North Bay, Ontario
| North Bay | ||
|---|---|---|
| City (single-tier) | ||
| City of North Bay | ||
|
Main Street | ||
| ||
| Nickname(s): "Gateway to the North" [1] | ||
| Motto: Gateway of the North | ||
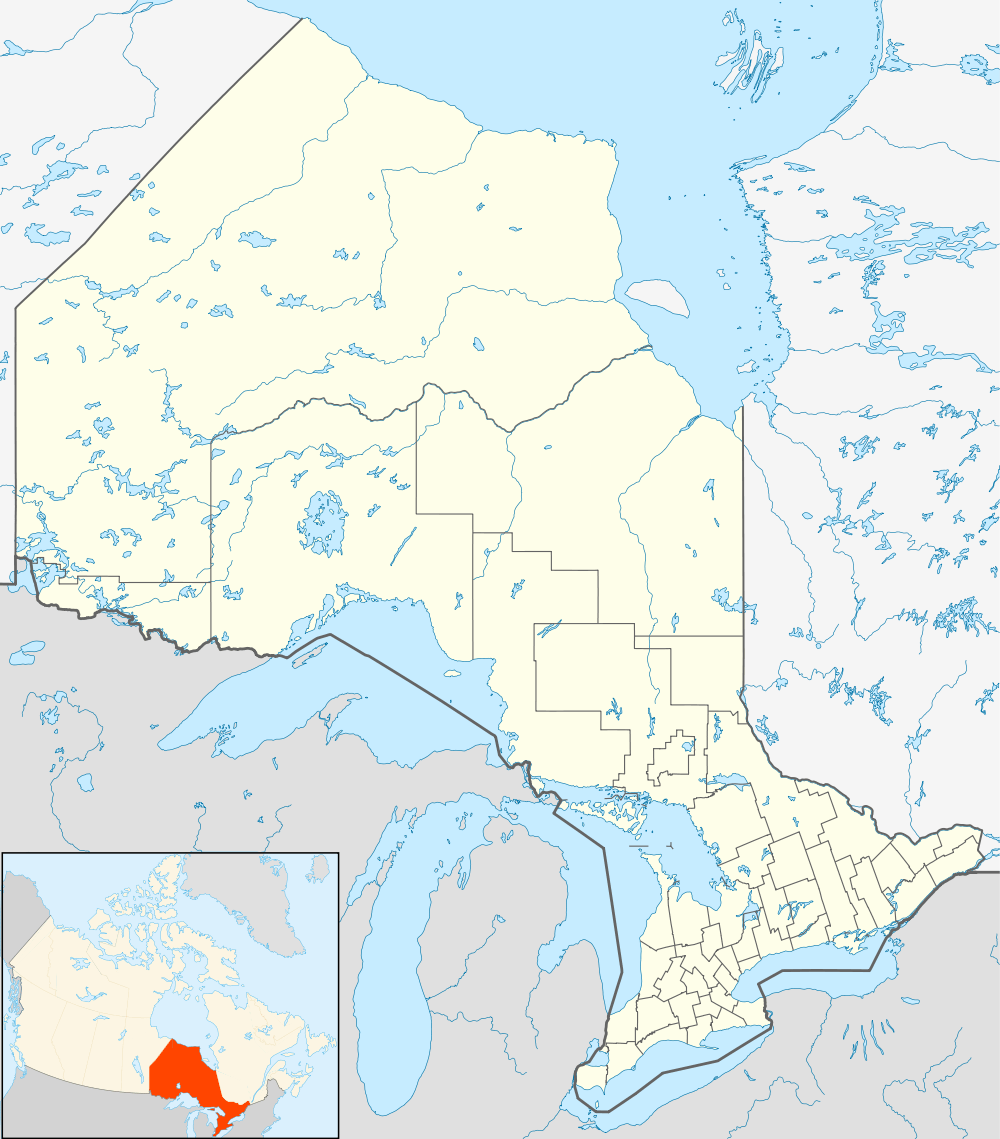 North Bay Location of North Bay, Ontario | ||
| Coordinates: 46°18′N 79°27′W / 46.300°N 79.450°WCoordinates: 46°18′N 79°27′W / 46.300°N 79.450°W | ||
| Country | Canada | |
| Province | Ontario | |
| District | Nipissing | |
| Established | 1891 | |
| Government | ||
| • Type | City | |
| • Mayor | Al McDonald | |
| • Governing Body | North Bay City Council | |
| • MP | Anthony Rota | |
| • MPP | Vic Fedeli | |
| Area[2] | ||
| • Land | 319.05 km2 (123.19 sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 788.48 km2 (304.43 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 197 m (646 ft) | |
| Population (2011)[2] | ||
| • City (single-tier) | 53,651 (Ranked 92nd) | |
| • Density | 168.2/km2 (436/sq mi) | |
| • Metro | 64,043 | |
| • Metro density | 81.2/km2 (210/sq mi) | |
| Time zone | EST (UTC-5) | |
| • Summer (DST) | EDT (UTC-4) | |
| Postal Code span | P1A, P1B, P1C | |
| Area code(s) | Area codes 705 and 249 | |
| Highways |
| |
| Website | Official website | |
| [3] | ||
North Bay is a city in Northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is the seat of Nipissing District, and takes its name from its position on the shore of Lake Nipissing.
