risked many merchant vessels and warships to maintain the island and the Axis made determined efforts to starve out the population.[1][2] The destruction of the Italian 10th Army in Egypt and Libya during Operation Compass (9 December 1940 – 9 February 1941) and defeat in the Italo-Greek War (28 October 1940 – 23 April 1941) led to German intervention in the Mediterranean. German bombers and submarines joined the blockade to neutralise and then invade Malta.
The British assembled large flotillas to escort convoys and sent fast warships, to make solo runs to the island and Magic Carpet trips by submarine. Hawker Hurricane and then Supermarine Spitfire fighters were carried by aircraft carriers on Club Runs from Gibraltar into range of Malta, then flown off to Malta to replace losses and supply reinforcements.[3] In mid-1942, air attacks on the island and on supply convoys neutralised Malta as an offensive base and Unternehmen Herkules (Operation Hercules), the culmination of Italian and German invasion plans was set for mid-July 1942. After the Axis victory in the Battle of Gazala (26 May – 21 June 1942), the capture of Tobruk and pursuit into Egypt, Hercules was postponed and then cancelled in November. The siege eased late in 1942, after Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October–11 November) and Operation Torch (8–16 November), captured territory and landing grounds in Libya and Algeria, bringing more land-based Allied aircraft into range for air cover of the Malta convoys.
Background
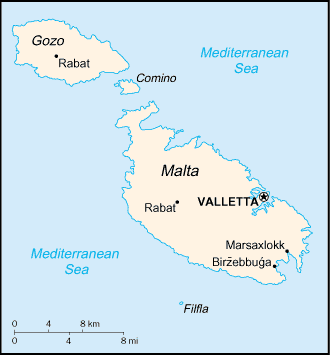
Malta, an island of 122 square miles (320 km2), had a population of 275,000. In the 1940s, Maltese agriculture could feed only one-third of its population. The proximity of Malta to the Sicilian Channel between Sicily and Tunis, was a threat to the sea route of Italy to Libya and a staging-post on the British Suez canal sea route to India, East Africa, the oilfields of Iraq and Iran, India and the Far East.[4][lower-alpha 1]
Malta had been a British colony since 1814. When Italy declared war on the Allies on 10 June 1940, the "Taranto Naval Squadron" did not sail to occupy Malta as suggested by Admiral Carlo Bergamini[4][5] With Italian bases in nearby Sicily, maintenance of British control was more difficult from more distant British bases in Gibraltar to the west and Cyprus, Egypt and Palestine to the east. Only two weeks after the Italian declaration of war, the Second Armistice at Compiègne ended British access to French Mediterranean Sea bases. The attack on Mers-el-Kébir (3 July 1940) hardened French antipathy towards Britain. Axis support of General Francisco Franco in the Spanish Civil War caused concern about security of British Gibraltar.
Italy, Sicily, Sardinia and Libya dominated the central Mediterranean and Italian conquest of Egypt would link Abyssinia, Italian Somaliland and Eritrea. The September 1940 Italian invasion of Egypt resulted in loss of Cyrenaica during Operation Compass in December. In January 1941 Germany sent the Afrika Korps to Libya in Unternehmen Sonnenblume, (Operation Sunflower) and the Fliegerkorps X of the Luftwaffe to Sicily in Unternehmen Mittelmeer (Operation Mediterranean) to protect Afrika Korps supply lines past Malta.[6]
Fliegerkorps X moved to Greece in April 1941 and the 23rd U-boat Flotilla was based at Salamis in September.[7] Resources available to sustain Malta were reduced when Japan declared war in December and raided the Indian Ocean in April, 1942.[8] Malta ceased to be an effective anti-convoy base in early 1942. Several warships were sunk in harbour and others were withdrawn. Supplies dwindled with the loss of convoys. An Axis invasion of Malta was planned as (Operation C3 and Unternehmen Herkules (Operation Herkules) but cancelled on 16 June.[9][10]
1940
July
In the Battle of Calabria (Battaglia di Punta Stilo), Regia Marina escorts (two battleships, 14 cruisers and 32 destroyers) of an Italian convoy engage battleships HMS Warspite, Malaya and Royal Sovereign and the aircraft carrier HMS Eagle.[11] Cruisers and destroyers covered convoys MF 1 (ME 1) with El Nil, Knight of Malta and Rodi and MS 1 (ME 1) with Kirkland, Masirah, Novasli, Tweed and Zeeland, from Malta to Alexandria.[11]
August, Operation Hurry
Twelve Hurricanes were flown off the carrier HMS Argus to Malta in the first Club Run to reinforce the air defences. Club Runs would continue until it was possible to fly the aircraft directly from Gibraltar.[12]
