2010 Mentawai earthquake and tsunami
 | |
 | |
| Date | October 25, 2010 |
|---|---|
| Origin time | 14:42:22 UTC |
| Magnitude | 7.7 Mw |
| Depth | 12.8 miles (20.6 km) |
| Epicenter | 3°27′50″S 100°05′02″E / 3.464°S 100.084°ECoordinates: 3°27′50″S 100°05′02″E / 3.464°S 100.084°E[1][2] |
| Areas affected |
Indonesia Malaysia |
| Casualties | 408 dead + 303 missing[3] |
The 2010 Mentawai earthquake occurred with a moment magnitude of 7.7 [1] on 25 October off the western coast of Sumatra at 21:42 local time (14:42 UTC).[4] The earthquake occurred on the same fault that produced the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. It was widely felt across the provinces of Bengkulu and West Sumatra and resulted in a substantial localized tsunami that struck the Mentawai Islands.[5]
Tectonic setting
The island of Sumatra lies above the Sunda megathrust, the interface between the subducting Australian Plate and the overriding Sunda Plate. Movement on this structure has been responsible for many large historical megathrust earthquakes. The most recent sequence of large ruptures started with the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and included the 2005 Nias–Simeulue earthquake and the 2007 Sumatra earthquakes.[6][7]
Earthquake
The earthquake occurred around 150 miles (240 km) west of Bengkulu, close to the Mentawai Islands, southwest of South Pagai. The USGS first reported the hypocenter of the quake at 20.5 miles (33.0 km) deep,[4] but later changed it to 8.8 miles (14.2 km) deep[8] and then 12.8 miles (20.6 km). The USGS also estimated the magnitude at 7.5 before revising the measurement to 7.7.[1] The intensity was MM IV in Bengkulu and MM III in Padang.[9]
The October 2010 earthquake is thought to have been a result of thrust faulting along or near the plate interface from the calculated focal mechanism and the focal depth. According to seismic hazard potentials and deformation features, the Sunda Trench can be divided into several segments. The southern segment lies to the south of Siberut Island. The rupture area of this earthquake is situated within the southern segment, where historical earthquakes include the earthquake of 1797 and the Mw ~ 9.0 1833 Sumatra earthquake.[1][10]
Unlike in 2004, the tsunami caused by the October 2010 earthquake did not propagate westwards and other Indian Ocean nations were unaffected. It has been suggested that the tremor may have been a large aftershock of the much larger Sumatran earthquakes of September 2007.[11] The earthquake occurred around seven hours after the eruption of Mount Merapi on the Indonesian island of Java. However, the two events are not thought to be linked.[12]
Impact
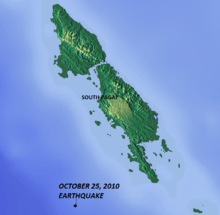
The earthquake's worst effects were felt on the remote Mentawai Islands. On the island of South Pagai, the tsunami that followed the earthquake reached a height of 3 m (9 ft) and swept as far as 600 m (1800 ft) inland. According to Indonesian officials, more than 20 villages were hit by the tsunami, displacing more than 20,000 people[12] and affecting about 4,000 households. The coastal village of Betu Monga on South Pagai was reported to have been destroyed with many residents still missing.[13] Many residents of the villages of Peurogat and Beleerakso were also reported to be missing.[12] Eighty percent of the houses in the North Pagai village of Muntei Baru were reported damaged or destroyed.[14]
According to a spokesperson for the Indonesian Agency for Meteorology, Climatology and Geophysics (BMKG), the quake was felt in several mainland towns, but no damage or deaths were reported.[15] The Mentawai Islands may have acted as a barrier, shielding the Sumatran coast by absorbing the brunt of the tsunami.[14] As of October 30, 2010, the confirmed death toll stands at 435, with 110 more unaccounted for. Many of the missing are believed to have been swept out to sea.[3]
Relief teams were initially unable to reach the islands due to poor weather conditions and rough seas. The Indonesian military was mobilized and international aid organizations also began a relief effort.[12][13] The first aid began to arrive on October 27, two days after the earthquake and tsunami.[14]
Tsunami
Many villages on the islands were affected by the tsunami, which reached a height of 3 m (9 ft) and swept as far as 600 m (1800 ft) inland. The tsunami caused widespread destruction that displaced more than 20,000 people and affected about 4,000 households. 435 people were reported to have been killed, with over 100 more still missing.[3] The subsequent relief effort was hampered by bad weather[13] and the remoteness of the islands, which led to delays in the reporting of casualties.[16]
Aftershocks
Several aftershocks have been recorded since the initial quake,[17] the more significant of which are listed below.
