Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Boston
| Archdiocese of Boston Archidioecesis Bostoniensis | |
|---|---|
|
Coat of arms of the Archdiocese of Boston | |
| Location | |
| Country | United States |
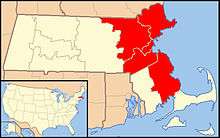
| Territory | Counties of Essex, Middlesex, Suffolk, Norfolk, and Plymouth (the towns of Mattapoisett, Marion, and Wareham excepted)[1] |
| Ecclesiastical province | Boston |
| Statistics | |
| Area | 2,465 sq mi (6,380 km2) |
| Population - Total - Catholics |
(as of 2013) 4,240,000 1,906,372 (45%) |
| Parishes | 288 |
| Information | |
| Denomination | Roman Catholic |
| Rite | Roman Rite |
| Established | April 8, 1808 |
| Cathedral | Cathedral of the Holy Cross |
| Patron saint | Saint Patrick |
| Current leadership | |
| Pope | Francis |
| Metropolitan Archbishop | Seán Patrick O'Malley |
| Auxiliary Bishops | |
| Vicar General | Peter J. Uglietto |
| Emeritus Bishops | |
| Map | |
 | |
| Website | |
|
www | |
The Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Boston (Latin: Archidioecesis Bostoniensis) is an ecclesiastical territory or Archdiocese of the Roman Catholic Church in the New England region of the United States. It comprises several counties of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. It is led by a prelate archbishop who serves as pastor of the mother church, Cathedral of the Holy Cross in the South End of Boston.
As of 2009, there are 292 parishes in the archdiocese.[2] In 2007, the archdiocese estimated that 1.8 million Catholics were in the territory, of whom about 315,000 regularly attended Mass.[3]
History
The original Diocese of Boston was canonically erected on April 8, 1808 by Pope Pius VII. It took its territories from the larger historic Diocese of Baltimore and consisted of the states of Connecticut, (future) Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island and Vermont.
In the nineteenth century, as Catholicism grew exponentially in New England, the Diocese of Boston was carved into smaller new dioceses: on November 28, 1843, Pope Gregory XVI erected the Diocese of Hartford; Pope Pius IX erected the Diocese of Burlington and the Diocese of Portland on July 29, 1853, the Diocese of Springfield on June 14, 1870, and the Diocese of Providence on February 16, 1872. On February 12, 1875, Pope Pius IX elevated the diocese to the rank of an archdiocese.
In the 1920s, Cardinal William O'Connell moved the chancery from offices near Holy Cross Cathedral in the South End to 127 Lake Street in Brighton.[4] "Lake Street" became shorthand for the Bishop and the office of the Archdiocese.[4]
At the beginning of the 21st century the archdiocese was shaken by accusations of sexual abuse by clergy that culminated in the resignation of its archbishop, Cardinal Bernard Francis Law, on December 13, 2002. In September 2003, the Archdiocese settled over 500 abuse-related claims for $85 million.[5]
In June 2004, the archbishop's residence and the chancery in Brighton and surrounding lands were sold to Boston College, in part to defray costs associated with abuse cases.[6][7][8] The offices of the Archdiocese were moved to Braintree, Massachusetts; Saint John's Seminary remains on that property.
Communications media
The diocesan newspaper The Pilot has been published in Boston since 1829.
The Archdiocese's Catholic Television Center, founded in 1955, produces programs and operates the cable television network CatholicTV. From 1964 to 1966, it owned and operated a broadcast television station under the call letters WIHS-TV.
Ecclesiastical province
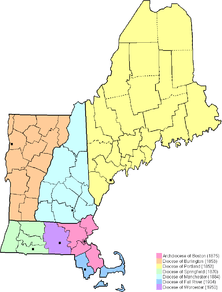
The Archdiocese of Boston is also metropolitan see for the Ecclesiastical province of Boston. This means that the archbishop of Boston is the metropolitan for the province. The suffragan dioceses in the province are the Diocese of Burlington, Diocese of Fall River, Diocese of Manchester, Diocese of Portland, Diocese of Springfield in Massachusetts, and the Diocese of Worcester.
Pastoral regions
The Archdiocese of Boston is divided into five pastoral regions, each headed by an episcopal vicar.
| Pastoral Region | Episcopal vicar | Location | Parishes | Notable parishes | Catholic institutions of higher education | High schools | Elementary schools | Cemeteries |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central | James Flavin | Boston (all neighborhoods), Brookline, Cambridge, Somerville, Winthrop | 64 | Cathedral, the Mission Church | Boston College, Emmanuel College, Our Lady of Grace Seminary (Boston), St. John's Seminary | 6 | 29 | 8 |
| Merrimack | Currently vacant | northern portion of Essex County and the northeastern portion of Middlesex County | 49 | Merrimack College | 3 | (TBD) | 4 | |
| North | Peter John Uglietto | southern portion of Essex County | 64 | Marian Court College | 4 | 6 (?) | 11 | |
| South | John Anthony Dooher | Plymouth County and most of Norfolk County | 59 | Labouré College | 3 | (TBD) | 3 | |
| West | Brian Kiely | southern portion of Middlesex County and the western portion of Norfolk County | 67 | Regis College | 3 | 11 | 7 |
Bishops

The following are lists of the Bishops and Archbishops of Boston, Auxiliaries of Boston, and their years of service. Also included are other priests of this diocese who served elsewhere as bishop.
