Maurice (emperor)
| Maurice | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Tremissis of Emperor Maurice. | |||||
| Emperor of the Byzantine Empire | |||||
| Reign | 14 August 582 – 27 November 602 | ||||
| Predecessor | Tiberius II Constantine | ||||
| Successor | Phocas | ||||
| Born |
539 Arabissus, Cappadocia | ||||
| Died |
27 November 602 (aged 63) Constantinople | ||||
| Spouse | Constantina | ||||
| Issue |
Theodosius Tiberius Petrus Paulus Justin Justinian Anastasia Theoctista Cleopatra | ||||
| |||||
| Dynasty | Justinian Dynasty | ||||
| Father | Paul | ||||
Maurice (Latin: Flavius Mauricius Tiberius Augustus; Greek: Φλάβιος Μαυρίκιος Τιβέριος Αὔγουστος) (539 – 27 November 602) was Eastern Roman Emperor from 582 to 602.
A prominent general in his youth, Maurice fought with success against the Sassanid Persians. Once he became Emperor, he brought the war with Sasanian Persia to a victorious conclusion: the Empire's eastern border in the Caucasus was vastly expanded and for the first time in nearly two centuries the Romans were no longer obliged to pay the Persians thousands of pounds of gold annually for peace.
Maurice campaigned extensively in the Balkans against the Avars – pushing them back across the Danube by 599. He also conducted campaigns across the Danube, the first Roman Emperor to do so in over two centuries. In the West, he established two large semi-autonomous provinces called exarchates, ruled by exarchs, or viceroys, of the emperor.
In Italy, Maurice established the Exarchate of Ravenna in 584, the first real effort by the Empire to halt the advance of the Lombards. With the creation of the Exarchate of Africa in 590, he further solidified the power of Constantinople in the western Mediterranean.
His reign was troubled by financial difficulties and almost constant warfare. In 602, a dissatisfied general named Phocas usurped the throne, having Maurice and his six sons executed. This event would prove cataclysmic for the Empire, sparking a twenty-six year war with Sassanid Persia which would leave both empires devastated prior to the Muslim conquests.
His reign is a relatively accurately documented era of Late Antiquity, in particular by the historian Theophylact Simocatta. The Strategikon, a manual of war which influenced European and Middle Eastern military traditions for well over a millennium, is traditionally attributed to Maurice.
Biography
Origins and early life
Maurice was born in Arabissus in Cappadocia in 539, the son of a certain Paul. He had one brother, Peter, and two sisters, Theoctista and Gordia, later the wife of the general Philippicus.[1] He is recorded to have been a native Greek speaker, unlike previous emperors since Anastasius I Dicorus.[2] He may have been a Cappadocian Greek,[3][4] or possibly he was a Hellenized Armenian.[5] This issue cannot be determined in any way.[6] The historian Evagrius Scholasticus records a (likely invented) descent from old Rome.[1]
Maurice first came to Constantinople as a notarius, and came to serve as a secretary to the comes excubitorum (commander of the Excubitors, the imperial bodyguard) Tiberius, the future Tiberius II (r. 578–582). When Tiberius was named Caesar in 574, Maurice was appointed to succeed him as comes excubitorum.[1][7]
Persian War and accession to the throne
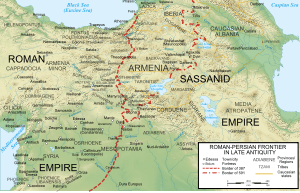
In late 577, despite a complete lack of military experience, Maurice was named as magister militum per Orientem, effectively commander-in-chief of the Byzantine army in the East, in the ongoing war against Sassanid Persia, succeeding the general Justinian. At about the same time, he was raised to the rank of patricius.[8] He scored a decisive victory against the Persians in 581. A year later, he married Constantina, the Emperor's daughter. On 13 August, he succeeded his father-in-law as Emperor. Upon his ascension he ruled a bankrupt Empire. At war with Persia, paying extremely high tribute to the Avars, and the Balkan provinces thoroughly devastated by the Slavs, the situation was tumultuous at best.
