Ocean Park Hong Kong
|
Main entrance of Ocean Park in 2013 | |
| Slogan |
去玩去癲嚟Ocean Park! WOW It's My Park |
|---|---|
| Location |
Wong Chuk Hang and Nam Long Shan Southern District Hong Kong |
| Coordinates | 22°14′45.1″N 114°10′33.3″E / 22.245861°N 114.175917°ECoordinates: 22°14′45.1″N 114°10′33.3″E / 22.245861°N 114.175917°E |
| Opened | 10 January 1977[1] |
| Area | 91.5 hectares (226 acres) |
| Rides | |
| Total | 44 |
| Roller coasters | 4 |
| Water rides | 2 |
| Website | Ocean Park Official Website |
| Ocean Park Hong Kong | |||||||||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 香港海洋公園 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 香港海洋公园 | ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||


Ocean Park Hong Kong, commonly known as Ocean Park, is a marine mammal park, oceanarium, animal theme park and amusement park, situated in Wong Chuk Hang and Nam Long Shan in the Southern District of Hong Kong. Opened in 1977 by the then Governor of Hong Kong Sir Murray MacLehose, Ocean Park became popular but by 2005 was unprofitable and widely expected to lose out to the new Hong Kong Disneyland.[2][3][4] However, the Park responded with a bold HK$5.5 billion development plan that saw it expand to over 80 attractions and rides, and steadily grow visitor numbers to 7.6 million in 2014, making it the world's 13th most visited theme park, and the largest theme park in Asia.[5][6] Half of all visitors now come from mainland China, in growth that parallels rising mainland tourist visitor levels to Hong Kong over the same period.[7]
Covering an area of 91.5 hectares (226 acres), the park is separated by a large mountain into two areas, The Summit (Headland) and The Waterfront (Lowland). These areas can be reached by a 1.5 kilometres (0.93 mi) cable car system, or the Ocean Express funicular railway. To ascend the Headland comprises several hills, visitors can use Hong Kong's second longest outdoor escalator.[8]
The theme park has various attractions and rides, including four roller coasters, and also animal exhibits with different themes, such as a giant panda habitat, rainforest and polar displays, as well as an aquarium featuring the world's largest aquarium dome. Between 1979 and 1997, Ocean Park was most famous for its signature killer whale, Miss Hoi Wai (海威小姐).
As well as being an amusement park, Ocean Park Hong Kong aims to merge entertainment and education, including conservation advocacy. However it has been criticised by wildlife advocates for practices including the wild capture of large sea animals, such as dolphins and orca, and the presentation of shows featuring such animals performing.[9][10][11]
In 2013-14, Ocean Park had a turnover of HK$2.0 billion, with earnings before tax of HK$633 million.[6]
History
Opened in January 1977 by the Governor of Hong Kong, Sir Murray MacLehose, Ocean Park was constructed as a subsidiary of the Hong Kong Jockey Club, with HK$150 million of funding. The land was provided free by the Hong Kong Government. Between 1982 and 1984, the Jockey Club put a further HK$240 million into developing facilities at Tai Shue Wan and thrill rides at the Summit.
Ocean Park ceased to be a Jockey Club subsidiary on 1 July 1987, becoming its own statutory body, with a Government-appointed Board. The Jockey Club established a HK$200 million trust to ensure the Park's continued development. At present, Ocean Park is managed by the Ocean Park Corporation, a financially independent, non-profit organisation.
In 2003, Allan Zeman, known for leading the creation of the popular Lan Kwai Fong entertainment district of Hong Kong, was appointed Chairman of Ocean Park Corporation, a position he held for 11 years.[6]
In 2005, the year that rival Hong Kong Disneyland opened, Ocean Park unveiled a Master Redevelopment Plan (MRP), under which older features at the park were rejuvenated and new areas developed. The number of attractions more than doubled, from 35 to over 80. The Lowland was redeveloped as a new area called the Waterfront, while the old 'Headland' became 'The Summit', with polar and rainforest exhibits. A dedicated thrill ride area, Thrill Mountain, opened, and the children's area was refurbished as Whisker's Harbour.
