Temperature record of the past 1000 years
- For information on the description of the Medieval Warm Period and Little Ice Age in various IPCC reports see MWP and LIA in IPCC reports
The temperature record of the past 1,000 years is reconstructed using data from climate proxy records in conjunction with the modern instrumental temperature record which only covers the last 150 years at a global scale. Large-scale reconstructions covering part or all of the 1st millennium and 2nd millennium have shown that recent temperatures are exceptional: the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change Fourth Assessment Report of 2007 concluded that "Average Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the second half of the 20th century were very likely higher than during any other 50-year period in the last 500 years and likely the highest in at least the past 1,300 years." The curve shown in graphs of these reconstructions is widely known as the hockey stick graph because of the sharp increase in temperatures during the last century. As of 2010 this broad pattern was supported by more than two dozen reconstructions, using various statistical methods and combinations of proxy records, with variations in how flat the pre-20th-century "shaft" appears. Sparseness of proxy records results in considerable uncertainty for earlier periods.[1]
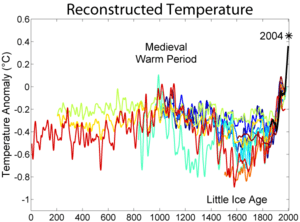
Individual proxy records, such as tree ring widths and densities used in dendroclimatology, are calibrated against the instrumental record for the period of overlap. Networks of such records are used to reconstruct past temperatures for regions: tree ring proxies have been used to reconstruct Northern Hemisphere extratropical temperatures (within the tropics trees do not form rings) but are confined to land areas and are scarce in the Southern Hemisphere which is largely ocean. Wider coverage is provided by multiproxy reconstructions, incorporating proxies such as lake sediments, ice cores and corals which are found in different regions, and using statistical methods to relate these sparser proxies to the greater numbers of tree ring records. The "Composite Plus Scaling" (CPS) method is widely used for large-scale multiproxy reconstructions of hemispheric or global average temperatures; this is complemented by Climate Field Reconstruction (CFR) methods which show how climate patterns have developed over large spatial areas, making the reconstruction useful for investigating natural variability and long-term oscillations as well as for comparisons with patterns produced by climate models.
During the 1,900 years before the 20th century, it is likely that the next warmest period was from 950 to 1100, with peaks at different times in different regions. This has been called the Medieval Warm Period, and some evidence suggests widespread cooler conditions during a period around the 17th century known as the Little Ice Age. In the hockey stick controversy, contrarians have asserted that the Medieval Warm Period was warmer than at present, and have disputed the data and methods of climate reconstructions.
General techniques and accuracy
By far the best observed period is from 1850 to the present day, with coverage improving over time. Over this period the recent instrumental record, mainly based on direct thermometer readings, has approximately global coverage. It shows a general warming in global temperatures.
Before this time various proxies must be used. These proxies are less accurate than direct thermometer measurements, have lower temporal resolution, and have less spatial coverage. Their only advantage is that they enable a longer record to be reconstructed. Since the direct temperature record is more accurate than the proxies (indeed, it is needed to calibrate them) it is used when available: i.e., from 1850 onwards.
Quantitative methods using proxy data
As there are few instrumental records before 1850, temperatures before then must be reconstructed based on proxy methods. One such method, based on principles of dendroclimatology, uses the width and other characteristics of tree rings to infer temperature. The isotopic composition of snow, corals, and stalactites can also be used to infer temperature. Other techniques which have been used include examining records of the time of crop harvests, the treeline in various locations, and other historical records to make inferences about the temperature. These proxy reconstructions are indirect inferences of temperature and thus tend to have greater uncertainty than instrumental data.
Most proxy records have to be calibrated against local temperature records during their period of overlap, to estimate the relationship between temperature and the proxy. The longer history of the proxy is then used to reconstruct temperature from earlier periods.
Proxy records must be averaged in some fashion if a global or hemispheric record is desired. The "Composite Plus Scaling" (CPS) method is widely used for large-scale multiproxy reconstructions of hemispheric or global average temperatures. This is complemented by Climate Field Reconstruction (CFR) methods which show how climate patterns have developed over large spatial areas.
