Zdeněk Zeman
|
| |||
| Personal information | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Full name | Zdeněk Zeman | ||
| Date of birth | 12 May 1947 | ||
| Place of birth | Prague, Czechoslovakia | ||
| Teams managed | |||
| Years | Team | ||
| 1974–1983 | Palermo (youth) | ||
| 1983–1986 | Licata | ||
| 1986–1987 | Foggia | ||
| 1987 | Parma | ||
| 1988–1989 | Messina | ||
| 1989–1994 | Foggia | ||
| 1994–1997 | Lazio | ||
| 1997–1999 | Roma | ||
| 1999–2000 | Fenerbahçe | ||
| 2000 | Napoli | ||
| 2001–2002 | Salernitana | ||
| 2003–2004 | Avellino | ||
| 2004–2005 | Lecce | ||
| 2006 | Brescia | ||
| 2006 | Lecce | ||
| 2008 | Red Star Belgrade | ||
| 2010–2011 | Foggia | ||
| 2011–2012 | Pescara | ||
| 2012–2013 | Roma | ||
| 2014 | Cagliari | ||
| 2015 | Cagliari | ||
| 2015–2016 | Lugano | ||
Zdeněk Zeman (born 12 May 1947) is a Czech-Italian football coach. Known for his offensive footballing tactics and use of the 4–3–3, he has managed numerous teams over the years, mostly in Italian football.
Career
Early years
Zeman's football coaching career started in Sicily, where he resided since the late 1960s. His first coaching experiences were for amateur football teams from Palermo neighborhood (Cinisi, Bacigalupo, Carini, Misilmeri, Esacalza). In 1974, thanks to his uncle Čestmír Vycpálek's aid, he had his first notable experience as part of the Palermo Calcio youth coaching staff, which ended in 1983.
In 1975 he graduated with honours at the ISEF of Palermo (a sports school) with a dissertation about sports medicine. In 1979 he finally obtained the patentino (a kind of license for coaching football at the professional level) at the Coverciano's school for football coaches.[1]
His first opportunity as professional head coach came from Licata, a small-medium city in the province of Agrigento, where he won Serie C2 with a team mainly composed of youngsters. In 1986, he then left Licata in order to join Foggia Calcio of Serie C1, but he was sacked before the end of the championship. In 1987 he became coach for Parma of Serie B, but was fired after just seven matches. In 1988 he returned to Sicily as coach of Messina, classified at the 8th place for the end of the season, also thanks to the goals of Salvatore Schillaci.[2]
Zemanlandia: from third division to Serie A with Foggia
In 1989 the Foggia chairman Pasquale Casillo, repented of having fired him a few years before, signs on Zeman again. It was to be the beginning of the miracle Foggia, also known as Zemanlandia (after Zeman himself), a team of, in those days, unknown players; amongst them, Giuseppe Signori and Francesco Baiano who regularly punched above their weight in the league. In two years the team got promoted to top-level Serie A.[3]
The first appearances of Foggia in Serie A are still quite unimaginable, with a team considered as extremely weak verging on the UEFA Cup qualification for three consecutive years. This was achieved playing an impressive, attacking style of play, with the 4–3–3 module a clear trademark of Zdeněk Zeman's football views. During those years at Foggia, players like Roberto Rambaudi, Luigi Di Biagio, Igor Shalimov, José Antonio Chamot, Dan Petrescu and Igor Kolyvanov came through. It is said that Zeman's tactics were inspired by his time playing, not football, but handball as a student.[4]
Lazio and Roma
In 1994, Zeman left Foggia for the greater challenge of Lazio, bringing the Biancocelesti to a 2nd and a 3rd place, before being fired in January 1997.[5] He is credited with launching the career of Alessandro Nesta whilst managing Lazio, giving the young defender many first team opportunities. In the next season, Zeman decided to stay in Rome, becoming the coach of A.S. Roma and the burgeoning talent of Francesco Totti.