† = deceased
Bishops of Boston
- † Jean-Louis Lefebvre de Cheverus (1808–1823) appointed Bishop of Montauban, France; future Cardinal
- † Benedict Joseph Fenwick, S.J. (1825–1846) died
- † John Bernard Fitzpatrick (1846–1866) died
Archbishops of Boston
- † John Joseph Williams (1866–1907), elevated to Archbishop when Boston became archdiocese in 1875; died
- † Cardinal William Henry O'Connell (1907–1944) died
- † Cardinal Richard Cushing (1944–1970) retired
- † Cardinal Humberto Sousa Medeiros (1970–1983) died
- Cardinal Bernard Francis Law (1984–2002) resigned, appointed Archpriest of the Basilica di Santa Maria Maggiore in 2004
- Cardinal Seán Patrick O'Malley, O.F.M.Cap. (2003–present)
Auxiliary Bishops
- Emilio S. Allué, S.D.B. (1996-2010) retired
- † Joseph Gaudentius Anderson (1909-1927) died
- Robert J. Banks (1985-1990) appointed Bishop of Green Bay
- † John P. Boles (1992-2006) retired
- † John Brady (1891-1910) died
- Daniel A. Cronin (1968-1970) appointed Bishop of Fall River
- † Richard J. Cushing (1939-1944) promoted to Archbishop here
- Thomas Vose Daily (1974-1984) appointed Bishop of Palm Beach
- † John Michael D'Arcy (1975–1985) appointed Bishop of Fort Wayne-South Bend, Indiana
- Robert P. Deeley (2012-2013) appointed Bishop of Portland
- John Anthony Dooher (2006–present)
- Walter James Edyvean (2001-2014) retired
- Roberto Octavio González Nieves, O.F.M. (1988-1995) appointed Coadjutor Bishop of Corpus Christi
- † Daniel Anthony Hart (1976-1995) appointed Bishop of Norwich
- Francis Xavier Irwin (1996-2009) retired
- Robert Francis Hennessey (2006–present)
- Alfred C. Hughes (1981-1993) appointed Bishop of Baton Rouge
- † Louis Francis Kelleher (1945-1946) died
- Arthur L. Kennedy (2010-present)
- Richard Lennon (2001-2006) appointed Bishop of Cleveland
- † Eric Francis MacKenzie (1950-1969) died
- † Joseph Francis Maguire (1971-1976) appointed Coadjutor Bishop of Springfield in Massachusetts
- † Thomas Francis Markham (1950-1952) died
- Richard Joseph Malone (2000-2004) appointed Bishop of Portland
- John Brendan McCormack (1995-1998) appointed Bishop of Manchester
- † John R. McNamara (1992-1999) resigned
- † Jeremiah Francis Minihan (1954-1973) died
- † John Joseph Mulcahy (1974-1992) retired
- William F. Murphy (1995-2001) appointed Bishop of Rockville Centre
- Mark William O'Connell (appointed 3 June 2016)
- † John Bertram Peterson (1927-1932) appointed Bishop of Manchester
- Robert P. Reed (appointed 3 June 2016)
- † Lawrence Joseph Riley (1971-1990) retired
- † Thomas Joseph Riley (1959-1976) retired
- † Joseph John Ruocco (1974-1980) died
- † Francis Spellman (1932-1939) appointed Archbishop of New York; Cardinal in 1946
- Peter John Uglietto (2010–present)
- † John Wright (1947-1950) appointed Bishop of Worcester; future Cardinal
Others
- † Edward Patrick Allen, appointed Bishop of Mobile in 1897
- Christopher J. Coyne, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of Indianapolis in 2011
- † John Joseph Glynn, appointed Auxiliary Bishop of U.S. Military in 1991
- † Matthew Harkins, appointed Bishop of Providence in 1887
- † James Augustine Healy, appointed Bishop of Portland in 1875
- † Lawrence Stephen McMahon, appointed Bishop of Hartford in 1879
- † John Joseph Nilan, appointed Bishop of Hartford in 1910
- Paul Fitzpatrick Russell, appointed nuncio, and titular Archbishop, in 2016
- † Edward Francis Ryan, appointed Bishop of Burlington in 1944
- † William Barber Tyler, appointed Bishop of Hartford in 1843
- † James Anthony Walsh, became superior general of Maryknoll; titular Bishop in 1933
- † Louis Sebastian Walsh, appointed Bishop of Portland in 1906
Seminaries
- Pope St. John XXIII National Seminary
- St. John's Seminary
- Redemptoris Mater Archdiocesan Missionary Seminary
Education
As of 2016, the diocese has 116 schools with about 38,000 students in pre-kindergarten through high school.[9]
In 1993 the archdiocese had 53,569 students in 195 archdiocesean parochial schools. Boston had the largest number of parochial schools: 48 schools with a combined total of about 16,000 students.[10]
Superintendents
- Br. Bartholomew Varden, C.F.X. (c. 1973–1975)[11]
- Eugene F. Sullivan (1978–1984)[12][13]
- Sr. Kathleen Carr, CSJ (1990–2006)[14]
- Mary Grassa O'Neill (2008–2014)[15]
- Mary E. Moran (2013–2014)[15]