September, Operation Hats
The Mediterranean Fleet escorted fast convoy MF 2 of three transports (carrying 40,000 short tons (36,000 t) of supplies including reinforcements and ammunition for the island's anti-aircraft defences) from Alexandria and collected another convoy from Gibraltar.[13] En route, Italian airbases were raided. The Regia Marina had superior forces at sea but missed the opportunity to exploit their advantage.[14]
October, Operation MB 6
Four ships of convoy MF 3 reached Malta safely from Alexandria and 3 ships returned to Alexandria as convoy MF 4.[13] The convoys were part of Operation MB 6 and the escort included four battleships and two aircraft carriers. An Italian attempt against the returning escort employing destroyers and torpedo boats ended in the Battle of Cape Passero, a British success.[15]
November, Operations Collar, White and Judgement

Five ship convoy MW 3 from Alexandria and four ship return convoy ME 3 arrived safely, coinciding with a troop convoy from Gibraltar and the air attack on the Italian battlefleet at the Battle of Taranto (Operation Judgement).[13][16]
In Operation White, twelve Hurricanes were flown off Argus to reinforce Malta but the threat of the Italian fleet lurking south of Sardinia prompted a premature fly-off from Argus and its return to Gibraltar. Eight Hurricanes ran out of fuel and ditched at sea, with seven pilots lost.[17]
The cruisers HMS Manchester and HMS Southampton sailing with 1,400 soldiers and RAF personnel from Gibraltar to Malta and Alexandria and survived attack by the Italian fleet at the Battle of Cape Spartivento.[18] The combined Operation MB 9 began with four ship convoy MW 4 from Alexandria with Memnon, Clan Macaulay, Clan Ferguson and HMS Breconshire. The unloaded Waiwera, Devis, Volo and Rodi from convoy MW 3 and SS Cornwall sailed in the return convoy ME 4.[13][19]
December
Convoy MW 5A with Lanarkshire and Waiwera carrying supplies and munitions and convoy MW 5B of Volo, Rodi and Devis, the tanker Pontfield, Hoegh Hood and ulster Prince from Alexandria and convoy ME 5 with the empty Breconshire, Memnon, Clan Macaulay and Clan Ferguson arrived safely at Alexandria.[20] Convoy MG 1 with Clan Forbes and Clan Fraser reached Gibraltar from Malta.[13][21]
1941
January, Operation Excess

Operation Excess delivered one ship from Gibraltar to Malta with three ships continuing on to Piraeus. The operation was coordinated with Operation MC 4, consisting of convoy MW 5 1⁄2 of Breconshire and Clan Macaulay from Alexandria to Malta and convoy ME 6, a return journey of ME 5 1⁄2 with Lanarkshire and Waiwera and ME 6 with Volo, Rodi, Pontfield, Devis, Hoegh Hood, Trocas and RFA Plumleaf. The convoys arrived safely with 10,000 short tons (9,100 t) of supplies but the Royal Navy lost the cruiser (HMS Southampton), with cruiser HMS Gloucester, aircraft carrier HMS Illustrious badly damaged and a destroyer damaged beyond repair.[22][lower-alpha 2] This was the first action to involve the Luftwaffe. The Italian torpedo boat Vega was sunk in the course of the operations.[24]
February
Operation MC 8 from 19–21 February, ran troops, vehicles and stores to Malta in the cruisers Orion, Ajax and Gloucester and the Tribal-class destroyers Nubian and Mohawk, covered by Barham, Valiant, Eagle, Coventry, Decoy, Hotspur, Havock, Hereward, Hero, Hasty, Ilex, Jervis, Janus and Jaguar. The return journey to Alexandria with the unloaded Breconshire and Clan Macaulay by 23 February was uneventful.[25]
March
Operation MC 9 covered convoy MW 6 consisting of Perthshire, Clan Ferguson, City of Manchester and City of Lincoln, which sailed from Alexandria on 19 March and arrived at Malta, returning by 26 March.[26]
April, Operation Temple
In Operation Dunlop, HMS Ark Royal sailed from Gibraltar on 24 April and flew off 24 Hurricanes at dawn on 27 April. Bristol Blenheims and Beaufighters were also flown in. Three battleships and an aircraft carrier covered the fast transport HMS Breconshire from Alexandria to Malta. The operation was coordinated with four ship convoy ME 7 from Malta to Alexandria.[27]
An Afrika Korps convoy of the German ships Aegina, Arta, Adana and Iserlhon with 3,000 troop reinforcements on board, the Italian Sabaudia loaded with ammunition and three Italian destroyer escorts was annihilated by the destroyers Jervis, Janus, Nubian and Mohawk, in the Battle of the Tarigo Convoy near the Kerkennah Islands off Tunisia, demonstrating the value of Malta as an offensive base.[28][29]