Maurice had to continue the war against the Persians. In 586, his troops defeated them at a major battle south of Dara. Despite a serious mutiny in 588, the army managed to continue the war and even secure a major victory before Martyropolis. In 590, the two Parthian brothers Vistahm and Vinduyih overthrew king Hormizd IV and made the latter's son, Prince Khosrau II, as the new king. However, the former Iranian commander-in-chief Bahram Chobin, who had rebelled against Hormizd IV, claimed the throne for himself and defeated Khosrau, who along with the two Parthian brothers subsequently fled to the Byzantine court. Although the Senate advised against it with one voice, Maurice helped Khosrau regain his throne with an army of 35,000 men. In 591 the combined Byzantine-Persian army under generals John Mystacon and Narses defeated Bahram Chobin's forces near Ganzak at the Battle of Blarathon. The victory was decisive; Maurice finally brought the war to a successful conclusion by means of a new accession of Khosrau.
Subsequently, Khosrau was probably adopted by the emperor. Khosrau further rewarded Maurice by ceding to the Empire western Armenia up to the lakes Van and Sevan, including the large cities of Martyropolis, Tigranokert, Manzikert, Ani, and Yerevan. Maurice's treaty brought a new status-quo to the east territorially, enlarged to an extent never before achieved by the Empire, and much cheaper to defend during this new perpetual peace – millions of solidi were saved by the remission of tribute to the Persians alone. Afterwards, Maurice imposed a union between the Armenian Church and the Patriarchate of Constantinople.
Balkan warfare
After his victory on the eastern frontier, Maurice was free to focus on the Balkans. The Slavs, having pillaged the Byzantine Balkan provinces for decades, probably began settling the land from the 580s on. The Avars took the strategically important fort of Sirmium in 582, using it as a base of operations against several poorly defended forts alongside the Danube. In 584 the Slavs threatened the capital and in 586 Avars besieged Thessalonica, while Slavs went as far as the Peloponnese. In 591 Maurice launched several campaigns against Slavs and Avars – with good prospect of turning the tide.
In 592 his troops retook Singidunum from the Avars. His commander-in-chief Priscus defeated Slavs, Avars and Gepids south of the Danube in 593. The same year he crossed the Danube into modern-day Wallachia to continue his series of victories. In 594 Maurice replaced Priscus with his rather inexperienced brother Peter, who despite initial failures, nonetheless scored another victory in Wallachia. Priscus, now in command of another army further upstream, defeated the Avars again in 595. The latter only dared to attack again peripherally in Dalmatia two years later. In 598 a treaty was signed with the Avar leader Bayan I, only to be broken for retaliation campaigns inside Avar homeland. In 599 and 601, the Byzantine forces wreaked havoc amongst the Avars and Gepids. In 602 the Slavs suffered a crushing defeat in Wallachia. The Byzantine troops were now able to hold the Danube line again. Meanwhile, Maurice was making plans for resettling devastated areas in the Balkans by using Armenian settlers.[9]
Measures of domestic policy

In the west, he organized the threatened Byzantine dominions in Italy and Africa into exarchates, ruled by military governors or exarchs, in 584 and 591 respectively. The exarchs had more or less complete military and civil authority. This was a remarkable exception to the usual separation of civil and military powers in that era. By founding the Exarchate of Ravenna, Maurice managed to slow the Lombard advance in Italy.
In 597, an ailing Maurice wrote his last will, in which he described his ideas of governing the Empire. His eldest son, Theodosius, would rule the East from Constantinople; his second son, Tiberius, would rule the West from Rome. Some historians believe he intended for his younger sons to rule from Alexandria, Carthage, and Antioch. His intent was to maintain the unity of the Empire, making this idea bear a strong resemblance to the Tetrarchy of Diocletian. However, Maurice's violent death prevented these plans from coming to fruition.
In religious matters, Maurice was very tolerant toward Monophysitism, although he was a supporter of the Council of Chalcedon. He clashed with Pope Gregory I over the latter's defense of Rome against the Lombards.[10]
Maurice's efforts to consolidate the Empire slowly but steadily found success, especially due to the peace with Persia. His initial popularity apparently declined during his reign, mostly because of his fiscal policies. In 588, he announced a cut in military wages by 25%, leading to a serious mutiny by troops on the Persian front. He refused to pay a very small ransom in 599 or 600 to free 12,000 Byzantine soldiers taken prisoner by the Avars. The prisoners were killed, and a protesting military delegation, headed by an officer named Phocas (subsequently emperor Phocas), was humiliated and rejected in Constantinople.