History


The site of North Bay was on the main canoe route west from Montreal. Apart from First Nations tribes, voyageurs and surveyors, there was little activity in the Lake Nipissing area until the arrival of the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) in 1882. The CPR started its westward expansion from Callander Station (later renamed Bonfield), Ontario; Bonfield was inducted into Canadian Railway Hall of Fame in 2002 as the CPR First Spike location.
That was the point where the Canada Central Railway (CCR) extension ended. The CCR was owned by Duncan McIntyre who amalgamated it with the CPR and became one of the handful of officers of the newly formed CPR. The CCR started in Brockville and extended to Pembroke. It then followed a westward route along the Ottawa River passing through places like Cobden, Deux-Rivières, and eventually to Mattawa at the confluence of the Mattawa and Ottawa Rivers. It then proceeded cross-country towards its final destination, Bonfield. Duncan McIntyre and his contractor James Worthington piloted the CCR expansion. Worthington continued on as the construction superintendent for the CPR past Bonfield. He remained with the CPR for about a year until he left the company. McIntyre was uncle to John Ferguson who staked out future North Bay after getting assurance from his uncle and Worthington that it would be the divisional and a location of some importance.
In 1882, John Ferguson decided that the north bay of Lake Nipissing was a promising spot for settlement. North Bay was incorporated as a town in 1891. The first mayor was John Bourke. More importantly, Bourke developed the western portion of North Bay after purchasing the interest of the Murray Brothers from Pembroke, who were large landholders in the new community. The land west of Klock Avenue (Algonquin Avenue) was known as the Murray block. Bourke Street is named after John Bourke. Murray Street is named after the Murrays.
North Bay was selected as the southern terminus of the Temiskaming and Northern Ontario Railway (T&NO) in 1902 when the Ross government took the bold move to establish a development road to serve the Haileybury settlement. During construction of the T&NO, silver was discovered at Cobalt and started a mining frenzy in the northern part of the province that continued for many years. The Canadian Northern Railway was subsequently built to North Bay in 1913.
The Georgian Bay Canal was a mammoth transportation system that proposed to connect the Great Lakes with the Atlantic Ocean. The entire passageway from the Ottawa River to Lake Nipissing and down the French River to Georgian Bay was surveyed in the first decade of the 20th century. Financing was a large obstacle and, as time passed, transportation patterns changed and interfered with the earlier practicality of the giant venture. Despite this, there were groups who still hoped it would happen as late as 1930.
North Bay grew through a strong lumbering sector, mining and the three railways in the early days. The town benefited from strong community leadership and people like Richardson, Milne, McNamara, Englands, Browning, McDougal, Carruthers, McGaughey, George W. Lee, Senator Gordon, T. J. Patton, Charlie Harrison, and many others are responsible for its development. In 1919, John Ferguson was elected mayor of North Bay and continued to serve as mayor until 1922. North Bay was incorporated as a city in August 1925.