After a good fourth place with some sparkling play, Zeman launched allegations about the abuse of pharmaceutical products in Italian football, citing former Juventus players Gianluca Vialli and Alessandro Del Piero (of using creatine) in July 1998. As a consequence, Courts begun a round of trials, until Juventus sport doctor Riccardo Agricola was found guilty of administering excessive pharmaceuticals to players between 1994 and 1998 and condemned to a 1-year and ten months jail term in 2004, even though he was absolved the next year by a Court of Appeal.[6] In the following 1998–1999 season Zeman reached a fifth-place finish with A.S. Roma, but was replaced by Fabio Capello during the summer of 1999.[7]
2000s
His next coaching adventures, for Fenerbahçe SK and S.S.C. Napoli, were not lucky; Zeman's coaching reputation quickly lost stock, leaving him unable to find a team willing to hire him. After three Serie B years at Salernitana (2 years, a 6th place, and a dismissal), and Avellino (second-last placed, with a young Vitali Kutuzov on team), in 2004 Serie A team Lecce gambled on him. Zeman, who had one of the youngest Serie A rosters at his disposal, answered with a good season, leading the team to a mid-table position giving talented youngsters like Valeri Bojinov and Mirko Vučinić an opportunity. At the end of the season, Zeman resigned. After nine months without a team, Zeman was appointed on 5 March 2006 as new coach of Brescia, taking in his first time ever a team in the half-season. However, Brescia, who were third-placed in Serie B when Zeman was hired, suffered a heavy falling down in terms of results, and the team wasn't able to maintain a place in the promotion playoffs, with 8 points in 11 matches. After the end of the season, Zeman resigned from Brescia, criticizing his players for not having accepted his tactics.
On 21 June 2006 Zeman returned to Lecce, signing a one-year contract with the giallorossi, who were then relegated to Serie B in 2005–2006. Because of poor results, he was then fired on 24 December and replaced by Giuseppe Papadopulo.
On 17 June 2008 Red Star Belgrade unveiled Zeman as their new head coach.[8] However, after only five competitive games as Red Star's head coach, on 6 September 2008 Zeman was sacked because of catastrophic results in Serbian League and UEFA Cup. During Zeman's management, Red Star hadn't managed to score in three matches of the domestic league and club found themselves on the bottom of the table for the first time in 24 years. Red Star were also eliminated in the qualifying round of the UEFA Cup by APOEL F.C. from Cyprus.[9]
2010s: back to Foggia, and Pescara
On 20 July 2010 it was confirmed that Zeman would take over as new head coach of his former club Foggia, rejoining chairman Pasquale Casillo and director of football Giuseppe Pavone as part of the trio who led the satanelli into Serie A back in the 1990s.[10] He left the club at the end of May, after ending the regular season in sixth place, and failing to qualify to the promotion playoffs despite his Foggia team being the team with the highest goalscoring ratio among all Italian professional leagues.
On 21 June 2011 Zeman was announced as new head coach/technical director of Serie B club Pescara, signing a one-year contract with the Adriatici.[11][12] At Pescara, Zeman fully regained his cult status thanks to a team composed of promising youngsters, many of them re-joining him from his previous season at the helm of Foggia (among them, Simone Romagnoli, Ciro Immobile and Lorenzo Insigne, and also Marco Verratti); under his tenure, the Biancazzurri from Abruzzo entered straight into the race for automatic promotion and provided a record goalscoring ratio for Italian standard (90 goals in 42 games, Serie B record). On 21 May 2012, Pescara won automatic promotion to Serie A following a 3–1 away win at Sampdoria, thus ensuring Zeman a top flight return at his first season as head coach. He went on to win the Serie B title in the final game of the season.[13][14]
2012–13: Return to Roma
On 4 June 2012 it was confirmed that Zeman would be new head coach of his former club Roma, signing a two-year contract, effective from 1 July 2012 to 30 June 2014; his staff will be composed by assistant manager Vincenzo Cangelosi, technical collaborator Giacomo Modica and fitness coach Roberto Ferola.[15] The agreement will mark Zeman's return at the Giallorossi after thirteen years. His appointment also led The Wall Street Journal to unusually dedicate him an article, labelling him the "Soccer's Jedi".[16]
His second stint as Roma head coach became controversial after he decided to sideline a number of key players such as Maarten Stekelenburg, Pablo Osvaldo and, most significantly, vice-captain and one-club player Daniele De Rossi.[17] A successive decline in results then led to rumours involving the future of Zeman, with director of football Walter Sabatini explicitly confirming about a potential dismissal of the experienced Czech head coach at the end of January.