During Operation Temple, the freighter Parracombe sailed for Malta from Gibraltar on the night of 28/29 April, disguised as a Spanish merchantman and later the Vichy steamer Oued-Kroum and was lost on 2 May after striking a mine, which blew off the forepart of the ship. The ship sank with 21 Hurricanes, equipment, ammunition and military freight. but another ship reached Alexandria from Malta as convoy MD 3.[30]
May, Operations Tiger and Splice
Operation Tiger, a five ship supply convoy from Gibraltar to Alexandria coincided with reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet, six ship convoy MW 7 from Egypt to Malta and 48 more Hurricanes flown off HMS Ark Royal and Furious in Operation Splice. The only loss was the 9,200-gross register ton (GRT) cargo ship Empire Song, which hit a mine and sank with a cargo of 57 tanks, ten aircraft and several trucks. Tiger carried tanks Matilda and the new Crusader Tank for the Western Desert Campaign in North Africa. These had been intended to be sent around the Cape but were diverted via the Mediterranean and over 200 tanks reached Alexandria on 12 May. The Luftwaffe transferred much of its strength from Sicily to prepare for the Operation Barbarossa, the invasion of the USSR, relieving some of the pressure on Malta. The Malta-based submarine HMS Upholder attacked and sank the large Italian troop transport Conte Rosso.[31]
June, Operation Tracer
Supply convoys became very difficult, with convoys from Alexandria under attack from Luftwaffe and Regia Aeronautica bases in Crete and Libya, while convoys from Gibraltar were attacked from Sardinia and Sicily. Submarines were used to bring in urgent supplies. On 14 June, HMS Ark Royal and the new carrier HMS Victorious, coming east from Gibraltar, flew off 46 Hurricanes to Malta, 42 of which arrived safely.[32]
July, Operation Substance
Six ship convoy GM 1 ran from Gibraltar to Malta, escorted by six destroyers and covered by Ark Royal, Renown, Nelson, cruisers and destroyers (Operation Substance). On 23 July, south of Sardinia, there were sustained Italian air attacks. One cruiser was hit and a destroyer sunk. The 12,000 GRT steamer Sydney Star was torpedoed by an Italian MAS boat and crippled but the Australian destroyer HMAS Nestor assisted her safe arrival to harbour and she was seaworthy again by September. All six ships eventually reached Malta and seven ships returned to Gibraltar as convoy MG 1. An Italian raid to sink the transports in Grand Harbour failed and 65,000 short tons (59,000 t) of supplies were landed.[33]
September
Operations Status I and II, Propeller and Halberd

Ark Royal and Furious flew off over 50 Hurricanes to Malta in operations Status I and Status II. Empire Guillemot reached Malta from Gibraltar as Operation Propeller and another ship completed the trip independently.[34] The 19,000 GRT Italian transports MS Neptunia and Oceania were sunk by the submarine Upholder.[35] Nine ship convoy GM 2 from Gibraltar to Malta and the one ship return convoy MG 2 were escorted by Nelson, Rodney, Prince of Wales and Ark Royal as Operation Halberd. Italians ships attempted intercept but the British capital ships returned to Gibraltar, with Nelson damaged by a torpedo. The 10,000 GRT transport Imperial Star was sunk by an aerial torpedo but the rest of the convoy reached Malta and landed 85,000 short tons (77,000 t) of supplies.[36]
October
Force K was formed at Malta to strike at Axis shipping. It consisted of the cruisers HMS Aurora and Penelope and the destroyers HMS Lance and Lively. One of four ships sailing independently from Malta to Gibraltar was lost.[37]
November
Force K intercepted an Italian convoy off Cape Spartivento and sank all seven transports and two Italian destroyers.[38] More Hurricanes were flown off from Ark Royal and Argus, sailing from Gibraltar (Operation Perpetual, 10–12 November 1941). On the return leg, U-81 torpedoed Ark Royal, which sank the next day.[39] An attempt to supply Malta (Operation Astrologer, 14–15 November 1941) by two unescorted freighters, Empire Defender and Empire Pelican, ended with Italian Savoia-Marchetti SM.79 torpedo-bombers sinking both ships south of Galite Islands.[40]
December, First Battle of Sirte
An Italian battlefleet covered a convoy bound for Benghazi. A flotilla from Alexandria planned to link with Force K from Malta but the submarine HMS Urge torpedoed and damaged Vittorio Veneto and the Italians retired.[41]