The Dionne Quintuplets were born in Corbeil, Ontario, on the southern outskirts of North Bay in 1934. Their births had a tremendous impact on tourism in the area. In fact, the Dionnes may have saved the economy in the district during the Depression and beyond. North Bay and area lived off this legacy well into the 1960s. Many visitors to the area discovered lakes and summer retreats that were easily accessible and the businesses thrived on the tourist dollars.
In January 1968, the City of North Bay amalgamated with West Ferris and Widdifield townships.
In 1951, as a result of rising tensions in the Cold War, the Royal Canadian Air Force established an air base at North Bay, part of an expanding national air defence network to counter the threat of nuclear attack against North America by Soviet bombers. Construction of RCAF Station North Bay (in 1966 retitled "Canadian Forces Base North Bay" and in 1993 as "22 Wing/Canadian Forces Base North Bay") took three years, during which it became the largest industry in the community, a status it held for more than four decades. In October 1963, the North American Air Defence Command (NORAD) opened its Canadian operations centre at the base. Manned by American as well as Canadian military personnel, the centre, situated 60 storeys underground to withstand a nuclear strike, monitored Canada's northern, east-central and Atlantic airspace, identifying and tracking all air traffic in this airspace, and responding to airborne emergencies, crime, and suspicious, unknown and potentially hostile aircraft. In 1983 this responsibility was expanded to all of Canada, and in October 2006 the base's NORAD operations (as of 1981, called North American Aerospace Defence Command) moved into a new, state-of-the-art facility above ground where it continues to provide surveillance, identification and tracking of aircraft, and warning and response to emergencies, attacks and other crises, for the air sovereignty of Canada and North America. In summer of 2013, the base commenced surveillance of space via SAPPHIRE, Canada's first military satellite, that was launched into orbit from India in February.[4]
Beginning in the 1990s the base weathered a series of massive cuts by the federal government, at one point was earmarked to close. Subsequently, a large portion of its infrastructure, including all of its airfield assets, such as hangars, fuel depot and control tower, were sold or demolished. By the 21st Century the base was no longer the city's top industry.[4]
The United States Air Force also maintains a unit varying from 34 to 38 personnel at the base, called 1 Air Force. Detachment 2.
One by-product of the air base's creation in 1951 was extension of the existing airport's runways to handle the largest military aircraft. The long runways at North Bay have been maintained as an alternate landing site for Toronto's Pearson International Airport and were used during the September 11 crisis as an emergency landing site for several international aircraft. It was also a designated emergency field for NASA's Space Transportation System, better known as the Space Shuttle.
The current engines driving North Bay's economy are the university and college population as well as the North Bay Regional Health Centre, newly opened in January 2011.[5] Tourism and a stable provincial government service centre also contribute to the robust economy.
On March 17, 2007, North Bay was announced as the winner of 2007 Kraft Hockeyville contest. North Bay received $50,000 to upgrade their local arena, Memorial Gardens, and also hosted an NHL pre-season game between the New York Islanders and the Atlanta Thrashers.
In 2009, multiple film productions came to the city, most notably The Kids in the Hall's eight-part TV miniseries for CBC Television, Death Comes to Town. North Bay's downtown, Memorial Gardens, and Trinity United Church were among the filming locations, as well as the neighbouring communities of Mattawa and Sturgeon Falls.[6]
Statistics Canada's 2011 census showed a decrease in residents, from 53,966 in 2006 to 53,651 in 2011, a decrease of 0.6%.[2] There is also a growing trend in post secondary students who decide to come to Canadore College and Nipissing University who wish for a quieter atmosphere than larger universities tend to have. However, these students are not counted in the census, as the census date falls in May after the end of the postsecondary school year and thus most students from out of town have gone home for the summer.
Geography

North Bay is located approximately 330 km (210 mi) north of Toronto, and differs in geography from Southern Ontario in that North Bay is situated on the Canadian Shield. This gives rise to a different and more rugged landscape.
North Bay is geographically unique in that it straddles both the Ottawa River watershed to the east and the Great Lakes Basin to the west. The city's urban core is located between Lake Nipissing and the smaller Trout Lake.