Considerable care must be taken in the averaging process; for example, if a certain region has a large number of tree ring records, a simple average of all the data would strongly over-weight that region, and statistical techniques are used to avoid such over-weighting. In the Mann, Bradley & Hughes 1998 and Mann, Bradley & Hughes 1999 CFR reconstructions, principal components analysis was used to combine some of these regional records before they were globally combined. An important distinction is between so-called 'multi-proxy' reconstructions, which attempt to obtain a global temperature reconstruction by using multiple proxy records distributed over the globe and more regional reconstructions. Usually, the various proxy records are combined arithmetically, in some weighted average. More recently, Osborn and Briffa used a simpler technique, counting the proportion of records that are positive, negative or neutral in any time period.[2] This produces a result in general agreement with the conventional multi-proxy studies.
The 2007 IPCC Fourth Assessment Report cited 14 reconstructions, 10 of which covered 1,000 years or longer, to support its conclusion that "Average Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the second half of the 20th century were very likely higher than during any other 50-year period in the last 500 years and likely the highest in at least the past 1,300 years".[3]
Qualitative reconstruction using historical records
It is also possible to use historical data such as times of grape harvests, sea-ice-free periods in harbours and diary entries of frost or heatwaves to produce indications of when it was warm or cold in particular regions. These records are harder to calibrate, are often only available sparsely through time, may be available only from developed regions, and are unlikely to come with good error estimates. These historical observations of the same time period show periods of both warming and cooling.
Limitations
The apparent differences between the quantitative and qualitative approaches are not fully reconciled. The reconstructions mentioned above rely on various assumptions to generate their results. If these assumptions do not hold, the reconstructions would be unreliable. For quantitative reconstructions, the most fundamental assumptions are that proxy records vary with temperature and that non-temperature factors do not confound the results. In the historical records temperature fluctuations may be regional rather than hemispheric in scale.
In a letter to Nature Bradley, Hughes & Mann (2006) pointed at the original title of their 1998 article: Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the past millennium: inferences, uncertainties, and limitations[4] and pointed out more widespread high-resolution data are needed before more confident conclusions can be reached and that the uncertainties were the point of the article.
Development and controversy
In the 1960s, Hubert Lamb generalised from historical documents and temperature records of central England to propose that the North Atlantic region had seen a Medieval Warm Period from around 900 to 1300, followed by Little Ice Age. This was the basis of a "schematic diagram" featured in the IPCC First Assessment Report beside cautions that the medieval warming might not have been global. The use of proxy indicators to get quantitative estimates of the temperature record of past centuries developed sporadically from the 1930s onwards, and Bradley & Jones 1993 introduced the "Composite Plus Scaling" (CPS) method used by most later large scale reconstructions.[5][6] Their study was featured in the IPCC Second Assessment Report, which included its graph of decadal average hemispheric temperatures back to 1400. There was increasing political dispute over the implications of the science, and over proposed ratification of the 1997 Kyoto Protocol.
In 1998 Michael E. Mann, Raymond S. Bradley and Malcolm K. Hughes developed new statistical techniques to produce Mann, Bradley & Hughes 1998 (MBH98), the first eigenvector-based climate field reconstruction (CFR). This showed global patterns of annual surface temperature, and included a graph of average hemispheric temperatures back to 1400 with shading emphasising that uncertainties (to two standard error limits) were much greater in earlier centuries.[7] The study was disputed by the fossil fuel funded George C. Marshall Institute and Willie Soon and Sallie Baliunas, who said that the reconstruction only went back to 1400 to avoid showing the Medieval Warm Period.
Jones et al. 1998 independently produced a CPS reconstruction extending back for a thousand years, and Mann, Bradley & Hughes 1999 (MBH99) used the MBH98 methodology to extend their study back to 1000.[8][9] The term hockey stick was coined by the climatologist Jerry Mahlman, to describe the pattern this showed, envisaging a graph that is relatively flat to 1900 as forming an Ice hockey stick's "shaft", followed by a sharp increase corresponding to the "blade".[10][11]
A version of the MBH99 graph was featured prominently in the 2001 IPCC Third Assessment Report (TAR), which also drew on Jones et al. 1998 and three other reconstructions to support the conclusion that, in the Northern Hemisphere, the 1990s was likely to have been the warmest decade and 1998 the warmest year during the past 1,000 years. The graph was featured in publicity, and became a focus of dispute for those opposed to the strengthening scientific consensus that late 20th century warmth was exceptional.[12] When the IPCC TAR was still in draft, Fred Singer held a press event saying "We don't accept this" with Wibjörn Karlén who alleged that MBH99 showed neither a Medieval Warm Period nor a Little Ice Age, an inaccurate claim echoed soon afterwards by John Lawrence Daly.
