Ordos (city)
| Ordos 鄂尔多斯市 • ᠣᠷᠳᠣᠰ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ | |
|---|---|
| Prefecture-level city | |
|
Genghis Khan Memorial in Ordos City | |
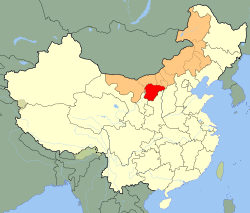 Ordos City (red) in Inner Mongolia (orange) | |
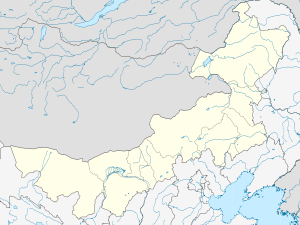 Ordos Location of the city centre in Inner Mongolia | |
| Coordinates: 39°36′N 109°47′E / 39.600°N 109.783°ECoordinates: 39°36′N 109°47′E / 39.600°N 109.783°E | |
| Country | China |
| Region | Inner Mongolia |
| Municipal seat | Dongsheng District |
| Area | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 86,752 km2 (33,495 sq mi) |
| • Urban | 2,137 km2 (825 sq mi) |
| • Metro | 2,137 km2 (825 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 1,305 m (4,281 ft) |
| Highest elevation | 2,149 m (7,051 ft) |
| Lowest elevation | 850 m (2,790 ft) |
| Population (2014 est.) | |
| • Prefecture-level city | 2,035,653 |
| • Density | 23/km2 (61/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 582,544 |
| • Urban density | 270/km2 (710/sq mi) |
| • Metro | 582,544 |
| • Metro density | 270/km2 (710/sq mi) |
| Time zone | China Standard (UTC+8) |
| Postal code | 017000 |
| GDP (2015) |
CNY 422.61 billion (US$ 67.85 billion) |
| GDP per capita (2015) |
CNY 207,569 (US$ 31,200) |
| Licence plate prefixes | 蒙K |
| Administrative division code | 150600 |
| ISO 3166-2 | CN-15-06 |
| Website |
www |
| Ordos | |||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simplified Chinese | 鄂尔多斯 | ||||||||
| Traditional Chinese | 鄂爾多斯 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Mongolian name | |||||||||
| Mongolian Cyrillic | Ордос хот | ||||||||
| Mongolian script | ᠣᠷᠳᠣᠰ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Ordos (Mongolian: ᠣᠷᠳᠣᠰ ᠬᠣᠲᠠ Ордос қота Ordos qota; simplified Chinese: 鄂尔多斯市; traditional Chinese: 鄂爾多斯市; pinyin: È'ěrduōsī) is one of the twelve major subdivisions of Inner Mongolia, China. It lies within the Ordos Loop of the Yellow River. Although mainly rural, Ordos is administered as a prefecture-level city. Its administrative seat is situated in Dongsheng which had a population of 582,544 inhabitants as of the 2010 census. Another Banner is being urbanized quickly around the city of Ejin Horo with about 251,894 inhabitants at the 2010 census which is the seat of Ordos Airport.
Ordos is known for its lavish government projects, including the new Kangbashi District, a large District with abundant infrastructure, seldom used by residents and frequently described as a "ghost city".[1][2] It hosted the 2012 Miss World Final.
Etymology
The area had been administered under the Ih Ju League, also spelled Ikh Juu (Mongolian: ᠶᠡᠬᠡ ᠵᠤᠤ ᠠᠶᠢᠮᠠᠭ Yeke Juu ayimaγ; Chinese: 伊克昭盟; pinyin: Yīkèzhāo Méng) since the 17th century, and was redesignated a prefecture-level city and renamed to Ordos on 26 February 2001. "Ordos" means "palaces" in the Mongolian language.[3] Ordos originally referred to a tribe belonging to the Yeke Juu (Ike Chao ‘great monastery’) league and later included the tribe’s area, hence the Ordos, or Ordus, the area within the big bend of the Yellow River. Mongolian ordu(n), ord ‘court, residence of a ruler; palace; camp’, also for 'camp bodyguards'. According to Ramstedt -s is a plural suffix; further: ordu, orda; Turkic orta ‘a center’; Mongolian > Turkish orda ‘camp’ > Hindi urdū > English "horde." [4] The name is sometimes claimed to be related to the eight white yurts of Genghis Khan.[5] Linguistically, the Ordos dialect of Mongolian is quite different from neighboring Chakhar Mongolian.