Death
In 602, Maurice, always dealing with the lack of money, decreed that the army should stay for winter beyond the Danube, which would prove to be a serious mistake. The exhausted troops mutinied against the Emperor. Probably misjudging the situation, Maurice repeatedly ordered his troops to start a new offensive rather than returning to winter quarters. After a while, his troops gained the impression that Maurice no longer mastered the situation, proclaimed Phocas their leader, and demanded that Maurice abdicate and proclaim as successor either his son Theodosius or General Germanus. Both men were accused of treason, but riots broke out in Constantinople, and the emperor left the city with his family for Nicomedia. Theodosius headed east to Persia, but historians are not sure whether he had been sent there by his father or if he had fled there. Phocas entered Constantinople in November and was crowned Emperor, while his troops captured Maurice and his family.
Maurice was murdered on 27 November 602 (some say 23 November). It is said that the deposed emperor was forced to watch his six sons executed before he was beheaded himself. Empress Constantina and her three daughters were spared and sent to a monastery. The Persian King Khosrau II used this coup and the murder of his patron as an excuse for a renewed war against the Empire.
Legacy
Maurice is seen as an able emperor and commander-in-chief, though the description by Theophylact may be a bit too glorifying. He possessed insight, public spirit, and courage. He proved his expertise on military and foreign affairs during his campaigns against Persians, Avars and Slavs, and also during peace negotiations with Khosrau II. His administrative reforms reveal him as a farsighted statesman, all the more since they outlasted his death by far and were the basis for the introduction of such themes as military districts.
His court still used Latin, as did the army and administration, and he promoted science and the arts. Maurice is traditionally named as author of the military treatise Strategikon, which is praised in military circles as the only sophisticated combined arms theory until World War II. Some historians now believe the Strategikon is the work of his brother or another general in his court, however.
His greatest weakness was his inability to judge how unpopular his decisions were. As summarized by the historian C. W. Previté-Orton, listing a number of character flaws in the Emperor's personality:
His fault was too much faith in his own excellent judgment without regard to the disagreement and unpopularity which he provoked by decisions in themselves right and wise. He was a better judge of policy than of men.[11]
It was this flaw that cost him throne and life, and thwarted most of his efforts to prevent the disintegration of the great empire of Justinian I.
The demise of Maurice was a turning point in history. The resulting war against Persia weakened both empires, enabling the Slavs to permanently settle the Balkans and paving the way for Arab/Muslim expansion. English historian A.H.M. Jones characterizes the death of Maurice as the end of the era of Classical Antiquity, as the turmoil that shattered the Empire in the next four decades permanently and thoroughly changed society and politics.
Family relations
Maurice's marriage was fertile and produced nine known children:
- Theodosius (4 August 583/585 – after 27 November 602). According to John of Ephesus, he was the first heir born to a reigning emperor since the reign of Theodosius II (408–450).[12] He was appointed Caesar in 587 and co-emperor on 26 March 590.
- Tiberius (died 27 November 602).
- Petrus (died 27 November 602).
- Paulus (died 27 November 602).
- Justin (died 27 November 602).
- Justinian (died 27 November 602).
- Anastasia (died c. 605).
- Theoctista (died c. 605).
- Cleopatra (died c. 605).
A daughter Miriam/Maria is recorded by the 12th-century chronicler Michael the Syrian and other eastern sources as married to Khosrau II, but not in any Byzantine Greek ones; she is probably legendary.
His brother Petrus (c. 550 – 602) became the curopalates and was killed at the same time as Maurice was. Petrus married Anastasia Aerobinda (born c. 570), daughter of Areobindus (born c. 550), and had female issue.
His sister Theoctista (c. 540 – after 582) married a husband who died before 582, and had a daughter Gordia (c. 560 – after 597), who married Marinus (c. 555 – after 597), son of Nerses (c. 530 – after 595) and wife Hesychia (born c. 535), by whom she had a daughter Theoctista (c. 575/c. 580 – after 597), married to Christodorus or Christodoros (born c. 570) and had issue.
His sister Gordia (c. 550 – after 602) married Philippicus (c. 550 – Chrysopolis, 614), General, comes excubitorum and magister militum in 582, by whom she had a daughter, who married Artabastus (Artavazd) Mamikonian (born c. 565), and had issue.