In 2003, as lobbying over the 1997 Kyoto Protocol intensified, Soon and Baliunas published a paper claiming greater medieval warmth, and on this basis the Bush administration chief of staff Philip Cooney deleted references to climate reconstructions from the first Environmental Protection Agency Report on the Environment. The paper was quickly dismissed by scientists in the Soon and Baliunas controversy, but on July 28, Republican Jim Inhofe spoke in the Senate speech citing Soon and Baliunas to claim "that man-made global warming is the greatest hoax ever perpetrated on the American people".[13] Later in 2003, Stephen McIntyre and Ross McKitrick published McIntyre & McKitrick 2003 disputing the data used in MBH98 paper. They were given extensive publicity, and met Inhofe as well as making a presentation sponsored by the George C. Marshall Institute and the Competitive Enterprise Institute. In 2004 Hans von Storch published criticism of the statistical techniques as tending to underplay variations in earlier parts of the graph, though this was disputed and he later accepted that the effect was very small.[14] In 2005 McIntyre and McKitrick published criticisms of the principal components analysis methodology as used in MBH98 and MBH99. Their analysis was subsequently disputed by published papers including Huybers 2005 and Wahl & Ammann 2007 which pointed to errors in the McIntyre and McKitrick methodology. In June 2005 Rep. Joe Barton launched what Sherwood Boehlert, chairman of the House Science Committee, called a "misguided and illegitimate investigation" into the data, methods and personal information of Mann, Bradley and Hughes. At Boehlert's request a panel of scientists convened by the National Research Council was set up, which reported in 2006 supporting Mann's findings with some qualifications, including agreeing that there were some statistical failings but these had little effect on the result.[15] Barton and U.S. Rep. Ed Whitfield requested Edward Wegman to set up a team of statisticians to investigate. The Wegman Report supported McIntyre and McKitrick's view that there were statistical failings, but did not quantify whether there was any significant effect. It included an extensive network analysis which has been discredited by expert opinion and found to have issues of plagiarism. Arguments against the MBH studies were reintroduced as part of the Climatic Research Unit email controversy, but dismissed by eight independent investigations.
The test in science is whether findings can be replicated using different data and methods. More than two dozen reconstructions, using various statistical methods and combinations of proxy records, have supported the broad consensus shown in the original 1998 hockey-stick graph, with variations in how flat the pre-20th century "shaft" appears.[1] The 2007 IPCC Fourth Assessment Report cited 14 reconstructions, 10 of which covered 1,000 years or longer, to support its strengthened conclusion that it was likely that Northern Hemisphere temperatures during the 20th century were the highest in at least the past 1,300 years.[16]
See also
- CLIWOC - Climatological database for the world's oceans
- Dendroclimatology
- Table of historic and prehistoric climate indicators
Notes
- 1 2 Frank et al. 2010.
- ↑ Osborn & Briffa 2006; "A New Take on an Old Millennium". RealClimate. 2006-02-09.
- ↑ IPCC 2007, A: Palaeoclimatic Perspective; see also Jansen et al. 2007, Sec. 6.6.1.1 What Do Reconstructions Based on Palaeoclimatic Proxies Show?.
- ↑ Mann, Bradley & Hughes 1999.
- ↑ Weart 2011c, Fingerprints (1990s-2000s)
- ↑ Jones et al. 2009.
- ↑ Wahl & Ammann 2007
- ↑ Weart 2011c, The Hockey Stick and Beyond
- ↑ Folland et al. 2001, 2.3.2.2 Multi-proxy synthesis of recent temperature change
- ↑ Richard Monastersky (September 5, 2003). "Climate Science on Trial". Chronicle of Higher Education. Retrieved 28 July 2013.
- ↑ BBC News, 16 July 2004.
- ↑ "Part three: Hockey stick graph took pride of place in IPCC report, despite doubts".
- ↑ Revkin, Andrew C. (5 August 2003), "Politics Reasserts Itself in the Debate Over Climate Change and Its Hazards", New York Times, retrieved 2012-02-26.
- ↑ The Decay of the Hockey Stick, Nature "Climate Feedback" blog post by von Storch. "...we do not think that McIntyre has substantially contributed in the published peer-reviewed literature to the debate about the statistical merits of the MBH and related method." (comment by von Storch & Zorita, May 7, 2007 07:35 PM, in response to multiple comments on their failure to acknowledge McIntyre and McKitrick's contributions)
- ↑ Pearce 2010_pt4, "Part four: Climate change debate overheated after sceptics grasped 'hockey stick'".
- ↑ Jansen et al. 2007, Section 6.6: The Last 2,000 Years.