The first of the new developments, the Amazing Asian Animals, showcasing some of the Asia's endangered creatures, including giant pandas, red pandas, Chinese giant salamanders, Asian small-clawed otters and the Chinese alligators, and Ocean Express, a funicular train system capable of transporting 5,000 visitors per hour between the Summit and the Waterfront, were launched in 2009.
In January 2011, the new flagship attraction area Aqua City was opened. The zone features the Grand Aquarium, designed by the Pritzker Prize-winning architect Frank Gehry, displaying some 5,000 fish from over 400 species, and the world's first and only 360° water screen show Symbio.[12]
In June, the Rainforest, an integrated theme zone featuring over 70 exotic animal species, was opened.
In March 2012, new attraction zone Old Hong Kong opened, evoking the streetscapes and spirit of Hong Kong between the 1950s and the 1970s from various perspectives. In April, the newly refurbished Hong Kong Jockey Club Sichuan Treasures opened. In July, the final element of the redevelopment, Polar Adventure, opened, featuring animals such as penguins, Pacific walruses, spotted seals, northern sea lions, snowy owls and Arctic foxes, aiming to highlight some of the conservation issues they face.
A 20,000 sq ft shark aquarium opened in July 2014 at the former Atoll Reef site.
Attractions
Ocean Park now comprises two main attraction areas: the Waterfront and the Summit, subdivided into eight attraction zones: Amazing Asian Animals, Aqua City, Whiskers Harbour, Marine World, Polar Adventure, Adventure Land, Thrill Mountain and the Rainforest.
The Summit (高峰樂園)
Marine World (海洋天地)


This area was formerly known as two distinct areas: Marine Land (海洋天地) and Headlands Rides (山上機動城).
- Pacific Pier (太平洋海岸) – Mimics the rocky habitat of seals and sea lions on the Northern Californian coast. Allows visitors to walk under the pier to view these marine mammals in the water, complete with simulated waves.
- Chinese Sturgeon Aquarium – Yangtze River Exploration (中華鱘館- 長江足跡) – The 3,500 square-metre freshwater aquarium houses rare Chinese sturgeon along with other native species of the Yangtze River in an educational exhibit on this fragile ecosystem.
- Ocean Park Tower (海洋摩天塔) – One of the tallest observation towers in Southeast Asia. Rises 200 metres above sea level with a rotating observation deck at the top offering 360° views of the South China Sea, as well as Aberdeen and the islands of Lantau, Lamma and Cheung Chau.
- Sea Jelly Spectacular (水母萬花筒) – Opened in 2006. Southeast Asia's first standalone sea jelly exhibit. Showcases an underwater 'garden' of over 1,000 sea jellies from around the globe, set to lighting, music and multimedia special effects.
- The Dragon (瘋狂過山車) – Hong Kong's largest roller coaster featuring two giant loops on a 842-metre-long track
- The Abyss (極速之旅) – A Turbo Drop type of amusement ride, the Abyss raises passengers up 62 metres (203 ft) in 20–25 seconds before thrusting them downward at speeds of up to 65 km/h, faster than freefalling. Passengers feel a force of minus one (−1) G.
- Flying Swing (飛天鞦韆) – Swings passengers up 7 metres (23 ft) into the air at 11 rpm in an undulating wave motion. It has 32 single-seater gondolas.
- Crazy Galleon (沖天搖擺船) – A suspended ship that tilts passengers back and forth through a 75° arc, 15 metres above the ground.
- Ferris wheel (摩天巨輪) – 27 metres (89 ft) tall, with 18 gondolas.[13]
- The Eagle (翻天飛鷹) – Hoists passengers 31 metres (102 ft) into the air and whirls them around at a maximum gyro drive speed of 22 rpm. It has 28 gondolas, each seating two people.
- Marine World Games Zone (海洋世界攤位遊戲)
- Garden of Joy (怡庭) – Landscaped with flowing streams, bridges, lush greenery and multi-coloured koi fish.
Thrill Mountain (動感天地)
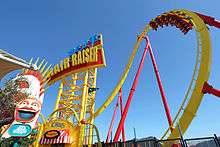
Thrill Mountain was opened in December 2011. It is a carnival-themed area of 222,800 square feet. It offers five rides, eight booth games, as well as food, beverages and merchandise.