MV Breconshire was escorted from Malta by Force B to rendezvous with Force K near the Gulf of Sirte. Soon after, the British came across Italian battleships escorting a convoy to Tripoli. The ensuing engagement is known as the First Battle of Sirte.[42]
After seeing Breconshire safely into Malta, Force K sailed again to search for the Tripoli convoy. While off Tripoli, they ran into a minefield. HMS Neptune and Kandahar were sunk, Aurora and Penelope being damaged.[43]
Four-ship convoy ME 8 reached Alexandria safely from Malta.[44]
1942
January
Six ships sailed from Alexandria in Operation MF3. Aircraft sank 6,655-ton Thermopylae in convoy MW8A and the remaining five arrived at Malta. Three ships made the return trip safely. The destroyer, HMS Gurkha was torpedoed by German submarine U-133 and sank.[45]
In Operation T18 an Italian battleship convoy with five merchantmen sailed for Tripoli North Africa, losing Victoria to a torpedo attack by Swordfish of 830 Squadron FAA. At the end of the month the submarines Ultimatim and Upholder sank two more Italian transport ships.[46]
February
During German air raids on Malta, HMS Maori was sunk in Grand Harbour.[47]
Three ship convoy MW 9 from Alexandria (Operation MF5) failed to reach Malta. SS Clan Chattan was sunk by Axis aircraft, SS Clan Campbell was bombed and forced to seek shelter in Tobruk and SS Rowallan Castle was disabled. Rowallan Castle was scuttled by Lively after the escort was warned that the Italian battleship Caio Duilio had sailed from Taranto to intercept the convoy.[48]
March
Operations Spotter, Picket and MG 1
| Type | No. | Sunk | Dgd | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cruisers | 4 | – | 3 | |||
| AA Ships | 1 | – | – | |||
| Destroyers | 18 | 3 | 2 | |||
| Submarines | 5 | 1 | – | |||
| Freighters | 4 | 1 | – | |||
| Freighters arriving | 3 | sunk in dock |
||||
On 6 March, Operation Spotter, a club run by the aircraft carriers Eagle and Argus flew off the first 15 Spitfire reinforcements for Malta. An earlier attempt had been abandoned but the right external ferry tanks were fitted; seven Blenheims flew direct from Gibraltar. On 10 March the Spitfires flew their first sorties against a raid by Ju 88s escorted by Bf 109 fighters.[50]
Operation MG 1 began with convoy MW 10 of four ships sailing from Alexandria at 7:10 a.m. on 20 March, each with a navy liaison party and Defensively equipped merchant ship (DEMS) gunners, supplemented by service passengers. The convoy was escorted by Force B, the cruisers HMS Cleopatra, Dido, Euryalus, the anti-aircraft cruiser Carlisle and the 22nd Destroyer Flotilla. The 5th Destroyer Flotilla sailed from Tobruk, sweeping for submarines before joining the convoy on 21 March. Clan Campbell struggled to keep up because of engine-trouble and the convoy timetable was not met. Several British submarines participated near Messina and Taranto to watch for Italian ships. Long Range Desert Group parties were to attack the airfields at Martuba and Tmimi in Cyrenaica as RAF and FAA aircraft bombed them, to ground Ju 88 bombers and 201 Group RAF provided air cover and reconnaissance of the convoy route. A club run, Operation Picket with Argus, Eagle and Force H was used as a decoy but the Spitfire ferry tanks were found to be defective and the run was called off.[51]
On 22 March, when MW 10 was through Bomb Alley, news arrived that an Italian squadron had sailed and from 10:35 a.m. – 12:05 p.m. five Italian torpedo-bomber attacks were made with no hits. In the afternoon, German and Italian attacks began, which combined bombing and torpedo launching, again with no effect. Smoke was seen at 2:10 p.m. and the escorts moved to intercept in rough seas as the convoy was hidden by a smoke screen. Italian cruisers opened fire then turned to lure the British cruisers towards Littorio but they turned back towards the convoy. The exchange was the beginning of the Second Battle of Sirte and Axis aircraft concentrated on the convoy which manoeuvred so effectively that no ship was hit but the ships and close escort fired much of their ammunition. During the battle near the convoy, the escorts kept laying smoke screens and the Italians came within 8 nmi (9.2 mi; 15 km) of the convoy as Force B dodged around in the smoke, attacking at every opportunity.[52]