North Bay, critically situated at the junctions of Highway 11 and Highway 17, remains a major transportation centre for Northern Ontario. It is the southern terminus of the Ontario Northland Railway, and is served by the Jack Garland Airport.
The area of North Bay contains a number of ancient volcanic pipes, including the Manitou Islands and Callander Bay and many exposed dykes and five named batholiths (Timber Lake, Mulock, West Arm, Powassan and Bonfield).
Climate
The climate in North Bay is common to most places in Northern Ontario. North Bay tends to be a less humid climate than that found in Southern Ontario due somewhat to the distance from the Great Lakes and less warm than some other locations in Northern Ontario due to cooling from Lake Nipissing. On May 31, 2002, a tornado caused minor damage near the city. Two more tornadoes touched down on Lake Nipissing on August 20, 2009. This storm was a part of a chain of tornadoes that caused large amounts of damage in other parts of Ontario.[7] The weather box below shows climate normals for the airport, at an elevation of 358 m, but the majority of the city, including the downtown core, sits at an elevation of 201 m.
The highest temperature ever recorded in North Bay was 37.2 °C (99 °F) on 1 July 1931.[8] The coldest temperature ever recorded was −44.4 °C (−48 °F) on 26 January 1892.[8]
| Climate data for North Bay Airport, 1981−2010 normals, extremes 1887−present[lower-alpha 1] | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 12.8 (55) |
12.8 (55) |
25.2 (77.4) |
29.9 (85.8) |
32.2 (90) |
36.1 (97) |
37.2 (99) |
34.4 (93.9) |
34.4 (93.9) |
27.8 (82) |
21.1 (70) |
14.4 (57.9) |
37.2 (99) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −7.6 (18.3) |
−5.3 (22.5) |
0.6 (33.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
16.7 (62.1) |
21.6 (70.9) |
24.0 (75.2) |
22.7 (72.9) |
17.7 (63.9) |
10.3 (50.5) |
2.8 (37) |
−4.1 (24.6) |
9.0 (48.2) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −12.5 (9.5) |
−10.4 (13.3) |
−4.5 (23.9) |
4.0 (39.2) |
11.2 (52.2) |
16.3 (61.3) |
18.9 (66) |
17.7 (63.9) |
13.0 (55.4) |
6.2 (43.2) |
−0.8 (30.6) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
4.2 (39.6) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −17.4 (0.7) |
−15.4 (4.3) |
−9.6 (14.7) |
−1.2 (29.8) |
5.6 (42.1) |
11.0 (51.8) |
13.7 (56.7) |
12.7 (54.9) |
8.2 (46.8) |
2.0 (35.6) |
−4.4 (24.1) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
−0.6 (30.9) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −44.4 (−47.9) |
−42.8 (−45) |
−37.2 (−35) |
−21.7 (−7.1) |
−9.4 (15.1) |
−6.1 (21) |
−2.2 (28) |
0.0 (32) |
−5.0 (23) |
−12.8 (9) |
−26.1 (−15) |
−43.3 (−45.9) |
−44.4 (−47.9) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 68.9 (2.713) |
57.1 (2.248) |
64.6 (2.543) |
71.6 (2.819) |
96.3 (3.791) |
98.3 (3.87) |
99.4 (3.913) |
90.6 (3.567) |
115.4 (4.543) |
106.6 (4.197) |
98.1 (3.862) |
77.8 (3.063) |
1,044.6 (41.126) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 19.3 (0.76) |
11.8 (0.465) |
31.8 (1.252) |
56.3 (2.217) |
93.1 (3.665) |
98.0 (3.858) |
99.4 (3.913) |
90.6 (3.567) |
115.2 (4.535) |
99.1 (3.902) |
65.5 (2.579) |
22.7 (0.894) |
802.8 (31.606) |
| Average snowfall cm (inches) | 65.3 (25.71) |
58.6 (23.07) |
39.5 (15.55) |
16.7 (6.57) |
3.2 (1.26) |
0.1 (0.04) |
0.0 (0) |
0.0 (0) |
0.1 (0.04) |
8.1 (3.19) |
38.0 (14.96) |
70.1 (27.6) |
299.6 (117.95) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 18.6 | 15.3 | 13.4 | 13.0 | 14.1 | 14.0 | 12.6 | 11.9 | 14.0 | 15.5 | 17.7 | 20.1 | 180.3 |