- Hair Raiser (動感快車) – Hong Kong's first and only floorless roller coaster. Riders are plunged towards the South China Sea with their legs dangling in the air. The ride travels at up to 4.0G during acceleration and 88 kilometres per hour – the fastest roller coaster in Hong Kong.
- Whirly Bird (超速旋風) – A chair swing ride standing 30 metres (98 ft) tall, allowing passengers to control their vintage plane, lifting and dipping it through a joystick.
- Bumper Blaster (橫衝直撞) – Colourful bumper cars that can carry two in each car.
- Rev Booster (雷霆節拍) – Strong musical rhythms drive sudden reversals in direction, generating body-twisting centrifugal force.
- The Flash (翻天覆地) – A ride that spins riders up to 22 metres (72 ft) into to air, and rotates at a full 360°, reaching a G-force of 3.9G and a top speed of 60 km/hour.
- Bungee Trampoline (威水笨豬跳) – A trampoline that allows visitors to jump really high while strapped in bungee harnesses, to get the idea of bungee jumping.
Adventure Land (急流天地)
- Mine Train (越礦飛車) – A steel "mine train" roller coaster perched on the edge of a cliff overlooking Aberdeen Harbour.
- Raging River (滑浪飛船) – A log flume-type water ride that takes passengers through "tropical waterfalls", narrow ravines and finishes by shooting them down a slide at almost 60 km/h.
Polar Adventure (冰極天地)

Polar Adventure was opened on 13 July 2012, featuring the North Pole Encounter, South Pole Spectacular and Arctic Fox Den, as well as the Arctic Blast roller coaster. Animals include king penguins, southern rockhopper penguins, gentoo penguins, pacific walruses, spotted seals, Steller sea lions, snowy owls and Arctic foxes.
The attraction's carbon footprint is reduced through environmental technology including a ventilation system that recycles residual cool air to cool down the Life Support System (LSS) and plant room area before being discharged, which it is claimed cut electricity consumption by a third.
- Arctic Blast (極地時速) – A steel "roller coaster" located in the Polar Adventure with various dips and side turns. It is suitable for the whole family.[14]
- North Pole Encounter (北極之旅) – visitors can meet Pacific walruses and spotted seals, and other animals from the North Pole including northern sea lions and snowy owls. The animals can also be viewed via an underwater tunnel.
- South Pole Spectacular (南極奇觀) – houses three penguin species: king penguins, southern rockhopper penguins and gentoo penguins. The viewing chamber, glass-panelled floors, walkways and balconies overlooking the water allow visitors to see the penguins from different angles.
- Arctic Fox Den (雪狐居) – visitors can see Arctic foxes here to learn about their behaviour and the impact of humans on their habitat.
The Rainforest (熱帶雨林天地)

The Rainforest was opened on 14 June 2011. Dozens of avian, terrestrial and aquatic animals living inside buttress roots accompany visitors on their immersive exploration of biodiversity.
- The Rapids (熱帶激流) – A family river rapids ride along a rushing river that surrounds the themed zone.
- Expedition Trail (熱帶雨林探險徑) – A walk-through rainforest exhibits where, visitors can meet some of the world's most striking tropical species, including the kinkajou, capybara, green anaconda and green aracari.
- Rainforest Why Zone (雨林求知地帶) – Trainers explain about rainforest animals in the wild and in captivity.
The Waterfront (海濱樂園)

.jpg)
Aqua City (夢幻水都)
Aqua City was opened in January 2011 and occupies around 200.000 square feet. It features:
- Grand Aquarium (海洋奇觀) – Inside the Grand Aquarium, visitors can get up close to some 5,000 fish from over 400 species, such as the scalloped hammerhead and manta ray. Strolling through the Reef Tunnel and Panoramic Ocean Gallery, visitors can see the world's largest viewing dome in an aquarium, at 5.5 metres in diameter, and a 13-metre acrylic viewing panel, one of the largest in the world. It also features the world's first and only 360° water screen show Symbio! and Hong Kong's only restaurant inside an aquarium.
- Sea Life Carousel (環迴水世界) – Hong Kong's largest carousel, 15.1 metres across, with 61 carriers in 13 different designs inspired by endangered sea animals, holding up to 81 passengers.