German air attacks continued and Force B turned for Alexandria, very short of fuel as Force K joined the convoy for the last leg. The convoy had been ordered to disperse, three ships diverting southwards and Clan Campbell making straight for Grand Harbour, the diversions being calculated to bring the ships back together just short of Malta by daylight on 23 March. The detours were a mistake and Pampas was hit by a bomb during the morning but kept going, reaching Malta. Talabot was also frequently attacked but arrived undamaged, except from some small bombs dropped by a Bf 109 fighter-bomber. Clan Campbell was sunk 20 nmi (23 mi; 37 km) from Malta and Breconshire arrived on 25 March after several tows from destroyers and tugs reached Marsaxlokk harbour. Unloading of the ships was very slow and Luftwaffe attacks on 26 March sank Breconshire in the evening and continued bombing Valetta harbour into the night. Talabot and Pampas were set on fire before unloading, only 4,952 short tons (4,492 t) of the 29,500 short tons (26,800 t) of supplies were landed and several destroyers were seriously damaged.[53]
April, Operation Calendar
The island had ceased to be an effective offensive base and Axis convoys were mostly untroubled. Several submarines and destroyers were bombed and sunk in harbour and naval units were ordered to leave for Gibraltar or Alexandria. Not all arrived safely. Forty-seven Spitfires were flown off to Malta from the American carrier USS Wasp (Operation Calendar), escorted by the battlecruiser Renown, cruisers HMS Cairo and Charybdis and six British and US destroyers. Most of the aircraft were destroyed on the ground by bombing.[54]
May, Operations Bowery and LB
The submarine HMS Olympus struck a mine and sank while leaving Malta with the survivors of submarines HMS Pandora, P36 and P39 on board. In Operation Bowery, 64 Spitfires were flown off to Malta from Wasp and Eagle and a second batch of 16 fighters were flown in from Eagle in Operation LB.[55]
June, Operation Style
On 20 May, SS Empire Conrad departed from Milford Haven, Wales with a cargo of 32 Spitfires in cases. The aircraft were all Spitfire Mk VcT. Also on board were the ground crew who were to assemble them, a total of over 110 men. Empire Conrad was escorted by the 29th ML Flotilla and the corvette HMS Spirea. The convoy was later joined by the Minesweepers HMS Hythe and Rye. Empire Conrad arrived at Gibraltar on 27 May. The aircraft were transferred to the aircraft carrier HMS Eagle where they were assembled. On 2 June, Eagle departed from Gibraltar escorted by the cruiser Charybdis and destroyers HMS Antelope, Ithuriel, Partridge, Westcott and Wishart. On 3 June, the aircraft were flown off Eagle, bound for Malta. Twenty-eight arrived safely, with the other four being shot down en route.[56]
June
Operation Julius (Harpoon and Vigorous)

The arrival of more Spitfires from Eagle and the transfer of German aircraft to the Russian Front eased the pressure on Malta but supplies were needed. Operation Julius was planned to send two convoys sailed simultaneously from both ends of the Mediterranean.[57] A convoy of 11 transports from Haifa, Palestine and Port Said, Egypt (Operation Vigorous) and one of six transports from Gibraltar (Operation Harpoon). Both had strong naval escorts. Strong Axis naval and air forces attacked both convoys. Two ships from Harpoon with 15,000 short tons (14,000 t) of supplies reached Malta for the loss of four transports and two destroyers (HMS Bedouin and the Polish Kujawiak).[lower-alpha 3] Vigorous was attacked by aircraft, torpedo boats and submarines over four days, threatened by a strong Italian battlefleet and eventually returned to Alexandria. No transports reached Malta and a cruiser (HMS Hermione), three destroyers (HMS Hasty, Airedale and the Australian Nestor) and two transports were sunk. The battleship Littorio and cruiser Trento were damaged by air attacks and Trento was later sunk by the submarine HMS Umbra.[58]
July
More Spitfires were flown off to Malta from Eagle. HMS Welshman made an independent supply run.[59]
August, Operation Pedestal
The supply situation had become critical, particularly aviation fuel. The largest convoy to date was assembled at Gibraltar (Operation Pedestal). It consisted of 14 transports, including the large oil tanker SS Ohio. These were protected by powerful escort and covering forces: 44 warships, including three aircraft carriers (Eagle, Indomitable and Victorious) and two battleships (Nelson and Rodney). A diversionary operation was staged from Alexandria. The convoy was attacked fiercely. Three transports reached Malta on 13 August and another on 14 August. Ohio arrived on 15 August, heavily damaged by air attacks and under tow by destroyers HMS Penn and Ledbury. The rest were sunk. Ohio later broke in two in Valletta Harbour but not before much of her cargo had been unloaded. The aircraft carrier Eagle, cruisers Cairo and Manchester and the destroyer HMS Foresight were sunk and there was serious damage to other warships. The Italian losses were two submarines and damage to two cruisers.[60]
