1seg
| List of digital television broadcast standards |
|---|
| DVB standards (countries) |
| ATSC standards (countries) |
|
| ISDB standards (countries) |
| DTMB standards (countries) |
| DMB standard (countries) |
| Codecs |
| Frequency bands |
1seg (ワンセグ wansegu) is a mobile terrestrial digital audio/video and data broadcasting service in Japan, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Uruguay, Peru and the Philippines. Service began experimentally during 2005 and commercially on April 1, 2006. It is designed as a component of ISDB-T, the terrestrial digital broadcast system used in Japan, the Philippines, Argentina, Brazil, Chile, Peru and Uruguay, as each channel is divided into 13 segments, with a further segment separating it from the next channel; an HDTV broadcast signal occupies 12 segments, leaving the remaining (13th) segment for mobile receivers, hence the name, "1seg" or "One Seg".
Its use in Brazil was established in late 2007 (starting in just a few cities), with a slight difference from the Japanese counterpart: it is broadcast under a 30 frame/s transmission setting (Japanese broadcasts are under the 15 frame/s transmission setting).
Technical information
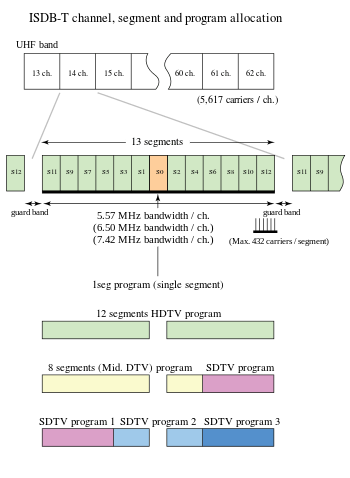
The ISDB-T system uses the UHF band at frequencies between 470 and 770 MHz (806 MHz in Brazil), giving a total bandwidth 300 MHz. The bandwidth is divided into fifty name channels 13 through 62. Each channel is 6 MHz wide consisting of a 5.57 MHz wide signalling band and a 430 kHz guard band to limit cross channel interference. Each of these channels is further divided into 13 segments, each with 428 kHz of bandwidth. 1 seg uses a single of these segments to carry the 1seg transport stream.
1seg, like ISDB-T uses QPSK for modulation, with 2/3 forward error correction and 1/4 guard ratio. The total datarate is 416 kbit/s.
The television system uses a H.264/MPEG-4 AVC video stream and a HE-AAC audio stream multiplexed into a MPEG transport stream. The maximum video resolution is 320x240 pixels, with a video bitrate of between 220 and 320 kbit/s. Audio conforms to HE-AAC profile, with a bitrate of 48 to 64 kbit/s. Additional data (EPG, interactive services, etc.) is transmitted using BML and occupies the remaining 10 to 100 kbit/s of bandwidth.
Conditional access and copy control are implemented in 1seg broadcasting by the use of Broadcast Flag-like structure contained in the "Copy Control Descriptor" within the broadcast. The broadcast contents themselves are not encrypted, but the Copy Control information forces the device to encrypt stored recordings and disallows making a copy of the recording.
Broadcast Markup Language
Broadcast Markup Language (BML), is a data-transmission service allowing text to be displayed on a 1seg TV screen.
The text contains news, sports, weather forecasts, Earthquake Early Warning, etc. free of charge. Further information can be found through links to content on websites, frequently those belonging to the television station itself.
EPG (program guides) is not included, but transmitted in separate stream (EIT).
Multiple-program arrangement
On June 23, 2008, broadcaster Tokyo MX officially began using multiple-program arrangement (マルチ編成 Maruchi hensei) technology to simultaneously broadcast two programs on a single divided segment. Most 1seg receivers manufactured after September 2008 are compatible with this technology. Multiple-program arrangement in 1seg is named as 1seg2 or Oneseg2 (ワンセグ2 Wansegu tsū).
NHK Educational TV (from 1 April 2009) and Nara Television (奈良テレビ放送 Nara terebi hōsō) (from 1 December 2009) are also started for several number of programs.
Popularity
Until the end of March 2008, Japanese regulation required that the programs on 1seg were fundamentally the same as those broadcast on the equivalent HDTV channel. On April 1 the regulation was revised, and experimental programs by 1seg or third parties have begun airing on several stations.
On January 16, 2008, JEITA released their monthly shipping survey showing approx. 4.806 million mobile phones were sold in Japan in November 2007. Of these, approx. 3.054 million phones, 63.5% of the total, can receive 1seg broadcasts.[1]
In the fiscal year of 2007, on average 45% of mobile phones had 1seg reception capability out of the 22.284 million units sold. The percent increased from 26.8% in April 2007 to 64.2% at end of fiscal year March 2008.[2]
Receivers


- Electronic dictionary
- (Japanese) Sharp Papyrus PW-TC900
- (Japanese) Sharp Papyrus PW-TC920
- (Japanese) Sharp Papyrus PW-TC930
- (Japanese) Sharp Papyrus PW-TC980
- PC connect type
- (Japanese) Pixela PC
- (Japanese) Monster TV 1D PC card Type II 1seg receiver by SKNET
- (Japanese) Cowon D2TV
- and more.
- Car navigation system
- (Japanese) Sanyo One-seg & car navigation system
- and more.
- Handheld game console
- (Japanese) 1seg PSP-2000 Tuner
- (Japanese) Nintendo DS (via an add-on called "DS Telebi")
- Portable devices
- Set top box
- Others
- (Japanese) Sony Walkman NW-A919
- (Japanese) Kodak 3-inch OLED TV
- and more.
- Mobile Phones
- The first mobile phone handsets for 1seg were sold by KDDI to consumers in autumn 2005. Today, almost all mobile phones sold in Japan feature a 1seg antenna (only for Android phones, iOS users must purchase a third-party 1seg antenna separately).
See also
- Digital terrestrial television
- DMB - South Korea
- DVB-H
- ISDB-T
References
- ↑ Source; the article of Yomiuri Shimbun 2008-01-16, area version 13S page 8, and (Japanese language);2007 fiscal year monthly base shipment quantity (2007年度移動電話国内出荷実績、ワンセグ搭載比率(%))
- ↑ 2007年度移動電話国内出荷実績; (2007 fiscal year mobile phone ship out record) (In Japanese)
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 1seg. |
- "TV programs go mobile as One Seg services begin". The Japan Times. 2006-04-01. Archived from the original on 2008-01-10.
- One-Seg service for Mobile DevicesPDF file, Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG)
- Digital Broadcasting Experts Group (DiBEG) promote ISDB-T
- ISDB-T, Application, Present and Future, PDF File
- Mobile phone and PHS operators which provide 1seg phone receivers.
- (Japanese) Association for promotion of Digital Broadcasting (Japanese)
- (Japanese) 1seg promotion site (Japanese)
- ACCESS Ginga Edition for 1Seg in Brazil
- GPS fitted with ISDB-T OneSeg sales grow in Brazil