On 2 February 2013, Zeman was relieved from his coaching post after a 2–4 home loss to Cagliari that left Roma in 8th position after 23 matches, and was replaced by the club's technique coach Aurelio Andreazzoli.[18][19] After being sacked, player Miralem Pjanić commented that hiring Zeman had been a good decision, believing that the club's athletic all-attacking style of play the team's main strength, albeit also being one of its biggest weaknesses.[20] Zeman initially stated that he was not bitter about being sacked by Roma[21] and played down the rumours of his retirement,[22] although he later revealed in an interview with Italian sports newspaper La Gazzetta dello Sport that he was still critical towards the team over his sacking.[17]
2014–15: Cagliari
On June 2014, Zeman returned into football management, being appointed new head coach of Serie A club Cagliari after a successful takeover led by entrepreneur Tommaso Giulini. On the fifth game of the season Zeman got a surprising but deserved victory of 1–4 playing away against Internazionale, briefly staving off rumors of dismissal after a mediocre start of season. However, he was sacked on 23 December 2014 following a poor run, which saw Cagliari achieve only two wins in their sixteen league fixtures, leaving them in eighteenth place in the relegation zone.[23]
On 9 March 2015, just a few months after originally being sacked, Cagliari reappointed Zeman as head coach, the club having sacked Gianfranco Zola.[24] Zeman resigned from the post after just five games, in which Cagliari picked up just one point from the available 15.[25]
2015–16: Lugano
In June 2015, Zeman signed a contract with newly promoted Swiss Super League club FC Lugano.[26] On 26 May 2016, Zeman helped the club avoid relegation with a 3–0 win over FC St. Gallen. On 29 May, however, Lugano were defeated 1–0 by last placed FC Zürich in the 2016 Swiss Cup Final.[27] He left the club at the end of the season.[28]
Personal life
Son of a medician and a housewife, Zeman is also related to Čestmír Vycpálek, former Juventus player and coach, who was his uncle from his mother's side. In 1968 Zeman went to Palermo in order to visit him; however, at that same time his country was invaded by Warsaw Pact troops, so he decided to stay indefinitely in Italy.[1]
He successively obtained Italian citizenship in 1975 and later married a woman from Palermo, Chiara Perricone, with whom he had two children named Karel and Andrea; Karel successively went on into following his father's footsteps by becoming a football manager, starting at amateur level with teams such as Bojano and Manfredonia[29] before taking over his first professional role at Lega Pro Seconda Divisione outfit Fano in March 2012.[30] He then served as head coach of Qormi in Malta before becoming boss of Sardinian Serie D amateurs Selargius in the summer of 2014, contemporaneously to his father's appointment at Cagliari.[31]
His appeal has stretched outside the football world, with singer/songwriter (and well-known A.S. Roma fan) Antonello Venditti, dedicating a song called La coscienza di Zeman (Zeman's conscience) to him. Zeman was also the "guru" who inspired the character Frengo by Italian comedian Antonio Albanese. He was also the subject for a number of biopics, mostly covering his early Foggia years, such as Zemanlandia.[32] Zeman is also known for being a heavy smoker and an iconic man of very few words with a cult following throughout Italy that goes across all football rivalries.[33][34]
Tactics
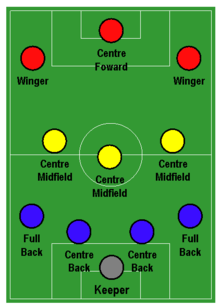
Based on Dutch Totaal Voetbal, Zdeněk Zeman has described the concept of his 4–3–3 system as "geometry", and his teams also known for approaching a football philosophy clearly based on lively, quick, attacking play, the offside, and zonal marking. His teams are well known for their fast, spectacular, aggressive, and offensive style of play, as well as their ability to score many goals, but also for the corresponding tendency to concede them.[35][36][37][38]
A respected and experienced manager, his coaching techniques, especially in regards to athletic preparation, fitness, and training (a field for which he has a particular interest), are also proverbial for their effort and diligence. Notable features of his system are the use of a high defensive line, the offside trap, high pressing, and zonal marking, as well as short first touch passes and one-twos played on the ground, although the deep-lying playmaker in his formation must also be competent at providing long passes and switching the play. The wingers in his system are set to move inside the channels, and usually play a free creative role. All of these elements combined made Zeman's tactics solid, spectacular and extremely versatile: they are effective against top teams as well as weaker ones.[35][36][37]
Having the right players for his tactical system is essential; usually the characteristics needed by his players are:[35][39]
- Sweeper Keeper: In addition to being a good shot-stopper, the goalkeeper must be capable of reading the game, and quick to come off his goal-line; he must also have good dribbling ability and distribution.