| Average rainy days (≥ 0.2 mm) | 3.9 | 2.2 | 5.2 | 9.6 | 13.8 | 14.0 | 12.6 | 11.9 | 13.9 | 13.9 | 10.2 | 4.6 | 115.7 |
| Average snowy days (≥ 0.2 cm) | 17.7 | 14.8 | 10.6 | 5.8 | 1.0 | 0.03 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.17 | 3.0 | 11.4 | 18.2 | 82.7 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 86.4 | 116.5 | 151.0 | 190.5 | 235.2 | 245.8 | 266.1 | 224.8 | 154.4 | 118.3 | 64.6 | 69.0 | 1,922.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 30.8 | 40.1 | 41.0 | 46.9 | 50.7 | 52.1 | 55.8 | 51.2 | 40.9 | 34.9 | 22.7 | 25.7 | 41.1 |
| Source: Environment Canada[9][8][10] | |||||||||||||
Economy

North Bay is more economically diverse than many other Northern Ontario communities, although a large percentage of the city's jobs are public sector in nature with health, education and government dominating the list of the city's top employers.[11]
North Bay is the home of Nipissing University, founded in 1992 (previous name North Bay Normal School 1909-1953, North Bay Teachers College 1953-1973, Nipissing University affiliated to Laurentian University 1973-1992, independent public university separated from Laurentian University in 1992.), and of Canadore College, founded in 1967. Approximately 10,000 full-time students (and thousands more part-time students) are enrolled at the two post-secondary institutions, which share a campus in the west end of the city.
Between the early 1950s and 1990s 22 Wing/Canadian Forces Base North Bay was the community's leading industry. The cuts to the base by the federal government mentioned above, plus dramatic reductions in the number of its personnel—at one time 2,200 military members and civilian employees; in 2013 about 750—has resulted in a loss of tens of millions of dollars to the community, an impact felt by all North Bay's business sectors.[4]
North Bay is also home to The Algonquin Regiment, A Coy, a Canadian Force Army Reserve unit. B Coy of The Algonquin Regiment is located in Timmins.
The service industry, tourism, and transportation also play a significant role in the city's economy, as well as primary industry companies.
In recent years the city has gained prominence as a hub of arts and culture in Ontario, due to its vibrant community of artists, musicians, actors and writers. In 2004, the TVOntario program Studio 2 selected North Bay as being one of the top three most artistically talented communities in the province.
In August 2009, the comedy troupe The Kids in the Hall began filming their mini-series Death Comes to Town on location in North Bay. The city also has a long history of hosting film productions. In 1942 Captains of the Clouds was filmed in North Bay at the height of the Second World War. The film starred James Cagney as a Canadian bush pilot and also featured an appearance of famed fighter pilot Billy Bishop. The city has continued to host film productions, including the 2013 horror film The Colony starring Laurence Fishburne and Bill Paxton, and the drama Still Mine, featuring the actor James Cromwell in an award winning role. Another film production that occurred in North Bay was the 2014 thriller film Backcountry that starred Canadian actress Missy Peregrym.

Neighbourhoods
The city includes the neighbourhoods of Birchaven, Camp Champlain, Champlain Park, Cooks Mills, Eastview, Feronia, Gateway, Graniteville, Hornell Heights, La Fuente(Lobby Bar), Lounsbury, Kenwood Hills, Marshall Park, P.J. Clowe Rotary Park, Nipissing Junction, Pinewood, Sage, Ski Club, St. John's Village, Sunset Park, Thibeault Terrace, Thorncliff, Trout Mills, Tweedsmuir, Wallace Heights, West Ferris and Widdifield.