- Old Hong Kong (香港老大街) – Offers an immersive experience of culture, history, and delicacies of Hong Kong between the 1950s and the 1970s. It features a replica of Edinburgh Place Ferry Pier's clock tower and its signature toll, a manually retrofitted heritage tramcar and rows of tong lau-style apartment buildings. Visitors can also try more than 70 types of local street food and beverage that evoke the flavour of old Hong Kong. The area also provides a wide array of classic booth games.
- Waterfront Plaza (海濱樂園廣場) – Features a lively carnival setting with a rotating mix of shows, magic and other acts performed by clowns, acrobats and jugglers. This area sets the backdrop for many of Ocean Park's festive events.
Amazing Asian Animals (亞洲動物天地)
- Giant Panda Adventure (大熊貓之旅) – A purpose-built habitat that houses two rare giant pandas - Ying Ying and Le Le, as well as red pandas. It also houses the critically endangered Chinese giant salamander.
- Panda Village (熊貓山莊) – displays Asian small-clawed otters and a variety of Asian bird life in a woodland setting.
- Gator Marsh (鱷魚潭) – A wetland setting, featuring endangered Chinese alligators from Yangtze River, grass carps and other Asian fish.
- Goldfish Treasures (金魚寶殿) – A goldfish pavilion featuring the latest and rarest varieties such as the Black Oranda and Blue Phoenix Eggfish. Explains the history and importance of the goldfish in Chinese culture.
- Hong Kong Jockey Club Sichuan Treasures (香港賽馬會四川奇珍館) – Home to one of Ocean Park's giant pandas, An An, and two golden monkeys, Le Le and Hu Hu, from Sichuan. The exhibit also acts as a resource centre on the care and conservation of this species. Jia Jia also once lived there until its death.
- Emerald Trail (自然大揭秘) – A verdant garden featuring natural settings with flowers, tall trees, stone bridges and gentle pools.
Whiskers Harbour (威威天地)
Whiskers Harbour, previously called Kid's World, features attractions for younger children, over an area 14,200 square metres.
- Balloon Up-up-and-away (昇空奇遇) – A hot air balloon-themed Ferris wheel for very young visitors.
- Clown a Round (小丑旋風) – This merry-go-round has clown cars for younger kids to whirl around in.
- Frog Hopper (蛙蛙跳)– A kid's version of a thrill ride. Young visitors strap into the mechanised 'frog', hop high into the air and land back on their feet.
- Merry-go-round (幻彩旋轉馬)– A classic children's merry-go-round with gilded fairytale horses.
- Bouncer House (彈彈屋) – An inflatable, fully padded, covered house for children to bounce around in.
- Whiskers Harbour Playground (威威天地遊樂場) – A safe, child- (and parent)-friendly haven for kids to run around and explore slides, see-saws, tunnels and jungle gyms.
- Interactive Shadow Play (互動影子樂) – Kids get to play simple spelling and skill games on interactive multimedia screens. Correct answers are rewarded with audiovisual presentations.
- Animal Story Corner (動物故事坊) – Children can explore interactive educational displays about different land, air and sea animals, and what makes each of them distinct.
- Whiskers Harbour Games Zone (威威天地攤位遊戲) – The area offers over twenty classic arcade games.
- Toto the Loco (砵砵火車頭) – A small train that takes young visitors through a mini forest to meet clowns playing accordions, cellos and violins.

Former attractions
Former attractions of Ocean Park include:
- Atoll Reef. It was located in Marine Land, the former name of an area now part of Marine World. Closed in early 2011 after 34 years of operation, many of the animals were transferred to the new Grand Aquarium.[15]
- Middle Kingdom. Opened in 1990, this area featured traditional Chinese culture and heritage. It closed in 2001,[16][17] however, the Middle Kingdom Restaurant is still in operation.
- The Bird Paradise (雀鳥天堂) area, located in Tai Sue Wan near Adventure Land, closed down in 2013. It contained The Aviaries (百鳥居) and Flamingo Pond (紅鸛池). Plans are underway to redevelop this area.[18]
Shows

Symbio! (雙龍奇緣)
- In front of the Grand Aquarium in Aqua City, the Lagoon hosts Symbio!, a night time show that features the world's first and only 360° water screen. The show also features lighting, fireworks and sound effects, set against a soundtrack. It illustrates the symbiotic relationship between humans and nature through the story of two dragons.