References
- Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K.; Mann, M.E. (August 2006), "Authors were clear about hockey-stick uncertainties", Nature, 442 (7103): 627, Bibcode:2006Natur.442..627B, doi:10.1038/442627b, PMID 16900179.
- Briffa, K. (2000), "Annual climate variability in the Holocene: interpreting the message of ancient trees", Quaternary Science Reviews, 19 (1-5): 87–105, Bibcode:2000QSRv...19...87B, doi:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00056-6.
- Folland; et al. (2001), "Chapter 2: Observed Climate Variability and Change", Missing or empty
|title=(help) in IPCC TAR WG1 2001. - IPCC (2007), "Summary for Policymakers", Missing or empty
|title=(help) in IPCC AR4 WG1 2007. - Jansen; et al. (2007), "Chapter 6: Palaeoclimate", Missing or empty
|title=(help) in IPCC AR4 WG1 2007. - IPCC TAR WG1 (2001), Houghton, J.T.; Ding, Y.; Griggs, D.J.; Noguer, M.; van der Linden, P.J.; Dai, X.; Maskell, K.; Johnson, C.A., eds., Climate Change 2001: The Scientific Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Third Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-80767-0 (pb: 0-521-01495-6).
- IPCC AR4 WG1 (2007), Solomon, S.; Qin, D.; Manning, M.; Chen, Z.; Marquis, M.; Averyt, K.B.; Tignor, M.; Miller, H.L., eds., Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis, Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-88009-1 (pb: 978-0-521-70596-7).
- Jones, P. D.; Briffa, K. R.; Barnett, T. P.; Tett, S. F. B. (1998), "High-resolution palaeoclimatic records for the last millennium: interpretation, integration and comparison with General Circulation Model control-run temperatures", The Holocene, 8 (4): 455–471, doi:10.1191/095968398667194956.
- Mann, M.E.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K. (23 April 1998), "Global-scale temperature patterns and climate forcing over the past six centuries" (PDF), Nature, 392: 779–787, Bibcode:1998Natur.392..779M, doi:10.1038/33859.
- Mann, M.E.; Bradley, R.S.; Hughes, M.K. (1999), "Northern hemisphere temperatures during the past millennium: Inferences, uncertainties, and limitations" (PDF), Geophysical Research Letters, 26 (6): 759–762, Bibcode:1999GeoRL..26..759M, doi:10.1029/1999GL900070.
- Mann, M.E.; Jones, P.D. (August 2003), "Global Surface Temperatures over the Past Two Millennia", Geophysical Research Letters, 30 (15): 1820, Bibcode:2003GeoRL..30oCLM5M, doi:10.1029/2003GL017814.
- McIntyre, S.; McKitrick, R. (2005), "Hockey sticks, principal components, and spurious significance", Geophysical Research Letters, 32 (3): L03710, Bibcode:2005GeoRL..3203710M, doi:10.1029/2004GL021750.
- Mitchell; et al. (2007), "Chapter 12. Detection of Climate Change and Attribution of Causes", Missing or empty
|title=(help) in IPCC AR4 WG1 2007; - North, Gerald R.; Biondi, Franco; Bloomfield, Peter; Christy, John R.; Cuffey, Kurt M.; Dickinson, Robert E.; Druffel, Ellen R.M.; Nychka, Douglas; Otto-Bliesner, Bette; Roberts, Neil; Turekian, Karl K.; Wallace, John M. (June 2006), Surface temperature reconstructions for the last 2,000 years, Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press, p. 146, ISBN 0-309-10225-1
- Osborn, T. J.; Briffa, K. R. (2006), "The Spatial Extent of 20th-Century Warmth in the Context of the Past 1200 Years", Science, 311 (5762): 841–844, Bibcode:2006Sci...311..841O, doi:10.1126/science.1120514, PMID 16469924.
- Powell, Alvin (April 24, 2003), "Sun's warming is global: CfA lecture links solar activity and climate change", Harvard University Gazette, retrieved 2007-04-17.
- Wahl, E.R.; Ammann, C.M. (November 2007), "Robustness of the Mann, Bradley, Hughes reconstruction of Northern Hemisphere surface temperatures: Examination of criticisms based on the nature and processing of proxy climate evidence" (PDF), Climatic Change, 85 (1–2): 33–69, doi:10.1007/s10584-006-9105-7.
External links
- A collection of various reconstructions of global and local temperature from centuries on up
- An NOAA collection of individual data records
- Surface Temperature Reconstructions for the Last 2,000 Years