Personage of legends
The first legendary stories on the life of the emperor Maurice are recorded in the ninth century, in the work of the Byzantine historian Theophanes the Confessor. According to his chronicle (Chronographia), the death of the imperial family is decided by a divine intervention: Christ has asked the emperor to choose between a long reign on his empire or the death and acceptance in the kingdom of heaven. Maurice prefer the second choice.[13] The same story has been reported by a short syriac hagiography on the life of the emperor, which was sanctified later by the Byzantine Orthodox Church.[14] According to the syriac authors, the emperor asked in prayer to receive a punishment in this world and a "perfect reward" in the kingdom of heaven. The choice is offered here by an angel: “
”(The angel) saw him while he was praying and said," You're tired God with your requests since a long time. You asked God and you requires to suffer here (bottom) the punishment of the sin of which you would not be worthy of the perfect reward, and not to be deprived on his account from the perfect reward. I can attest to you that you have made a sin which deprive yourself of the higher reward; however you will have the fate of the saints. If you want to keep your kingdom and the lives of your children for long time, ceases to address this demand and in the resurrection your reward will be that of the just. If you want the highest reward and to be punished here, this shall be your punishment: you will be deprived of your kingdom, your children will be slaughtered before your eyes, and in the end your enemies will burn you. So choose what you want. ”[15]
According to another legend of the same text, Maurice had also prevented a nurse to substitute his own son to one of his children and so save from the executioner at least one of the heirs of te empire.[16] This legend will not cease to amplify in the Balkans. Maurice was the last emperor of a Illyrian dynasty whose origin is in the center of the Balkans, in the city of Justiniana Prima, and the peoples of the region identified themselves with his family. Romanian authors noted parallels between the legends on the death of the prince Constantin Brâncoveanu and stories about the death of the Byzantine imperial family. Just before the execution, the gypsy nurse of the youngest son of Brancoveanu, replaces the prince by his own son, to save at least one heir of the royal family. Like the Byzantine emperor, the Romanian ruler refused.[17] The angel’s proposal to the emperor to choose between a long life in this world and the life in the kingdom of heaven as the motif of the death of nine princes are recurrent in the epic tradition of the Albanian and south Slavs mountaineers.[18] The central personage of the Albanian Cycle of Kreshniks, Gjeto Muji (Muji the foundling), his wife Ajkuna (or Kuna according to the songs) reflect – for the Albanian scholars – the names and the history of Emperor Maurice and his wife Aelia Constantina. The nine Tiberii were remembered in Albanian songs as the nine dibrans. Also in the Montenegrin epic the legendary prince Nahod Momir (Momir the foundling) and her sister Grozdana are related to the emperor and his sister Gordia. The epic epithet the "foundling" reflect the episode of Maurice adoption by the Emperor Tiberius, and by the imperial dynasty of Justin. In the Bosnian epic, the emperor is called Mouio Tcarevitch (Mouio the son of the emperor).[19]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 855
- ↑ Treadgold, pg. 227
- ↑ Stark, Freya (2012). Rome on the Euphrates: The Story of a Frontier. Tauris Parke Paperbacks. p. 390. ISBN 978-1-84885-314-0.
Byzantium reverted to Greek (Maurice, born in Cappadocia, was its first Greek emperor); and trade and diplomacy were honored from the very founding of the Imperial city as never in Rome before.
- ↑ Corradini, Richard (2006). Texts and identities in the early Middle Ages. Verl. der Österr. Akad. der Wiss. p. 57. ISBN 978-3-7001-3747-4.
Emperor Maurice who is said to be the first emperor "from the race of the Greeks," ex Graecorum genere.
- ↑ John H. Rosser. Historical Dictionary of Byzantium. — Second edition. — Scarecrow Press, 2011. — P. 199.:"Armenians were a significant minority within the empire. In the sixth century, Justinian I's General Narses was Armenian. The emperor Maurice (582-602) may have been Armenian. In the ninth and 10th centuries there were several Armenian emperors, including Leo V, Basil I, Romanos I Lekapenos, and John I Tzimiskes. Theodora, the wife of Theophilios, was Armenian."
- ↑ Kazhdan (1991), p. 1318
- ↑ Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 856
- ↑ Martindale, Jones & Morris (1992), p. 856–857
- ↑ The Armenian History attributed to Sebēos, Part 1, translation and notes, trans. R.W. Thomson; comm. J.D. Howard-Johnston, Translated Texts for Historians 31 (Liverpool, 1999) p.56
- ↑
 Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Maurice". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
Herbermann, Charles, ed. (1913). "Maurice". Catholic Encyclopedia. New York: Robert Appleton Company. - ↑ Previté-Orton, Charles William, The shorter Cambridge medieval history (Cambridge: University Press, 1952), p. 203.