- Wing Backs: They must be offensive wing backs, not merely defensive minded full Backs. The use of quick, hard-working attacking wing backs is one of the most important aspects of Zeman's tactics and formation, as they often overlap with the wingers to provide crosses into the box, whilst also returning to defend.
- Center Backs: Complete and strong, with good heading ability, marking, tackling, jumping, pace, positioning and acceleration, as well as good technique and ball playing ability.
- Central Midfielders: The center midfielder in Zeman's system is a complete player who is a hybrid of a defensive midfielder, a box-to-box midfielder, and a deep-lying playmaker. The centre-midfielder, therefore, must be effective defensively, but he must also be equally capable of creating plays and making offensive runs into the area. He must be a quick, hardworking, physically fit, and strong player, as well as being creative, and a good long passer and tackler. The left & right centre midfielders must also be hard-working and well rounded box-to-box players, with good technique, offensive capabilities, and passing ability.
- Wing Forward: Zeman's formation makes a fundamental use of hard-working wingers with pace, stamina, and good creative and technical ability. Instead of hugging the touchline like traditional wingers, however, in his system, they are set to move into channels, often functioning as inverted wingers or outside forwards. Although they are given more tactical freedom than most players in his formation, they must also be capable of scoring as well as making the right attacking movements.
- Central Forward: The striker must be a complete and intelligent team player, who is quick, strong, and an accurate finisher with both feet and head. The centre-forward must also have reliable technique and a good positional sense, as well as the ability to hold up the ball for team-mates when playing with his back to goal, in order to lay off the ball to players making attacking runs.
Honours
Manager
- Licata[2]
- Serie C2 (1): 1984–85
- Foggia[3]
- Pescara[14]
Individual
- Manager
- Silver Bench (1): 2011–12[40]
References
- 1 2 "Biografia". www.zeman.org (in Italian). Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Carriera". www.zeman.org (in Italian). Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- 1 2 Leonardo Gualano (27 March 2015). "Goal Racconta... - Quando Foggia diventò Zemanlandia: la storia della squadra più 'bella' degli anni '90" (in Italian). Goal.com. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ↑ SEBASTIANO MERCADANTE (30 May 2012). "Zeman, il mio allenatore di pallamano" (in Italian). La Repubblica. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ↑ "Zeman: Mourinho tecnico mediocre. Risposta: non so chi sia" (in Italian). Sky.it. 28 September 2009. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ↑ "Juventus keep titles from 'doping' era". espnfc.com. 2014. Retrieved 23 June 2014.
- ↑ "Addio Zeman" (in Italian). RAI.it. 2 June 1999. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- ↑ "Novi trener – Zdenjek Zeman" (in Serbian). Red Star Belgrade. 2008-06-17. Archived from the original on 2008-07-01. Retrieved 2008-06-17.
- ↑ "Zeman sacked". Archived from the original on 7 September 2008.
- ↑ "Zdenek Zeman è il nuovo allenatore del Foggia. Domani la presentazione" (in Italian). US Foggia. 2010-07-20. Retrieved 2010-07-20.