This convoy, especially the arrival of Ohio, was seen as Divine intervention by the people of Malta. August 15 is celebrated as the feast of St. Mary's Assumption and many Maltese attributed the arrival of Ohio into Grand Harbour as the answer to their prayers.[61] It had been agreed by military commanders at the time that if supplies became any lower, they would surrender the islands (the actual date, deferred as supplies were received, was referred to as the target date).[62] At that time, to stretch the supply of flour, the Maltese mixed flour with potato peelings, making a sort of brown bread. The situation became so dire that bread once again became white when there were no more potato peelings to add to flour. Pedestal delivered 12,000 long tons (12,000 t) of coal, 32,000 long tons (33,000 t) freight and 11,000 long tons (11,000 t) of oil on Ohioof the 121,000 long tons (123,000 t) on the ships when the convoy began. The commodities landed were enough for Malta to last out until mid-November and on 16 August, 29 Spitfires reached Malta of 32 flown from Furious in Operation Baritone.[63][64]
September
The submarine HMS Talisman was lost on a supply run from Gibraltar, either stranded in a minefield or depth-charged by Italian torpedo boats north-west of Malta on 17 September.[65] Attacks on Axis convoys to North Africa deprived the Axis armies of 300,000 long tons (300,000 t) of supplies, using the fuel delivered by Ohio.[66]
October
Magic Carpet rides by submarine reached Malta on 2 October (Rorqual), 3 October (Parthian) and on 6 October Clyde arrived with petrol and other stores, departing for Beirut on 8 October carrying survivors from Pedestal. From 28–30 October, Operation Train was conducted, Furious flying off 29 Spitfires for Malta of which 27 arrived.[64] During the Second Battle of El Alamein (23 October–11 November) the Malta air and sea forces significantly reduced the quantity of supplies reaching the Axis forces in North Africa.
November, Operations Stoneage and Crupper

One independently routed freighter reached Malta from Alexandria but 2,609-ton Ardeola and 1,947-ton Tadorna were captured while trying to reach Malta from Gibraltar as Operation Crupper. Minelayers Welshman and Manxman made successful supply runs. Later that month, four ship convoy MW 13, carrying 35,000 short tons (32,000 t) of supplies, escorted by three cruisers and ten destroyers reached Malta from Alexandria. The cruiser HMS Arethusa was seriously damaged and returned to Alexandria; by 26 November the MW 13 ships had landed a sufficient quantity of stores to "considerably ease" the state of siege and the Malta submarines were able to increase the number of patrols; Force K was re-established and 821 Squadron FAA with Fairey Albacores arrived.[67]
December, Operation Portcullis
In Operation Portcullis, five ship convoy MW 14 arrived from Port Said with 55,000 short tons (50,000 t) of supplies as the first to arrive without loss since 1941. Nine more ships arrived in convoys MW 15 to MW 18, delivering 18,200 short tons (16,500 t) of fuel and another 58,500 short tons (53,100 t) of general supplies and military materiel by the end of December and thirteen ships returned to Alexandria as convoys ME 11 and ME 12. The resultant increase in civilian rations helped to stave off the general decline in health of the population, which had been a cause of an outbreak of poliomyelitis.[68]
Aftermath
Analysis
There were 35 big supply operations to Malta from 1940–1942. Eight were frustrated or suffered severe losses from Axis forces: Operations White, Tiger, Halberd, MF5, MG1, Harpoon, Vigorous and Pedestal. There were long periods when no convoy runs were even attempted and only a trickle of supplies reached Malta by submarine, or by fast warship. The worst period for Malta was from December 1941 – October 1942, when Axis forces had the upper hand, achieving complete air and naval supremacy in the central Mediterranean (called the Italian Mare Nostrum by Benito Mussolini).