- Kathleen Power Mears (2014–present)[15]
High schools
- Academy of Notre Dame, Tyngsboro
- Archbishop Williams High School, Braintree
- Arlington Catholic High School, Arlington
- Austin Preparatory School, Reading
- Bishop Fenwick High School, Peabody
- Boston College High School, Dorchester
- Cardinal Spellman High School, Brockton
- Cathedral High School, Boston
- Catholic Memorial High School, West Roxbury
- Central Catholic High School, Lawrence
- Cristo Rey Boston High School, Dorchester
- Elizabeth Seton Academy, Boston
- Fontbonne Academy, Milton
- Lowell Catholic High School, Lowell
- Malden Catholic High School, Malden
- Marian High School Framingham
- Matignon High School, Cambridge
- Mount Alvernia High School, Newton
- Saint Joseph Preparatory Boston
- Newton Country Day School, Newton
- Notre Dame Academy, Hingham
- Notre Dame High School, Lawrence
- Pope John XXIII High School, Everett
- Presentation of Mary Academy, Methuen
- Sacred Heart High School, Kingston
- Saint Clement High School, Medford
- St. John's Preparatory School, Danvers
- St. Mary's High School, Lynn
- Saint Sebastian's School, Needham
- Ursuline Academy, Dedham
- Xaverian Brothers High School, Westwood
Former high schools
- Cardinal Cushing High School, South Boston
- Christopher Columbus High School. Boston
- Don Bosco Technical High School, Boston (closed 1998)
- Holy Trinity High School, Roxbury (closed 1966)
- Hudson Catholic High School, Hudson (closed 2009)
- Keith Academy, Lowell
- Keith Hall, Lowell
- Monsignor Ryan High School, South Boston
- North Cambrdige Catholic High School
- St. Clare's High School, Roslindale
- Savio Preparatory High School, East Boston (closed 2007)
- Trinity Catholic High School, Newton (closed 2012)
- Our Lady of Nazareth Academy, Wakefield (closed 2009)
See also
- Catholic Church by country
- Catholic Church in the United States
- Ecclesiastical Province of Boston
- Global organisation of the Catholic Church
- List of Roman Catholic archdioceses (by country and continent)
- List of Roman Catholic dioceses (alphabetical) (including archdioceses)
- List of Roman Catholic dioceses (structured view) (including archdioceses)
- List of the Catholic dioceses of the United States
- Sexual abuse scandal in the Catholic archdiocese of Boston
- Steward Health Care System, a company operating the former archdiocesan hospitals of Caritas Christi Health Care
References
- ↑ "Archdiocese of Boston". Catholic-Hierarchy.org. David M. Cheney. Retrieved 23 January 2015.
- ↑ Paulson, Michael (May 1, 2009). "Diocese makes financial progress". The Boston Globe. Retrieved May 25, 2009.
- ↑ Kerber, Ross (January 29, 2007). "Bless you, we take Visa". The Boston Globe. Retrieved January 29, 2007.
- 1 2 Changes come to Lake Street. The Boston Globe, May 24, 2007
- ↑ Kevin Cullen and Stephen Kurkjian (September 10, 2003). "Church in an $85 million accord". Boston Globe.
- ↑ Diocesan headquarters sold to BC The Boston Globe, April 21, 2004.
- ↑ Statement of the Archdiocese of Boston and Boston College on sale of part of Brighton campus The Boston Globe, April 20, 2004.]
- ↑ Oslin, Reid, "Campus Construction Update: Stokes, Brighton Campus Projects Begin", The Boston College Chronicle, September 9, 2010
- ↑ http://catholicschoolsboston.org
- ↑ Nealon, Patricia. "Parochial pupils add X factor to city school-choice equation." Boston Globe. April 28, 1993. Retrieved on September 28, 2013.
- ↑ O'Connor, Thomas H. (2004-01-01). Boston's Histories: Essays in Honor of Thomas H. O'Connor. UPNE. ISBN 9781555535827.
- ↑ "Lakeland Ledger - Google News Archive Search". news.google.com. Retrieved 2016-01-07.
- ↑ "Gainesville Sun - Google News Archive Search". news.google.com. Retrieved 2016-01-07.
- ↑ "Sister Kathleen Carr to step down as school superintendent". www.thebostonpilot.com. Retrieved 2016-01-07.
- 1 2 3 "Boston Archdiocese appoints career educator as superintendent of Catholic schools - The Boston Globe". BostonGlobe.com. Retrieved 2016-01-07.
External links
- Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Boston Official Site
- Catholic Hierarchy Profile of the Archdiocese of Boston
- Boston Globe / Spotlight / Abuse in the Catholic Church
- Boston Catholic Insider (critical blog)
- Boston Catholic Schools
Coordinates: 42°12′47″N 71°02′29″W / 42.21306°N 71.04139°W