Emperors of the Sky (天上王者)
- An educational bird show featuring birds of prey including steppes eagles, Lanner falcons, striated caracaras and turkey vultures, along with 70 other species of birds, at the newly refurbished Bird Theatre in Amazing Asian Animals.
Ocean Theatre (海洋劇場)
- Located in Marine World, the Ocean Theatre currently shows "Sea Dreams!", a production featuring the Park's marine animal stars in a story about the importance of marine conservation.
Whiskers' Theatre (威威劇場)
- Located in Whiskers Harbour, Whiskers Theatre features two shows, "Sea Lion Fun Time" and "Whiskers and Friends". The former explores a day in the life of the Park's sea lions, while the latter is a variety show starring the Park's mascots.
Animals
Ocean Park holds over 12,000 animals and highlights its educational and scientific research programmes, alongside the animal displays and entertainment.[19]
The Park has had success breeding rare shark species, bottlenose dolphins, sea lions, sea horses, penguins, anacondas, red-handed tamarins, Pygmy marmosets and several species of sea jellies. Endangered birds and butterflies are also hatched and reared at Ocean Park.
- Giant pandas

A pair of giant pandas, a male named An An (安安) and a female called Jia Jia (佳佳), were given to Ocean Park by China in 1999. The pair were given permanent homes in the 'Hong Kong Jockey Club Sichuan Treasures' area. In 2007, two more pandas were given to Hong Kong to mark the 10th anniversary of Hong Kong's return to Chinese sovereignty. The pair of two-year-old pandas, a male called Le Le (樂樂) and a female named Ying Ying (盈盈), arrived at Ocean Park from the China Conservation and Research Centre in Wolong in Sichuan province. After quarantine, they made their first public appearance in Giant Panda Adventure on 1 July 2007.[20] A new compound was prepared at the park to house them on their arrival. In August 2015, Jia Jia became the oldest breeding panda in the world at the age of 37. Sadly, Jia Jia began to suffer the effects of advanced aging in October 2016, refusing most food and fluids and rapidly losing weight. On October 16, after having been found unable to walk, her vets decided to euthanize her. Then age 38 (114 in panda years), she was sometimes billed as the oldest panda in the world. She was definitely known to be the oldest panda in captivity. Although there is no such certain data regarding pandas in the wild, their life expectancy in the wild is 15 to 20 years, giving the claim a good likelihood of being correct. [21]
- Dolphins
The Park's Marine Mammal Breeding and Research Centre (MMBRC) houses a total of nine Indo-Pacific bottlenose dolphins. Previously in July 2009, Domino and Domisa, two dolphins from Bayworld in Port Elizabeth, South Africa, arrived at Ocean Park. The dolphins, a father and daughter pair, were separated to ensure that they do not mate with each other. They formed part of Ocean Park's breeding programme.[22] In May 2001, two of Ocean Park's female dolphins, Ada and Gina delivered two healthy calves, a female and male respectively, the world's first two bottlenose dolphin calves as a result of artificial insemination. This marked an important stage in reproductive physiology and controlled breeding of marine mammals.
- Chinese sturgeon
The Chinese sturgeon were introduced to the park in 2008, and as of 2013, Ocean Park houses nine Chinese sturgeons, displayed in Chinese Sturgeon Aquarium – Yangtze Exploration. To mark China's hosting the Olympic Games, the Chinese Central Government made a gift of five rare Chinese sturgeon, symbolising the five Olympic rings, with Ocean Park as the recipient. Two were bred by the Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute and three by the Beijing Aquarium. The fish made their debut on 20 June 2008.[23] However one of them died after a few days, apparently bitten by a barracuda. On 14 July 2008, it was announced that Hong Kong would receive another five sturgeons from the Chinese National Aquatic Wildlife Conservation Association in time for 8 August opening ceremony, to complement the four fish already in situ. The park's management decided to evict its sharks from their aquarium in favour of the new arrivals.[24] On 12 December 2008, a second sturgeon died from an infection. A third one died from an injury and two nine-year-old sturgeon were found to be ill in January 2009. The two sick fish, measuring 2.3m and 1.5m, were returned to the Yangtze River Fisheries Research Institute for expert care.[25]
- Orca – Miss Hoi Wai (海威小姐)
Hoi Wai was a female Orca, who was captured near Iceland in 1975 and kept at Ocean Park between January 1979 and April 1997.[26][27] Hoi wai was about 5 metres (16 ft) long and weighed about 1,800 kilograms (4,000 lb).[28] In Hong Kong, Miss Hoi Wai (海威小姐) is still considered an icon and celebrity to this day.
