Zala County (former)
| Zala County Comitatus Zaladiensis Zala vármegye | |||||
| County of the Kingdom of Hungary | |||||
| |||||
|
Coat of arms | |||||
 | |||||
| Capital | Zalaegerszeg 46°51′N 16°51′E / 46.850°N 16.850°ECoordinates: 46°51′N 16°51′E / 46.850°N 16.850°E | ||||
| History | |||||
| • | Established | 12th century | |||
| • | Treaty of Trianon | 4 June 1920 | |||
| Area | |||||
| • | 1910 | 5,995 km2 (2,315 sq mi) | |||
| Population | |||||
| • | 1910 | 466,333 | |||
| Density | 77.8 /km2 (201.5 /sq mi) | ||||
| Today part of | Slovenia, Croatia, Hungary | ||||
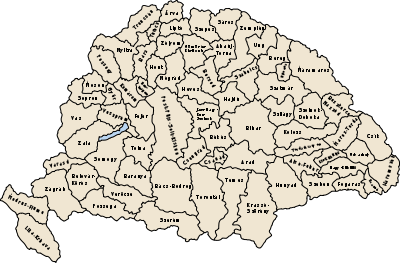
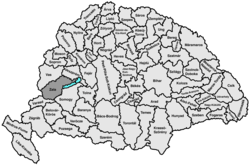
Zala was an administrative county (comitatus) of the Kingdom of Hungary. Its territory is now in southwestern Hungary, northern Croatia and eastern Slovenia. The territory of the county comprised what is now the Hungarian county Zala and part of Veszprém county, the Croatian region of Međimurje to the south-west of it, bordered by the river Drave, and a small region around Lendava in Slovenia. The capital of the county was Zalaegerszeg.
Geography
Zala county shared borders with the Austrian land Styria and the Hungarian counties Vas, Veszprém, Somogy, Belovár-Körös and Varasd (the latter two in Croatia-Slavonia). The river Drava (Hungarian: Dráva) river formed its southern border, Lake Balaton its eastern border. The rivers Mura and Zala flowed through the county. Its area was 5974 km² around 1910.
History
Zala county arose as one of the first comitati of the Kingdom of Hungary.
In 1920, by the Treaty of Trianon, the south-west of the county became part of the newly formed Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (from 1929 as Yugoslavia). The remainder stayed in Hungary. Yugoslavian part of it was occupied and annexed again by Hungary between 1941 and 1945 during World War II. In 1950, as part of the Communist reforms of local government, the county's borders were re-drawn again. A small part of former Vas county, north of Zalaegerszeg, went to Zala county. The part of Zala county north of Lake Balaton went to Veszprém County.
Since 1991, when Slovenia and Croatia became independent from Yugoslavia, the part of former Zala county between the rivers Mura and Drave is part of Croatia (region of Međimurje). The area around Lendava is in Slovenia.
Demographics
In 1900, the county had a population of 437,116 people and was composed of the following linguistic communities:[1]
Total:
- Hungarian: 324,087 (74.1%)
- Croatian: 84,904 (19.4%)
- German: 4,917 (1.1%)
- Slovak: 218 (0.1%)
- Romanian: 159 (0.0%)
- Serbian: 13 (0.0%)
- Ruthenian: 2 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 22,816 (5.2%)
According to the census of 1900, the county was composed of the following religious communities:[2]
Total:
- Roman Catholic: 402,773 (92.2%)
- Jewish: 13,967 (3.2%)
- Calvinist: 11,793 (2.7%)
- Lutheran: 8,251 (1.9%)
- Greek Catholic: 68 (0.0%)
- Greek Orthodox: 108 (0.0%)
- Unitarian: 32 (0.0%)
- Other or unknown: 124 (0.0%)
According to the census of 1910, the county had 466,333 inhabitants.

Population by language (1910 census):[3]
- Hungarian: 347,167 (74.45%)
- Croatian: 91,909 (19,71)
- German: 3,889 (0.83%)
- Slovak: 233
- Serbian: 56
- Romanian: 44
- Ruthenian: 3
- Other: 23,032 (4.94%)
Population by religion (1910 census):[4]
- Roman Catholic: 433,145 (92.88%)
- Jewish: 12,829 (2.75%)
- Calvinist: 11,738 (2.52%)
- Lutheran: 8,220 (1.76%)
- Greek Catholic: 117
- Greek Orthodox: 110
- Unitarian: 37
- Other: 74 (0.15%)
Subdivisions
In the early 20th century, the subdivisions of Zala county were:
| Districts (járás) | |
|---|---|
| District | Capital |
| Alsólendva | Alsólendva, SI Lendava |
| Balatonfüred | Balatonfüred |
| Csáktornya | Csáktornya, HR Čakovec |
| Keszthely | Keszthely |
| Letenye | Letenye |
| Nagykanizsa | Nagykanizsa |
| Nova | Nova |
| Pacsa | Pacsa |
| Perlak | Perlak, HR Prelog |
| Sümeg | Sümeg |
| Tapolca | Tapolca |
| Zalaegerszeg | Zalaegerszeg |
| Zalaszentgrót | Zalaszentgrót |
| Urban districts (rendezett tanácsú város) | |
| Nagykanizsa | |
| Zalaegerszeg | |
The towns of Prelog and Čakovec are in Croatia; Lendava is in Slovenia.
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
- ↑ "KlimoTheca :: Könyvtár". Kt.lib.pte.hu. Retrieved 2012-12-06.
- ↑
- ↑
.svg.png)