Geography and climate
Ordos's prefectural administrative region occupies 86,752 square kilometres (33,495 sq mi) and covers the bigger part of the Ordos Desert, although the urban area itself is relatively small. It borders the prefecture-level divisions of Hohhot to the east, Baotou to the northeast, Bayan Nur to the north, Alxa League to the northwest, Wuhai to the west, the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region to its southwest, and the provinces of Shaanxi and Shanxi to the south. The maximal north-south extent is 340 km (210 mi), while from east to west it stretches for 400 km (250 mi).[6]
The area of Ordos Shi can roughly be divided into a hilly area in the east, high plateaus in the west and center, sandy deserts in the north and south, and plains at the southern bank of the Yellow River. The highest elevation, at 2,149 metres (7,051 ft), is located in the west, the lowest point, at 850 m (2,790 ft), is in the east.
There are two large deserts in the territory of Ordos Shi: Kubuqi Desert (库布其沙漠) in the north and the Maowusu Desert (毛乌素沙漠) in the south. The Kubuqi Desert occupies 19.2% of Ordos, or 16,600 km2 (6,400 sq mi), while the Maowusu Desert takes up 28.8% of the area, or 25,000 km2 (9,700 sq mi).
Ordos features a cold semi-arid climate (Köppen BSk), marked by long, cold and very dry winters; very warm, somewhat humid summers; and strong winds, especially in spring. The annual precipitation is 300 to 400 millimetres (11.8 to 15.7 in) in the eastern part of the city and 190 to 350 mm (7.5 to 13.8 in) in the western part. Most of the rain falls between July and September, with very little snow in winter; average annual evaporation reaches 2,000 to 3,000 mm (79 to 118 in). In the city proper, the monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from −10.5 °C (13.1 °F) in January to 21.0 °C (69.8 °F) in July, while the annual mean is 6.16 °C (43.1 °F). Sunshine duration averages 2,700 to 3,200 hours annually.[6]
| Climate data for Ordos (1971−2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 7.8 (46) |
13.9 (57) |
19.4 (66.9) |
32.2 (90) |
32.9 (91.2) |
32.2 (90) |
35.3 (95.5) |
33.3 (91.9) |
33.3 (91.9) |
24.4 (75.9) |
18.2 (64.8) |
10.6 (51.1) |
35.3 (95.5) |
| Average high °C (°F) | −4.8 (23.4) |
−1.3 (29.7) |
5.2 (41.4) |
14.1 (57.4) |
20.8 (69.4) |
25.0 (77) |
26.7 (80.1) |
24.5 (76.1) |
19.4 (66.9) |
12.6 (54.7) |
4.0 (39.2) |
−2.9 (26.8) |
11.9 (53.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −10.5 (13.1) |
−7.2 (19) |
−0.5 (31.1) |
7.7 (45.9) |
14.6 (58.3) |
19.1 (66.4) |
21.0 (69.8) |
19.1 (66.4) |
13.8 (56.8) |
6.8 (44.2) |
−1.7 (28.9) |
−8.3 (17.1) |
6.16 (43.08) |
| Average low °C (°F) | −14.7 (5.5) |
−11.5 (11.3) |
−5.4 (22.3) |
1.9 (35.4) |
8.4 (47.1) |
13.0 (55.4) |
15.8 (60.4) |
14.3 (57.7) |
8.8 (47.8) |
2.1 (35.8) |
−5.9 (21.4) |
−12.3 (9.9) |
1.2 (34.2) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −28.4 (−19.1) |
−27.5 (−17.5) |
−22.8 (−9) |
−11.6 (11.1) |
−4.8 (23.4) |
1.7 (35.1) |
9.1 (48.4) |
4.3 (39.7) |
−2.1 (28.2) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−21.8 (−7.2) |
−25.3 (−13.5) |
−28.4 (−19.1) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 2.1 (0.083) |
4.4 (0.173) |
10.8 (0.425) |
11.4 (0.449) |
25.8 (1.016) |
44.8 (1.764) |
105.7 (4.161) |
105.5 (4.154) |
44.7 (1.76) |
19.4 (0.764) |
5.3 (0.209) |
1.3 (0.051) |
381.2 (15.009) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 2.1 | 2.9 | 4.3 | 3.4 | 5.9 | 8.7 | 12.2 | 11.9 | 8.1 | 4.4 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 68.4 |
| Source: Weather China[6] | |||||||||||||
Economy
Ordos is one of the richest regions of China. With a nominal per-capita GDP of US$14,500 in 2008, it is ranked ahead of Beijing.[7] It is extremely rich in natural resources, having one sixth of the national coal reserves. The pillars of its economy are textiles (wool), coal mining, petrochemicals, electricity generation, and production of building materials.