Animal encounter programmes
Ocean Park runs a series of programmes called "Get Closer to the Animals" which offer supervised access to its resident animals, from swimming with dolphins to learning to be a panda keeper. Holders of a diving certificate can even enter the Grand Aquarium, while an overnight camp within its dome offers a drier way to view the underwater world. There are behind-the-scenes tours of many facilities, often including the chance to get close to animals such as penguins, seals and other polar animals.
Animal mascots
Ocean Park introduced a waving sea lion named Whiskers (known as Wai Wai in Chinese) as its major mascot in 2000. Subsequent members of the Ocean Park 'family' include James Fin (a shark), Jewel (a butterfly, now retired), Swift (a dolphin), Chief (a parrot), Professor (a turtle), Later Gator (an alligator), Redd (a red panda), Goldie (a goldfish), Tux (a penguin) and four giant pandas: An An, Jia Jia, Le Le and Ying Ying.
Internal transport

Ocean Park features a 1.5-kilometre (0.93 mi) long cable car system connecting the Waterfront and the Summit with an eight-minute journey, with views of the South China Sea. It has a capacity of 4,000 passengers per hour with 252 cable cars on two pairs of ropeways. Each car can hold six passengers.[29][30][31][32]
Hong Kong's second longest outdoor escalator system, at 225 metres long provides the main link between facilities at Tai Shue Wan and the Summit.[33] (The longest system is the Central-Mid-levels Escalators).
The 'Ocean Express' funicular railway system between the Summit and the Waterfront can carry 5,000 people per hour on its three-minute journey. This themed ride utilises multimedia effects to simulate the feeling of travelling into the depths of the sea.
Access
At present, most people reach the park via Citybus Ocean Park Express (Route 629) from Admiralty Station, which departs every 10 minutes and has a journey time of about 25 minutes. There are no intermediate stops between Admiralty and Ocean Park, but some departures during the day actually originate at the Star Ferry Pier, stopping at Exchange Square and Admiralty Station on the way.
Ocean Park Station, a new stop on the Hong Kong MTR, will reduce travelling time from Admiralty to four minutes.[34] The station will open with the rest of the line in December 2016.[35]
Conservation
Ocean Park puts much effort into education and research about animal conservation, by operating observatories, laboratories, an education department, and the Ocean Park Conservation Foundation, Hong Kong (OPCFHK), a fund that advocates, facilitates and participates in the conservation of wildlife and habitats, with an emphasis on Asia, through research and education. In 2013/2014, the foundation funded 44 conservation projects, covering 30 species in 12 countries with a total of HK$13 million (out of the Park's total turnover of HK$2 billion), a sharp increase over funding a few years earlier. The foundation was formed in 2005 from the merger of two earlier organisations, the Ocean Park Conservation Foundation (OPCF), founded 1993, and the Hong Kong Society for Panda Conservation (HKSPC), founded 1999.
Ocean Park Hong Kong was the first institution in the world to successfully artificially inseminate bottlenose dolphins, and has developed several new breeds of goldfish.
Since 2006, OPCFHK has collaborated with the Hong Kong Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department to handle cetacean stranding cases within Hong Kong waters. After the 2008 earthquake in Sichuan, OPCFHK established a Giant Panda Base Rebuilding Fund and donated equipment to the affected nature reserves.
Ocean Park has created education programmes, such as the Ocean Park Academy (OPA), begun in 2004, through which the Park runs educational tours for schoolchildren and workshops for teachers from the Hong Kong Institute of Education. Every year, the Park offers over 35 core courses for around 46,000 students on six big topics: giant pandas and red pandas, dolphins and sea lions, birds, fishes, plants, and mechanical rides.