At the end of 1942, despite the tactical defeat and ship losses, Operation Pedestal was a strategic success that revived Malta as an offensive base. Operations from Malta denied supplies to Axis forces in North Africa at the time of the battles around El Alamein, restricted the capabilities of the Axis armies in North Africa. The British victory at the Second Battle of El Alamein and the Allied Operation Torch changed the military balance in favour of the Allies. Axis forces in North Africa were then squeezed between the Eighth Army, advancing from Egypt and the Anglo-American First Army advancing from Algeria. Convoys henceforth had air protection flying from North Africa. The later invasions of Sicily and Italy were supported from Malta.
Casualties
From June 1940 to December 1943, about 1,600 civilians and 700 soldiers were killed on Malta. The RAF lost about 900 men killed, 547 aircraft on operations and 160 on the ground and Royal Navy losses were 1,700 submariners and 2,200 sailors; about 200 merchant navy men died. Of 110 voyages by merchant ships to Malta 79 arrived, three to be sunk soon after reaching the island and one ship was sunk on a return voyage. Six of seven independent sailings failed, three ships being sunk, two were interned by Vichy authorities and one ship turned back. The Mediterranean Fleet lost a battleship, two aircraft carriers, four cruisers, a fast minelayer, twenty destroyers and minesweepers and forty submarines. Many small ships were sunk and many surviving ships were damaged.[69]
See also
- Bonner Fellers - the US military attaché in Egypt whose reports to Washington were being read by the Axis
- Mediterranean U-boat Campaign (World War II)
- Club Run - aircraft deliveries to Malta, 1941–1942
- Force K
Notes
- ↑ Iran was occupied in the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran in 1941, to secure the oilfields and create a supply route to the Soviet Union.[4]
- ↑ The damage to Illustrious was severe but after repairs at Alexandria and in the US it returned to service in May 1943. HMS Gallant was mined off Pantellaria and towed to Malta where she was later sunk as a block ship.[23]
- ↑ Merlins over Malta () states that 25,000 tons were landed, enough to sustain the population for two to three months.
Footnotes
- ↑ Jackson 2006, p. 121.
- ↑ Smith 2010.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 56.
- 1 2 3 Bartimeus 1944, pp. 42–47.
- ↑ Di Cirella 2003.
- ↑ Potter & Nimitz 1960, pp. 521–527.
- ↑ Helgason 2012.
- ↑ Potter & Nimitz 1960, pp. 654–661.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 324.
- ↑ Greene & Massignani 2002, p. 225.
- 1 2 Greene & Massignani 2002, pp. 63–81.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 58, 61.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Hague 2000, pp. 192–193.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 61–62, 64, 73–74.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 78–80.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 82, 86–87.
- ↑ Greene & Massignani 2002, p. 115.
- ↑ Greene & Massignani 2002, pp. 115–128.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 94–97.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 106–108.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 107.
- ↑ Thomas 1999, p. 65.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 126, 128, 318.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 110–111, 113–114, 125–126.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 131.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 133–134.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 164–166, 250.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 158–159.
- ↑ Greene & Massignani 2002, pp. 162–164.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 165–167.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 167–176.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 177.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 184–185, 206–208, 212–213, 218.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 218–219.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 217.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 212–239.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 240–243.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 243–245.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 246–250.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 250–251.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 266.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 267–268.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 271–273.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 274–275.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 280–281.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 282–283.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 284.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 285–286.
- ↑ Roskill 1956, p. 73.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 291.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 293–295.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 300, 303.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 306–316.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 320–322.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 321–322, 328.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 211, 328.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 328–329.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 329–370.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 370.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 283, 372–380, 386–442, 454–455, 463.
- ↑ Castillo 2006, p. 207.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 283.
- ↑ Castillo 2006, p. 199.
- 1 2 Woodman 2003, pp. 450–457.
- ↑ DNC 1952, p. 376.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, p. 455.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 458–461.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 461–464.
- ↑ Woodman 2003, pp. 470–471.
References
- Bartimeus, W. M. (1944). East of Malta, West of Suez. New York/Boston: Little, Brown. OCLC 1727304.
- Castillo, Dennis Angelo (2006). The Maltese Cross: A Strategic History of Malta. Greenwood. ISBN 978-0-313-32329-4.