Waterfront development
The city has big plans for the waterfront. In the 1980s a mile long waterfront park/promenade was developed along the Lake Nipissing shoreline adjacent to the downtown core. Eventually such attractions as a mini-train ride and (more recently) two antique carousels (largely crafted by local artisans) were installed and quickly became very popular with tourists and locals alike. Now, work is getting underway on a large new multifaceted community park that will be developed on the former Canadian Pacific Railway yards that separated the downtown core from the existing waterfront park. In August 2009 a new pedestrian underpass opened connecting the downtown core to the waterfront for the first time since the CPR laid down tracks. Several more carousels, botanical gardens, a children's area and an extended mini-train ride will be among the park's attractions. The new community waterfront park is expected to transform the look and feel of the city centre and become a major tourist attraction for the city and region.
Media
Local newspaper is the North Bay Nugget.
Sports
Local teams
- Canadore College Panthers (Men's & Women's Volleyball/OCAA)
- Canadore College Panthers (Men's Basketball/OCAA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's & Woman's Hockey/OUA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's & Women's Soccer/OUA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's & Women's Volleyball/OUA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's & Women's Crosscountry Running/OUA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's Lacrosse/CUFLA)
- Nipissing University Lakers (Men's & Women's Basketball/OUA
- Nipissing University Lakers (Dance team)
- North Bay Bulldogs (Football/Northern Football Conference)
- North Bay Trappers Junior "A" (Hockey/Northern Ontario Junior Hockey League)
- North Bay Trappers Midget "AAA" (Hockey/Great North Midget AAA League)
- North Bay United (U-17 Men's Soccer)
- North Bay Stingers Midget Baseball (3 time provincial champions)
- Warriors of Hope Competitive Dragon Boat Team
- Nipissing Wild (Ontario Football Conference Varsity League)
- North Bay Battalion (OHL)
- North Bay Junior Varsity Bulldogs (Ontario Varsity Football league)
Kraft Hockeyville 2007
North Bay was crowned the winner of the Kraft Hockeyville competition in 2007. The New York Islanders and Atlanta Thrashers played an exhibition game at Memorial Gardens to a near capacity crowd.
North Bay Battalion
The North Bay Battalion is a major junior ice hockey team in the Ontario Hockey League based in North Bay, Ontario, Canada. The franchise was founded as the Brampton Battalion on December 3, 1996, and began play in 1998. Due to consistently poor attendance, the team relocated to North Bay prior to the 2013–14 OHL season.
Nipissing Lakers Hockey
The Nipissing Lakers are North Bay's newest hockey team. The Lakers are the 19th member of the Ontario University Athletics' Men's Hockey League (founded in 2009 in a partnership with Nipissing University and private investors). The Lakers play in historic Memorial Gardens (circa 1955) and share the building with the North Bay Trappers. Like their Northern Ontario counterparts in Thunder Bay (the Lakehead Thunderwolves), the Lakers attract an impressive number of local hockey supporters for their games in the OUA.
North Bay Trappers Junior "A"
The North Bay Trappers (formerly the North Bay Skyhawks) were relocated from Sturgeon Falls in 2002 (following the departure of the OHL's North Bay Centennials to Saginaw, Michigan). The Trappers are members of the 8 team NOJHL Junior "A" circuit (Northern Ontario Junior Hockey League). The Skyhawks/Trappers franchise has won 3 NOJHL championship titles (2002–03, 2003–04 & 2004–05). In April 2014 the Trappers were sold to become the Mattawa Blackhawks [12]
North Bay Bulldogs
The North Bay Bulldogs compete in the nine-team, Ontario-based NFC (Northern Football Conference). The Bulldogs were relocated from Brampton in 1991 to the Gateway City. The North Bay Bulldogs were welcomed into the Ontario Varsity Football League while losing all eight games (0–8) in their 2013 inaugural season.
Transportation

North Bay is located at the easternmost junction of Highway 11 and Highway 17, which are both segments of the Trans-Canada Highway. The two highways share a single route through the city core, between Algonquin Avenue and an interchange at Twin Lakes, along an urban limited-access road with reduced but not fully controlled access. Major arterial streets intersect directly with the highway, while minor streets end at a network of service roads connecting them to the arterials. At Algonquin Avenue, Highway 17 continues westward to Sturgeon Falls and Sudbury, while Highway 11 heads north toward Temiskaming Shores. At the eastern interchange, Highway 17 heads eastward toward Mattawa, Pembroke and Ottawa, while Highway 11 widens into a freeway and heads southerly toward Barrie and Toronto.