- 5.0 – October 25 15:21:12 UTC[18]
- 6.1 – October 25 19:37:30 UTC[19]
- 4.9 – October 25 22:10:03 UTC[20]
- 6.2 – October 25 22:59:53 UTC[21]
- 5.3 – October 26 10:51:25 UTC[22]
- 5.3 – October 26 11:33:21 UTC[23]
- 5.0 – October 26 19:40:41 UTC[24]
- 5.0 – October 26 23:09:47 UTC[25]
- 5.8 – October 26 23:45:38 UTC[26]
Early warning system problems
The BMKG issued a tsunami warning based on seismographic data.[27] An alert was broadcast from radios and mosque loudspeakers on the mainland, prompting thousands to flee to higher ground.[11] It was later cancelled, but officials said that a tsunami warning system installed following the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake and tsunami had failed to function properly. According to Indonesian officials, two of the system's buoys out at sea had been vandalized and were inoperative.[28] The claim of a breakdown was disputed by German officials who were working with the Indonesians to maintain and develop the system. Jörn Lauterjung, the head of the German-Indonesia Tsunami Early Warning Project, said that it had "worked very well", only one sensor had not been working and its failure had not harmed the system's operation.[29] However, the epicentre of the earthquake was so close to the islands that a warning would probably have been too late in any case, as the tsunami only took about five to ten minutes to reach Pagai.[13]
Response
-
 Indonesian President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono interrupted a state visit to Vietnam to head to the Mentawai Islands, which he toured on October 28.[30] Boediono, the Vice President of Indonesia, visited the disaster area by helicopter on October 27 and called for better coordination of the aid effort. He encouraged Indonesians to "be tough in facing disasters", saying that "we must be prepared for whatever happens, just as our ancestors were over thousands of years."[14]
Indonesian President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono interrupted a state visit to Vietnam to head to the Mentawai Islands, which he toured on October 28.[30] Boediono, the Vice President of Indonesia, visited the disaster area by helicopter on October 27 and called for better coordination of the aid effort. He encouraged Indonesians to "be tough in facing disasters", saying that "we must be prepared for whatever happens, just as our ancestors were over thousands of years."[14] -
 Australian Prime Minister Julia Gillard issued a statement of condolences, saying: "I deeply regret the loss of life and the damage caused, and, of course, our thoughts go out to the families and loved ones of the people affected". She told the Australian Parliament that "the Australian Government has offered assistance to the Government of Indonesia should this be needed."[31]
Australian Prime Minister Julia Gillard issued a statement of condolences, saying: "I deeply regret the loss of life and the damage caused, and, of course, our thoughts go out to the families and loved ones of the people affected". She told the Australian Parliament that "the Australian Government has offered assistance to the Government of Indonesia should this be needed."[31] -
 Canadian Foreign Affairs Minister Lawrence Cannon released a statement saying, "Canada’s condolences to the people of Indonesia following the recent natural disasters that have struck the country. "Canada is deeply concerned for the people of Indonesia, as they deal with the impacts of the recent tsunami and volcanic eruption,” said Minister Cannon. “On behalf of all Canadians, I offer our deepest sympathy to the families and friends of those killed, and wish a quick recovery to the injured. Canada stands ready to provide support to the people of Indonesia if requested. We have received no reports to date of Canadian deaths or injuries due to these disasters. Canadian officials in Ottawa and at the Canadian Embassy in Jakarta continue to monitor the impact of the disasters and remain in close contact with Indonesian authorities. We invite Canadian citizens in the affected area, even if they have not been affected by these events, to call home and reassure their loved ones."[32]
Canadian Foreign Affairs Minister Lawrence Cannon released a statement saying, "Canada’s condolences to the people of Indonesia following the recent natural disasters that have struck the country. "Canada is deeply concerned for the people of Indonesia, as they deal with the impacts of the recent tsunami and volcanic eruption,” said Minister Cannon. “On behalf of all Canadians, I offer our deepest sympathy to the families and friends of those killed, and wish a quick recovery to the injured. Canada stands ready to provide support to the people of Indonesia if requested. We have received no reports to date of Canadian deaths or injuries due to these disasters. Canadian officials in Ottawa and at the Canadian Embassy in Jakarta continue to monitor the impact of the disasters and remain in close contact with Indonesian authorities. We invite Canadian citizens in the affected area, even if they have not been affected by these events, to call home and reassure their loved ones."[32] -
 Chinese Foreign Affairs Minister Yang Jiechi said in a statement "I wish to extend... my solicitude and condolences to the people affected by the disaster."