The Marine Mammal Breeding and Research Centre (MMBRC) set up by Ocean Park serves as a centre to house nine dolphins and conduct research on the breeding of dolphins. MMBRC is divided into 6 separate activity zones, and provides behavioural training and basic husbandry to the dolphins. It also plays a part in research work on the echolocation capabilities of dolphins. For five weeks in 2013, MMBRC was open for public visits.
Criticism
Ocean Park has been criticised by wildlife advocates for certain practices including the wild capture of large sea animals, such as dolphins and orca, and the presentation of shows featuring such animals performing. Opponents have highlighted their views on international "Empty the Tanks" day – a non-violent multinational demonstration that aims to end the capture and sale of wild dolphins to marine parks, where the creatures are said to die younger and breed much less. There is concern for the psychological state of the mammals alongside their physiological needs. And the advocates say it sends the wrong message, not only to visitors but also to marine parks in mainland China, which, if they copied the Park's practices, could have a significant impact on wild populations.[9][10][11]
Major annual events
Ocean Park hosts five major events throughout the year: an Animal in High Definition Month, the Ocean Park Summer Splash, the Halloween Bash and Christmas and Chinese New Year celebrations.
Since 2008, the Park's annual Halloween events, held from September to 1 November, have become very popular, including among non-regular visitors. Themes such as "Fear Formula" and "Haunted Hong Kong" provide modern twists on the traditional haunted house along with various attractions and activities.
- Animal in High Definition Month
The Animal in High Definition Months enable visitors to encounter a variety of rare animals up close, with educational experts on hand to disseminate information about these creatures. The Animal in High Definition Month for 2010 had a reptile theme called, "Mighty Dragons". In 2012, the event let visitors explore Chinese national treasures, featuring the display of two Sichuan golden monkeys.
- Ocean Park Summer Splash
The event is held in summer every year, in which visitors partake in various wet and wild thrills including water games and water slides.
- Christmas Sensation
Christmas themed celebrations held from December to January every year.
- Chinese New Year Fiesta
Chinese New Year celebration events held around January to February every year. The celebration usually features lantern displays, God of Fortune visits, lion and dragon dances. In 2013, the CNY Fiesta featured a 12-metre spinning lantern, as well as a traditional Chinese drum show.
Future expansion
Ocean Park is planning to design a four-star, 495-room Ocean Hotel. Construction will start by the middle of 2014 at the earliest, with the hotel slated to open in 2017. Ocean Park will spend HK$2.5 billion on the hotel project and another HK$1.6 billion on land. Ocean Park's second hotel is expected to be completed by the end of 2018 or by early 2019.
Ocean Park will add 30 attractions in its latest round of development projects starting 2014. Among the new attractions will be a 400,000 sq ft Water World featuring an indoor surfing simulator, 13 slides, wave pools and a Lazy River. The park is also planning to provide free Wifi to visitors in the near future along with a smart phone application to check queue times at different attractions later in the year.
Awards
The park has won several awards, including The World's Seventh Most Popular Amusement Park and one of the "50 Most Visited Tourist Attractions in the world" by Forbes. In November 2012, Ocean Park became the first theme park in Asia to win the Applause Award from the International Association of Amusement Parks and Attractions.[8][36][37]
Incidents
- On 5 December 2010, seven tourists were injured when a train driver triggered the emergency braking system by mistake on the Ocean Express tunnel railway at the park. Ocean Park was required to install caps over the emergency brake button for their trains before reopening.
- A 50-year-old man, Cao Tao, on holiday from Hubei in China, fell to his death on 10 April 2014 as he was sitting on a railing, lost balance and fell 11 metres down from the area known as The Summit in Ocean Park.[38] Police said an initial investigation found nothing suspicious and indicated it was an accident.