Highway 11 and Highway 17 both formerly had business spur routes through downtown North Bay, Highway 11B and Highway 17B, although both have been decommissioned by the province and are now designated only as city streets. North Bay is also served by Highway 63, a route which extends northeasterly from the city toward Thorne, where it crosses the Ottawa River and becomes Quebec Route 101.
Due to the steep incline of Algonquin Avenue/Highway 11 as it enters North Bay from the north on Thibeault Hill, the southbound lanes are equipped with the only runaway truck ramp on Ontario's provincial highway system.[13]
North Bay is served by the North Bay/Jack Garland Airport, which also receives and services military flights on behalf of the adjacent 22 Wing/CFB North Bay, is home to Canadore College Aviation Campus, and site of numerous aviation companies, including Voyageur Airways and the Bombardier Aerospace CL-415 water bomber final assembly and flight testing facility.
Train and intercity bus service in the city operates from the North Bay railway station, a joint terminal on Station Road.
The city operates a public transit system, North Bay Transit.
Community profile
| Canada 2006 Census | Population | % of total population | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Visible minority group Source:[14] | |||
| Black | 350 | 0.7 | |
| Chinese | 255 | 0.5 | |
| Filipino | 55 | 0.1 | |
| Latin American | 30 | 0.1 | |
| South Asian | 240 | 0.5 | |
| Southeast Asian | 35 | 0.1 | |
| Other visible minority | 180 | 0.2 | |
| Total visible minority population | 1,145 | 2.1 | |
| Aboriginal group Source:[14] | First Nations | 1,485 | 2.8 |
| Métis | 1,615 | 3 | |
| Inuit | 15 | 0 | |
| Total Aboriginal population | 3,210 | 6 | |
| White | 48,880 | 91.8 | |
| Total population | 53,235 | 100 | |
| Historical populations | ||
|---|---|---|
| Year | Pop. | ±% |
| 1891 | 2,210 | — |
| 1901 | 2,350 | +6.3% |
| 1911 | 7,737 | +229.2% |
| 1921 | 10,692 | +38.2% |
| 1931 | 15,528 | +45.2% |
| 1941 | 15,411 | −0.8% |
| 1951 | 17,944 | +16.4% |
| 1961 | 23,781 | +32.5% |
| 1971 | 49,187 | +106.8% |
| 1981 | 51,268 | +4.2% |
| 1991 | 55,405 | +8.1% |
| 1996 | 54,332 | −1.9% |
| 2001 | 52,771 | −2.9% |
| 2006 | 53,966 | +2.3% |
| 2011 | 53,651 | −0.6% |
| In January 1968, the City of North Bay amalgamated with West Ferris and Widdifield townships. | ||
- North Bay census agglomeration population: 63,424[15]
- Land area: 314.92 km2 (121.59 sq mi)
- Median total income of persons 15 years of age and over ($): 20,802
- Median family income ($) All census families: 53,668
- Average value of dwelling ($): 160,000
- % of the population with a university certificate, diploma or degree: 50.7
(Based on the Canada 2006 Census)
Mother tongue demographics
- Total 63,424 (100.0%)
- English 48,870 (78.0%)
- French 10,245 (16.3%)
- Non-official language 2,890 (4.6%)
- English and French 481 (0.8%)
- English and non-official language 160 (0.3%)
- French and non-official language 10 (0.0%)
- English, French and non-official language 10 (0.0%)
Notable people
- Giles Blunt, author
- Gerald Bull, aerospace engineer, expert in ballistics, assassinated
- Chuck Cadman, Politician and Member of Parliament
- Jessica Cameron, Actress
- Harvey Charters, silver medalist at 1936 Olympics in canoeing
- Billy Coutu, NHL hockey player
- Ab DeMarco Sr, former NHL hockey player
- Nick Denis, former mixed martial arts fighter and biochemist
- Kevin Frankish, is a Toronto-area media personality. He co-hosts Breakfast Television on City.