Chinese Foreign Affairs Minister Yang Jiechi said in a statement "I wish to extend... my solicitude and condolences to the people affected by the disaster." -
 Philippines Foreign Affairs Secretary Alberto G. Romulo, who was in Hanoi, Vietnam to attend the 17th ASEAN Summit, has directed his department to get ready to provide Indonesia with assistance. The Philippines Embassy in Jakarta said in a statement that "The [Philippines] Embassy …stands ready to provide assistance, if needed," adding all Filipinos in Indonesia are safe.[33]
Philippines Foreign Affairs Secretary Alberto G. Romulo, who was in Hanoi, Vietnam to attend the 17th ASEAN Summit, has directed his department to get ready to provide Indonesia with assistance. The Philippines Embassy in Jakarta said in a statement that "The [Philippines] Embassy …stands ready to provide assistance, if needed," adding all Filipinos in Indonesia are safe.[33] -
 Portuguese President Cavaco Silva sent his Indonesian counterpart a letter of condolences. He expressed his and Portugal's support for the country in such troubling times.
Portuguese President Cavaco Silva sent his Indonesian counterpart a letter of condolences. He expressed his and Portugal's support for the country in such troubling times. -
 Japanese Prime Minister Naoto Kan and Minister for Foreign Affairs Seiji Maehara sent messages to President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono and Indonesian Minister of Foreign Affairs Marty Natalegawa expressing their condolences and sympathy.[34]
Japanese Prime Minister Naoto Kan and Minister for Foreign Affairs Seiji Maehara sent messages to President Susilo Bambang Yudhoyono and Indonesian Minister of Foreign Affairs Marty Natalegawa expressing their condolences and sympathy.[34] -
 United States President Barack Obama said in a statement: "Michelle and I are deeply saddened by the loss of life, injuries, and damage that have occurred as a result of the recent earthquake and tsunami in West Sumatra. At the same time, I am heartened and encouraged by the remarkable resiliency of the Indonesian people and the commitment of their Government to rapidly assist the victims. As a friend of Indonesia, the United States stands ready to help in any way. Meanwhile, our thoughts and prayers are with the Indonesian people and all those affected by this tragedy."[35]
United States President Barack Obama said in a statement: "Michelle and I are deeply saddened by the loss of life, injuries, and damage that have occurred as a result of the recent earthquake and tsunami in West Sumatra. At the same time, I am heartened and encouraged by the remarkable resiliency of the Indonesian people and the commitment of their Government to rapidly assist the victims. As a friend of Indonesia, the United States stands ready to help in any way. Meanwhile, our thoughts and prayers are with the Indonesian people and all those affected by this tragedy."[35]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Magnitude 7.7 – KEPULAUAN MENTAWAI REGION, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Google Maps". maps.google.com. Google. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- 1 2 3 Bayo Ismoyu (2010-10-30). "Indonesia Battles Disasters on Two Fronts". The Jakarta Globe. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- 1 2 "BBC News – Major earthquake strikes off Indonesia". bbc.co.uk. BBC. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ↑ "Tsunami Bulletin". Pacific Tsunami Warning Center. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ Sieh, K. "The Sunda megathrust: past, present and future" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ↑ Bürgmann, R. (2009). "Imperfect dominoes" (PDF). Nature Geoscience. 2: 78–88. Bibcode:2009NatGe...2...87B. doi:10.1038/ngeo422. Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ↑ msnbc.com staff and news service reports (2010-10-25). "Major quake hits Indonesia". msnbc.com. MSNBC. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/dyfi/events/us/a00043nx/us/index.html
- ↑ http://igpphome.ucsd.edu/~shearer/Files/Sumatra_Papers/deshon_grl05.pdf
- 1 2 "Sumatra earthquake and tsunami could herald bigger quake." The Great Beyond, Nature, October 27, 2010
- 1 2 3 4 Toni O'Loughlin in Jakarta, Robert Booth and Matthew Weaver (2010-10-27). "Indonesia death toll reaches 300 with more feared after twin disasters". The Guardian. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- 1 2 3 4 "Indonesia tsunami: Death toll soars to 282". BBC News Online, 19:47 GMT, 27 October 2010.