See also
- House of Fury, a 2005 Hong Kong film. One of the main protagonists works as a dolphin trainer at Ocean Park
- Allan Zeman, Chairman of Ocean Park from July 2003 to June 2014
References
- ↑ http://www.oceanpark.com.hk/html/en/footer/corporate-information/facts.html
- ↑ Allan Zeman: Hong Kong's Mouse Killer, Forbes, 13 Feb 2007
- ↑ Catching the Wave at Ocean Park, Citi International Case Competition 2008
- ↑ Varsity survey shows Ocean Park Challenged, Periscope, Joyce Lam, Chinese University of Hong Kong
- ↑ "TEA/AECOM 2014 Global Attractions Attendance Report Report" (PDF). Themed Entertainment Association. 2015. Retrieved June 4, 2015.
- 1 2 3 Ocean Park press release, 3 December 2014
- ↑ Ocean Park press release, 18 Feb 2011
- 1 2 "Corporate Information – General Facts". Ocean Park Corporation. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- 1 2 'Empty the tanks': Hong Kong's Ocean Park at centre of activists' battle to stop dolphin captivity, SCMP, 27 June 2015
- 1 2 Wild or captivity?, HK Dolphin Watch
- 1 2 Murky waters, China Daily, by Simon Parry, 16 March 2011
- ↑ Disney Rival Ocean Park to Woo Visitors With Egg-Shaped Hong Kong Aquarium Bloomberg.com Wendy Leung – 11 January 2011 12:01 PM GMT+0800
- ↑ Ferris Wheel | Ocean Park Hong Kong
- ↑ "Arctic Blast (Ocean park)". rcdb.com. Rollercoaster Database. Retrieved 3 September 2012.
- ↑ Ocean Park press release 02-01-2011
- ↑ Cheung Chi-fai, "Middle Kingdom to shut door on history", South China Morning Post, 2 March 2001
- ↑ Ocean Park press release, 02-03-2001
- ↑ "Tai Shue Wan Development at Ocean Park". Project Profile. May 2013
- ↑ Ocean Park visitor numbers slip on wet weather, new rules for mainland tourists, SCMP, 4 December 2014
- ↑ Diana Lee, Baby hopes for new HK celebrities, The Standard, 27 April 2007
- ↑ Matthew Young , The Mirror, 16 October 2016
- ↑ Ottermann, Birgit (1 July 2009). "PE dolphins ready for HK trip". News24. Retrieved 3 August 2009.
- ↑ ""Living fossil of fish" Chinese sturgeons debut in HK". Xinhua. 20 June 2008.
- ↑ Wu, Elaine (15 July 2008). "Ocean Park nets five more sturgeon". South China Morning Post.
- ↑ "HK returns sick sturgeon to China". BBC. 8 January 2009.
- ↑ "About Hoi Wai / Suzie (OO7901)". cetacousin.bplaced.net. Cetacean Cousins. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ↑ "They did not survive the show". orcahome.de. Stephan Jacobs. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ↑ Reeves, Randall R.; DeMaster, Douglass P.; Hill, Cynthia L.; Leatherwood, Stephen. "Survivorship of Odontocete Cetaceans at Ocean Park, Hong kong, 1974–1994". Asian Marine Biology. Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press. 11–12. Retrieved 3 July 2012.
- ↑ "Ocean Park: a wonderland in Hong Kong | gbtimes". Radio86.com. 22 February 1999. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ↑ "樂園1.5公里纜車 盡覽港半島景色". Tvbs.com.tw. Retrieved 17 March 2013.
- ↑ Bradsher, Keith (25 March 2007). "Taking to the Sky Above the City Crowds". The New York Times.
- ↑ "Hong Kong Attractions". The New York Times.
- ↑ Escalator, Ocean Park information
- ↑ "Journey Time". South Island Line (East). MTR Corporation.
- ↑ Hon, Isabelle (28 October 2015). "Ocean Park MTR Station Opens... Sort Of". HK Magazine.
- ↑ "Ocean Park, Hong Kong – World's Seventh Most Popular Amusement Park – Meet Pandas Here!". China Travel Golden Route. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- ↑ "The 50 Most Visited Places in The World". Itv News. Archived from the original on 20 August 2009. Retrieved 25 August 2009.
- ↑ Clifford, LO. "Mainland Chinese tourist plunges 11 metres to his death in Ocean Park accident". South China Morning Post. South China Morning Post. Retrieved 22 February 2015.
External links
- Official website
 Media related to Ocean Park, Hong Kong (category) at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Ocean Park, Hong Kong (category) at Wikimedia Commons