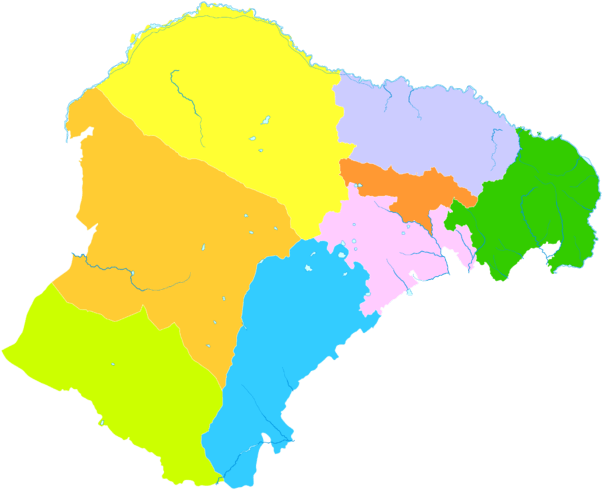
Administrative subdivisions
Ordos Shi is divided into two districts and seven banners:
| Map | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Name | Mongolian | Hanzi | Hanyu Pinyin | Population (2010) | Area (km²) | Density (/km²) | |
| Dongsheng District | ᠳ᠋ᠦᠩᠱᠧᠩ ᠲᠣᠭᠣᠷᠢᠭ (Düŋšėŋ toɣoriɣ) |
东胜区 | Dōngshèng Qū | 582,544 | 2,137 | 108 | |
| Hia'bagx District | ᠬᠢᠶᠠ ᠪᠠᠭᠰᠢ ᠲᠣᠭᠣᠷᠢᠭ (Kiy-a baγsi toɣoriɣ) |
康巴什区 | Kāngbāshí Qū | ||||
| Dalad Banner | ᠳᠠᠯᠠᠳ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Dalad qosiɣu) |
达拉特旗 | Dálātè Qí | 322,101 | 8,192 | 40 | |
| Jungar Banner | ᠵᠡᠭᠦᠨᠭᠠᠷ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Jegünɣar qosiɣu) |
准格尔旗 | Zhǔngé'ěr Qí | 356,501 | 7,535 | 36 | |
| Otog Front Banner | ᠣᠲᠣᠭ ᠤᠨ ᠡᠮᠦᠨᠡᠳᠦ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Otoɣ-un Emünedü qosiɣu) |
鄂托克前旗 | Ètuōkè Qián Qí | 68,282 | 12,318 | 6 | |
| Otog Banner | ᠣᠲᠣᠭ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Otoɣ qosiɣu) |
鄂托克旗 | Ètuōkè Qí | 148,844 | 20,064 | 4 | |
| Hanggin Banner | ᠬᠠᠩᠭᠢᠨ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Qaŋɣin qosiɣu) |
杭锦旗 | Hángjǐn Qí | 111,102 | 18,903 | 7 | |
| Uxin Banner | ᠦᠦᠰᠢᠨ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Üüsin qosiɣu) |
乌审旗 | Wūshěn Qí | 124,527 | 11,645 | 9 | |
| Ejin Horo Banner | ᠡᠵᠢᠨ ᠬᠣᠷᠣᠭᠠ ᠬᠣᠰᠢᠭᠤ (Ejin Qoroɣ-a qosiɣu) |
伊金霍洛旗 | Yījīnhuòluò Qí | 226,752 | 5,958 | 23 | |
Kangbashi New Area
A large, sparsely inhabited urban real estate development has been constructed 25 km (16 mi) from Dongsheng District. Intended to house a million people, it remains mostly uninhabited.[8][9] Intended to have 300,000 residents by 2010, government figures stated it had 28,000.[10] It has been the subject of several well publicized articles, including a feature illustrated series conducted by Al Jazeera in 2010.[11] The Daily Mail has documented Ordos/Kangbashi and other similar urban developments in China.[12][13]
Ordos Museum

In 2011, a 41,000-square-foot museum, entitled Ordos Museum (Chinese: 鄂尔多斯博物馆), was opened in Kangbashi. The museum, designed by China-based architectural practice MAD Studio, is focused on the history of the Ordos area, as well as on the culture and traditions of Inner Mongolia.[14]
Transportation