- 1 2 3 4 "We Couldn't Outrun Killer Wave: Villager". TheJakartaGlobe.com. The Jakarta Globe. 2010-10-28. Retrieved 2010-10-28.
- ↑ "108 dead, 500 missing after tsunami hits Indonesia". channelnewsasia.com. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ Nedi, John (2010-10-26). "Indonesia tsunami kills 113; scores more missing". news.yahoo.com. Yahoo. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Earthquake List for 10-degree Map Centered at 5°S, 100°E". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "The Associated Press: 7.7-magnitude quake hits off Indonesian island". Google. Associated Press. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ Agence France-Presse (2010-10-25). "Major 7.7 quake strikes Indonesia". montrealgazette.com. Montreal Gazette. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 4.9 – KEPULAUAN MENTAWAI REGION, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 6.2 – KEPULAUAN MENTAWAI REGION, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 5.3 – SOUTHWEST OF SUMATRA, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 5.3 – KEPULAUAN MENTAWAI REGION, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 5.0 – SOUTHWEST OF SUMATRA, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 5.0 – SOUTHWEST OF SUMATRA, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Magnitude 5.8 – KEPULAUAN MENTAWAI REGION, INDONESIA". earthquake.usgs.gov. USGS. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "Tsunami warning relaxed after Indonesia quake". Reuters. 2010-10-25. Retrieved 2010-10-26.
- ↑ Indonesian tsunami warning system 'was not working'. Daily Telegraph, 6:13PM BST, 26 October 2010.
- ↑ "Indonesian Volcano Unleashes Biggest Blast Yet". NPR. 2010-10-28. Archived from the original on 2010-10-30. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- ↑ "Toll Passes 270 in Indonesia Tsunami Disaster". The Jakarta Globe, October 27, 2010
- ↑ "Australia offers disaster assistance." Canberra Times, 28 October 2010
- ↑ "Canada Offers Condolences Following Natural Disasters in Indonesia". Foreign Affairs Canada. 2010-10-27.
- ↑ "World mourns over Indonesia's double disasters". The Jakarta Post. 2010-10-28. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- ↑ "Concerning the Earthquake off the Mentawai Island Group, West Sumatra Province, and the Eruption of Mt. Merapi on Central Java Island, the Republic of Indonesia (Messages of Sympathy from Prime Minister Naoto Kan and Minister for Foreign Affairs Seiji Maehara)". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan. October 27, 2010. Retrieved 2013-10-11.
- ↑ "Statement by the President on the Tsunami in Indonesia". Embassy of the United States Jakarta, Indonesia. 2010-10-26. Retrieved 2010-10-27.
External links
| Wikinews has related news: |
- 25 October 2010, Mw 7.7, Mentawai Region, Indonesia – International Tsunami Information Center
- The 25 October 2010 Mentawai Earthquake and Tsunami – University of Southern California