- Bobby Gimby, orchestra leader, singer/songwriter who wrote the Canadian Centennial song
- Mike Harris, former Premier of Ontario
- High Holy Days, rock music group
- Bill Houlder, former NHL player
- Troy Hurtubise, inventor
- Sam Jacks, inventor of ringette
- Byron M. Jones, Christian movie producer and managing partner of Pure Flix Entertainment
- Gordon Kannegiesser, former NHL player
- Sheldon Kannegiesser, former NHL player
- Larry Keenan, former NHL player
- Sean Kelly, glam-rock guitarist and vocalist
- Steve McLaren, former NHL/AHL Player
- Lise Meloche, Olympian (Biathlon: 1992 Albertville; 1994 Lillehammer)
- Gerry Mendicino, actor
- Andi Muise, model
- Chris Neil, NHL hockey player for the Ottawa Senators
- Claude Noël, former NHL head coach for the Winnipeg Jets
- Bryan Lee O'Malley, cartoonist, creator and author of the Scott Pilgrim series of graphic novels
- Mike O'Shea, CFL head coach for the Winnipeg Blue Bombers, and former CFL linebacker
- Barbara Olmsted, Olympian (Canoeing: 1984 Los Angeles (Bronze); 1988 Seoul)
- Nancy Olmsted, Olympian (Canoeing: 1984 Los Angeles; 1988 Seoul)
- Steve Omischl, world champion, freestyle skiing aerials
- Kate Pace, world downhill alpine ski champion
- Pete Palangio, former NHL player
- Tony Poeta, former NHL player
- Denis Rancourt, scientist, educational reform activist, former physics professor at the University of Ottawa
- Julia Rivard, Olympic athlete (canoe/kayak), business leader
- Craig Rivet, former NHL player
- Steve Shields, former NHL goalie
- Colin Simpson, bestselling author
- Lance Storm, professional wrestler
- Bert Templeton, hockey coach
- Scott Thompson, comedic actor
- Kenneth Thomson, 2nd Baron Thomson of Fleet
- Roy Thomson, Baron Thomson of Fleet
- Darren Turcotte, former NHL player
- Mike Yeo, former Minnesota Wild Head Coach
- Cartoonist Lynn Johnston lives just outside the city in nearby Corbeil, where the famous Dionne Quintuplets were also born. Roy Thomson, 1st Baron Thomson of Fleet started his empire in North Bay in 1931 when he purchased an AM radio station in Iroquois Falls, CFCH, and moved it to North Bay. Thomson Park in North Bay is named in his honour.
Sister cities
See also
References
- ↑ About North Bay | City of North Bay
- 1 2 3 "2011 Census Profile".
- ↑ Environmental Services | City of North Bay
- 1 2 3 22 Wing/Canadian Forces Base North Bay historical archives and active files
- ↑ North Bay Regional Health Centre Website
- ↑ IMDb link for filming locations
- ↑ Tornado causes minor damage in North Bay
- 1 2 3 "North Bay". Canadian Climate Normals 1961–1990. Environment Canada. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- ↑ "North Bay A". Canadian Climate Normals 1981–2010. Environment Canada. Retrieved April 12, 2014.
- ↑ "Daily Data Report for March 2012". Canadian Climate Data. Environment Canada. Retrieved 24 September 2016.
- ↑ Top 50 Employers - Workforce - Business in North Bay - City of North Bay
- ↑ NOJHL approves Jr. Trappers move to Mattawa - BayToday.ca
- ↑ "Northern Highways Program: 2010-2014. Ontario Ministry of Transportation.
- 1 2 "Pickering, Ontario (City) Census Subdivision". Community Profiles, Canada 2006 Census. Statistics Canada. Retrieved 2016-04-16.
- ↑ Canada 2006 Census Community Profiles: Census Agglomeration of North Bay. Statistics Canada.
- ↑ North Bay Did You Know
Notes
- ↑ Extreme high and low temperatures in the table below were recorded at North Bay from December 1887 to February 1982 and at North Bay Airport from March 1982 to present.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to North Bay, Ontario. |
-
 North Bay travel guide from Wikivoyage
North Bay travel guide from Wikivoyage - Official website
 |
Unorganized North Nipissing |  | ||
| Nipissing 10 Lake Nipissing |
|
Unorganized North Nipissing, East Ferris | ||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Callander |