Travel within Ordos City is primarily made by car or bus, using the city's network roads. Two tolled expressways, the G18 Rongcheng–Wuhai Expressway and the G65 Baotou–Maoming Expressway, provide connections with other towns and cities including Dongsheng.
There are no direct rail lines to the city. The closest is the Baoshen Line in Dongsheng.
Ordos Airport is to the south of the city.
Demographics
In the 2000 census, there were 1,369,766 inhabitants:
| ethnic group | population | share |
|---|---|---|
| Han | 1,207,971 | 88.19% |
| Mongols | 155,845 | 11.38% |
| Manchu | 2,905 | 0.21% |
| Hui | 1,861 | 0.14% |
| Tibetans | 1,023 | 0.07% |
Most people come from the Shanxi province, 30 km South of this city.
See also
- Ordos culture
- Ordos International Circuit
- Mausoleum of Genghis Khan
- New South China Mall and Chenggong, examples of other underused developments
- List of cities in the People's Republic of China by population
- List of cities in the People's Republic of China by GDP per capita
References
- ↑ Al-Jazeera (2009-11-09). "China's Empty City" (video). YouTube.
- ↑ Chohan, Usman W. "Erdos City – 鄂尔多斯市 The "Horde" That Wasn't". McGill University. Retrieved 2014-05-14.
- ↑ http://www.ordos.gov.cn/zjeedx/sqgk/ 市情概况
- ↑ G. John Ramstedt: Kalmückisches Wörterbuch, Helsinki, 1935, Suomalais-Ugrilainen Seura, and Ferdinand D. Lessing, ed.: Mongolian-English Dictionary, Bloomington, Ind., 1982, The Mongolia Society, Inc.
- ↑ W. R. Carles, "Problems in Exploration II. Ordos", in The Geographical Journal, Vol. 33, No. 6 (Jun., 1909), p. 669
- 1 2 3 Weather China
- ↑ GDP 2011 figure of Inner Mongolian divisions is from Inner Mongolian Statistical Yearbook 2012 ( ISBN 978-7-89468-268-0 /F.468)
- ↑ Time Photos of Ordos/Kangbashi, Time Photos Website 2011
- ↑ Gus Lubin (2011-06-13). "NEW SATELLITE PICTURES OF CHINA'S GHOST CITIES". Business Insider. Retrieved 2011-12-09.
- ↑ Barboza, David (2010-10-19). "A New Chinese City, With Everything but People". New York Times.
- ↑ "China's Ghost Town". AlJazeera. 10 November 2009. Retrieved 2010-12-21.
- ↑ The Ghost Towns of China...The Daily Telegraph 18 Dec 2010
- ↑ "Ordos: The biggest ghost town in China". BBC News. 2012-03-17.
- ↑ "Ordos Museum by MAD Architects". Inexhibit. Retrieved March 20, 2015.
External links
| Wikivoyage has a travel guide for Ordos City. |