- Di Cirella, A. C. G. (2003) [1996]. Per l'onore dei Savoia, 1943–1944: da un superstite della corazzata Roma [For the honour of Savoy, 1943–1944: From a Survivor of the Battleship Roma]. Testimonianze fra cronaca e storia, Guerre fasciste e seconda guerra mondiale [Testimonies of Events and History: Fascist Wars and World War II]. Milano: Mursia Editore. OCLC 499174431.
- Greene, J.; Massignani, A. (2002) [1998]. The Naval War in the Mediterrnean 1940–1943 (pbk. ed.). Rochester: Chatham. ISBN 978-1-86176-190-3.
- Hague, Arnold (2000). The Allied Convoy System 1939–1945. Annapolis, MD: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-1-55750-019-9.
- Helgason, Guðmundur. "23rd Flotilla". German U-boats of WWII - uboat.net. Retrieved 2012-06-20.
- H. M. Ships Damaged or Sunk by Enemy Action, 3rd September, 1939 to 2nd September, 1945 (PDF). London: Admiralty: Director of Naval Construction. 1952. OCLC 38570200. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Jackson, Ashley (2006). The British Empire and the Second World War. London: Hambledon Continuum. ISBN 978-1-85285-417-1.
- Potter, E. B.; Nimitz, C. W., eds. (1960). Sea Power. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall. OCLC 933965485.
- Roskill, S. W. (1956). The Period of Balance. History of the Second World War: The War at Sea 1939–1945. II. London: HMSO. OCLC 174453986. Retrieved 25 November 2016.
- Smith, G. (7 November 2010). "Royal Navy Vessels Lost at Sea, 1939–45". naval-history.com. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Thomas, D. A. (1999). Malta Convoys. Barnsley: Pen and Sword Books. ISBN 978-0-85052-663-9.
- Woodman, R. (2003). Malta Convoys 1940–1943 (pbk. ed.). London: John Murray. ISBN 978-0-7195-6408-6.
Further reading
- Hague, Arnold (4 December 2010). "The Supply of Malta 1940–1942". naval-history.com. Part 1. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Hammond, R. J. (2011). The British Anti-shipping Campaign in the Mediterranean 1940–1944: Comparing Methods of Attack (PhD). registration. University of Exeter. OCLC 798399582. Docket uk.bl.ethos.548977. Retrieved 31 October 2016.
- Playfair, Major-General I. S. O.; et al. (2004) [1st. pub. HMSO: 1960]. Butler, Sir James, ed. The Mediterranean and Middle East: British Fortunes Reach Their Lowest Ebb (September 1941 to September 1942). History of the Second World War, United Kingdom Military Series. III. Uckfield, UK: Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-067-2.
- Playfair, Major-General I. S. O.; et al. (2004) [HMSO 1966]. Butler, J. R. M., ed. The Mediterranean and Middle East: The Destruction of the Axis Forces in Africa. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series. IV. Uckfield: Naval & Military Press. ISBN 978-1-84574-068-9.
- Richards, Denis (1974) [1953]. Royal Air Force 1939–1945: The Fight At Odds. I (paperback ed.). London: [HMSO]]. ISBN 978-0-11-771592-9. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Richards, D.; St G. Saunders, H. (1975) [1954]. Royal Air Force 1939–45: The Fight Avails. II (repr. ed.). London: HMSO. ISBN 978-0-11-771593-6. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Roskill, S. W. (1957) [1954]. Butler, J. R. M., ed. The War at Sea 1939–1945: The Defensive. History of the Second World War United Kingdom Military Series. I (4th impr. ed.). London: HMSO. OCLC 881709135. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- Santoro, G. (1957). L'aeronautica italiana nella seconda guerra mondiale [The Italian Air Force in WWII] (PDF). II. [semi-official history] (1st ed.). Milano-Roma: Edizione Esse. OCLC 60102091. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
- The Rise and Fall of the German Air Force. Air 41/10 (Public Record Office War Histories ed.). Richmond, Surrey: Air Ministry. 2001 [1948]. ISBN 978-1-903365-30-4.
- Vego, M. (Winter 2010). "Major Convoy Operation To Malta, 10–15 August 1942 (Operation Pedestal)". Naval War College Review. 63 (1). ISSN 0028-1484. Retrieved 9 October 2016.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Malta convoys. |
- Mediterranean naval campaign
- HMS Naiad - Dido Class Cruiser
- Operation Harpoon
- Photos of Operation Pedestal
- Documentary film: Convoy to Malta
- MEDITERRANEAN CONVOY OPERATIONS (London Gazette)
- NZETC SPITFIRES OVER MALTA