- ↑ "Il Pescara sceglie Zeman Di Francesco verso Lecce" (in Italian). La Repubblica. 21 June 2011. Retrieved 22 June 2011.
- ↑ "Ufficiale: Zeman sarà presentato sabato" (in Italian). Delfino Pescara 1936. 21 June 2011. Retrieved 29 June 2011.
- ↑ Tullio Calzone (11 June 2015). "Pescara, ora Zeman è di troppo" (in Italian). Il Corriere dello Sport. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Il Pescara vince la Serie B. Playout tra Empoli-Vicenza" (in Italian). Il Corriere dello Sport. 26 May 2012. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ↑ "AS Roma announcement: Zdenek Zeman". AS Roma. 4 June 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
- ↑ "The Return of Soccer's Jedi". The Wall Street Journal. 3 June 2012. Retrieved 4 June 2012.
- 1 2 "Zeman still bitter over Roma sacking". Goal.com. 23 April 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- ↑ "OFFICIAL: ROMA SACK ZEMAN". Football Italia. 2 February 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2016.
- ↑ "AS Roma: Zdenek Zeman" (in Italian). A.S. Roma. 2 February 2013. Retrieved 2 February 2013.
- ↑ "Pjanic: Decision to sack Zeman was correct". Goal.com. 7 February 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- ↑ "Zeman not bitter about Roma sacking". Goal.com. 5 February 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- ↑ "Zeman rubbishes retirement rumours after Roma exit". Goal.com. 3 February 2013. Retrieved 23 April 2013.
- ↑ "Struggling Cagliari sack coach Zeman". Euronews. Reuters. 23 December 2014. Retrieved 23 December 2014.
- ↑ "Gianfranco Zola sacked as Serie A Cagliari rehire Zdenek Zeman". BBC Sport. BBC. 9 March 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ↑ "Zdenek Zeman leaves Cagliari for second time". BBC Sport. BBC. 21 April 2015. Retrieved 22 April 2015.
- ↑ Selene Scarsi (15 June 2015). "Zdenek Zeman set to take charge of Swiss side FC Lugano". ESPN FC. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "Zeman, niente coppa di Svizzera: il Lugano sbaglia rigore e perde a Zurigo" (in Italian). La Gazzetta dello Sport. 29 May 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ↑ "Zeman: 'Lugano not good enough'". Football Italia. 4 June 2016. Retrieved 6 June 2016.
- ↑ "Zeman jr tecnico del Manfredonia" (in Italian). Corriere della Sera. 13 August 2010. Retrieved 13 August 2010.
- ↑ "Fano: Karel Zeman nuovo tecnico" [Fano: Karel Zeman new trainer] (in Italian). La Gazzetta del Mezzogiorno. 20 March 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Anche Zeman jr in Sardegna: allenerà il Selargius" (in Italian). La Gazzetta dello Sport. 6 August 2014. Retrieved 26 August 2014.
- ↑ "Il Foggia dei miracoli nel film "Zemanlandia"" [The miracle Foggia depicted on "Zemanlandia"] (in Italian). La Repubblica - Bari. 24 September 2009. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Nostalgic scenes as an old favourite returns to Foggia". When Saturday Comes. 21 July 2010. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- ↑ "Legend of Calcio: Zdenek Zeman". Forza Italian Football. 5 April 2012. Retrieved 6 May 2012.
- 1 2 3 "Tattica". www.zeman.org (in Italian). Retrieved 12 May 2016.
- 1 2 "Zeman: "Roma, un giorno tornerò"". Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- 1 2 "La storia di Zeman". Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ "Il 4-3-3, modulo aggressivo". Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ "Il 4-3-3 di Zdenek Zeman". Retrieved 17 January 2015.
- ↑ "Juventus, Conte vince la panchina d'oro. Premiato anche Zeman" (in Italian). La Repubblica. 18 February 2013. Retrieved 12 May 2016.
External links
- (Italian) (English) Official Zdeněk Zeman's website
- (English) Unofficial Zdeněk Zeman's website - Fansite