- ↑ Lynda Garland, "Constantina, Wife of Maurice"
- ↑ Theophanes (the Confessor) et Roger Scott. The chronicle of Theophanes Confessor: Byzantine and Near Eastern history, AD 284-813. Clarendon Press, 1997, pp. 410
- ↑ ↑ Commemorated in November 28 according to the Typikon of the Great Church and in August 28, according to the Palestinian-Georgian Synaxarion, cf. Wortley J. "The legend of the Emperor Maurice", in: Actes du XVe Congrès International d’Etudes byzantines, (Athènes, 1976), tome IV, Athènes, 1980, pp. 382-391. .
- ↑ (fr) Nau, F. Les légendes syriaques d'Aaron de Saroug, de Maxime et Domèce, d'Abraham, maitre de Barsoma et de l'empereur Maurice. Turnhout: Brepols, 1981, pp. 774-775.
- ↑ Nau, 1981, pp. 776-778.
- ↑ Fochi A., Cântecul epic tradițional al românilor, Editura Știintifică și Enciclopedică. București, 1985,, pp. 104-105. ; Vrabie, Gh. Eposul popular românesc: Teme-motive, structuri poematice. Bucarest, 1983, pp. 227-229
- ↑ (sq) Shuka, G. Tridhjetë Këngë Dhe Legjenda Ballkanike: Studim Mbi Origjinën Historike. Tirana: Naimi, 2015, pp. 527-568
- ↑ Shuka, 2015, pp. 527-568.
Sources
- Bury, John Bagnell (1889). History of the Later Roman Empire. New York.
- Charles, R. H. (1916) The Chronicle of John, Bishop of Nikiu: Translated from Zotenberg's Ethiopic Text, Reprinted 2007. Evolution Publishing, ISBN 978-1-889758-87-9.;[1] also available free online [2]
- Ostrogorsky, George (1956). History of the Byzantine State. Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Kazhdan, Alexander, ed. (1991), Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6
- Meyendorff, John (1989). Imperial unity and Christian divisions: The Church 450-680 A.D. The Church in history. 2. Crestwood, NY: St. Vladimir's Seminary Press. ISBN 978-0-88-141056-3.
- Martindale, John R.; Jones, A.H.M.; Morris, John (1992), The Prosopography of the Later Roman Empire – Volume III, AD 527–641, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-20160-8
- Shlosser, Franziska E. (1994). The Reign of the Emperor Maurikios (582–602). A reassessment (Historical Monographs 14). Athens.
- Schreiner, Peter (1985). Theophylaktes Simokates: Geschichte. Stuttgart.
- Treadgold, Warren T. (1997), A History of the Byzantine State and Society, Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, ISBN 0-8047-2630-2
- Walford, Edward, transl. (1846) The Ecclesiastical History of Evagrius: A History of the Church from AD 431 to AD 594, Reprinted 2008. Evolution Publishing, ISBN 978-1-889758-88-6.[3]
- Whitby, Michael (1998), The Emperor Maurice and his Historian – Theophylact Simocatta on Persian and Balkan Warfare, Oxford University Press, ISBN 0-19-822945-3
- Whitby, Michael (2015). "MAURICE". Encyclopaedia Iranica.
External links
-
 Media related to Maurice at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Maurice at Wikimedia Commons -
 "Maurice, East Roman emperor". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
"Maurice, East Roman emperor". Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). 1911.
| Maurice (emperor) Born: 539 Died: 602 | ||
| Regnal titles | ||
|---|---|---|
| Preceded by Tiberius II Constantine |
Byzantine Emperor 582–602 with Tiberius II Constantine (582) Theodosius (590–602) |
Succeeded by Phocas |
| Political offices | ||
| Preceded by Imp. Caesar Flavius Tiberius Constantinus Augustus in 579, then lapsed |
Consul of the Roman Empire 583 |
Succeeded by Lapsed, Imp. Caesar Flavius Phocas Augustus in 603 |
- ↑ "The Christian Roman Empire series". Evolpub.com. Retrieved 2013-11-27.
- ↑ Roger Pearse (2002-10-26). "John, Bishop of Nikiu: Chronicle. London (1916). English Translation". Tertullian.org. Retrieved 2013-11-27.
- ↑ "The Christian Roman Empire series". Evolpub.com. Retrieved 2013-11-27.