Abolition of monarchy

The abolition of monarchy has occurred throughout history, either through revolutions, coups d'état, wars, or legislative reforms (such as abdications). The founding of the Roman Republic is a noteworthy example and became part of the nation's traditions including as justification for the assassination of Julius Caesar. The twentieth century saw a major acceleration of this process, with many monarchies violently overthrown by revolution or war, or else abolished as part of the process of decolonisation. By contrast, the restoration of monarchies is rare in modern times, with only two major examples, Spain and Cambodia.
17th-18th centuries
One of the earliest examples in modern times is the overthrow in 1649 of the English monarchy by the Parliament of England, led by Oliver Cromwell. The monarchy was restored in 1660 although in a more limited form moderated by an independent Parliament.
Anti-monarchism in the United States developed out of the gradual process of revolution that began as early as 1765, as colonists resisted the Stamp Act through boycott and the expulsion and condemnation of royal officials. While subjects of the United Kingdom, a unification of the limited King of England with the King of Scotland, colonists enjoyed a level of autonomy which increasingly clashed with royal and Parliamentary authority which did not consult colonial needs. With the Declaration of Independence in 1776, the most violent wave of anti-monarchical protest began, with the systematic destruction of the relics and symbols of monarchy. Examples can be found in the toppling of the equestrian statue of George III on Bowling Green in New York City. Monarchic loyalists were particularly affected with partisan attacks or harassment, with tens of thousands leaving for Canada, Britain, and other colonies.[1] Wealth or property which remained was typically confiscated. Thomas Paine, the famous author of the revolutionary pamphlet "Common Sense," extolled the colonists to finance the revolutionary war through this means. Even today, very few artifacts depicting the British monarchy from the colonial period can be found in the United States.
However, the most famous abolition of monarchy in history is that of the French monarchy in 1792, during the French Revolution. The French monarchy was later restored several times with differing levels of authority. Napoleon, initially a hero of the Republican revolution, crowned himself emperor in 1804 only to be replaced by the Bourbon Restoration in 1815 which in turn was replaced by the more liberal July Monarchy in 1830.
The 1848 Revolution was a more clear anti-monarchic uprising that replaced the succession of royal leaders with the short-lived Second French Republic. Napoleon III's Second French Empire from 1852 to 1870 retained republican aspects while placing himself in the center of the state until the losses in the Franco-Prussian War precipitated his fall resulting in the French Third Republic and the end of monarchy for good.
19th century
In 1858 the Mughal Empire came to an end after losing a war against Britain, and its Emperor, Bahadur Shah II, lost his throne. Between 1859 and 1861, four monarchies in Southern Europe ceased to exist: Parma, Modena, Tuscany and the Two Sicilies, when they all became part of the new Kingdom of Italy. The Second Mexican Empire collapsed in 1867, and its Emperor, Maximilian I of Mexico, was executed. The Second French Empire came to an end in 1870 after it had lost the war against Prussia, causing Emperor Napoleon III to lose his throne. He was the last monarch of France.
In Spain monarchy was abolished from 1873 to 1874 by the First Spanish Republic, but then restored until 1931. The monarchy of Tahiti came to an end in 1880 when France made it a colony and overthrew King Pōmare V. That of Burma was abolished in 1885, when the last king, Thibaw Min, lost his throne and the country was annexed by Britain. In Brazil, the monarchy was abolished in 1889, when Emperor Pedro II was overthrown by a republican military coup (the status of the republic was fully confirmed by a plebiscite in 1993 that resulted in 86.6% of the votes to the republican government). In 1893 foreign business leaders overthrew the Queen of the Kingdom of Hawaii. They established a republic, which joined the United States in 1898. The monarchy of Madagascar, known as the Merina Kingdom, came to an end in 1897 when France made it a colony and overthrew Queen Ranavalona III.
20th century
 |
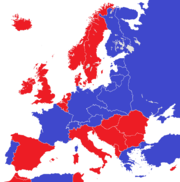 |
 |
| European states in 1914.[2] Monarchies (22)
Republics (4) |
European states in 1930.[3] Monarchies (20)
Republics (15) |
Present-day European states. Monarchies (12)
Republics (32) |
In 1910 the last emperor of Korea, Sunjong, lost his throne when the country was annexed by Japan. However, the Korean royal family was mediatised as a puppet family within the Japanese imperial family. Many of the Korean royals were forcibly re-educated in Japan and forced to marry Japanese royalty and aristocrats to meld the ruling families of the two empires. With the abolition of the Japanese aristocracy and cadet branches of the imperial family, the Korean royals officially lost their remaining status.
The monarchy of Portugal was also overthrown in 1910 (5 October), two years after the assassination of King Carlos I, ending the reign of Manuel II, who died in exile in England (1932), without issue.
The ancient monarchy of China ceased to exist in 1912 after the revolution of Sun Yat-sen overthrew Emperor Puyi. General Yuan Shikai, then provisional president, unsuccessfully tried to make himself a monarch in 1915.
World War I led to perhaps the greatest spate of abolition of monarchies in history. The conditions inside Russia and the poor performance in the war gave rise to a revolution which toppled the entire institution of the monarchy, followed by a second revolution against that government in October of the same year that executed Emperor Nicholas II and implemented a Marxist-Leninist government. The defeated German, Austro-Hungarian and Ottoman empires saw the abolition of their monarchies in the close aftermath of the war, ending the reigns of Wilhelm II, Charles I and Mehmed VI respectively. The monarchs of the constituent states within the German Empire, most importantly Ludwig III of Bavaria, Frederick Augustus III of Saxony and Wilhelm II of Württemberg, soon abdicated. During the war, monarchies were planned for the Grand Principality of Finland (to have a Finnish King), and for Lithuania (Mindaugas II of Lithuania), with a protectorate-like dependency of Germany. Both intended kings renounced their thrones after Germany's defeat in November 1918. King Nicholas I of Montenegro lost his throne when the country became a part of Yugoslavia in 1918.
After the death of the last Emperor, Bogd Khan, in 1924, Mongolia became a republic. In Spain the monarchy was again abolished in 1931 by the Second Spanish Republic (1931–1936/39). In 1947, General Franco declared Spain a realm, and appointed Juan Carlos of Bourbon his successor in 1969. The Prince of Spain became king at Franco's death in 1975, and constitutional monarchy was restored in 1978 under him.
World War II saw another spate of abolitions. In 1939 Italy invaded Albania and removed the reigning self-proclaimed King Zog and instated their own King Victor Emmanuel III as its new monarch. Italy, along with the eastern European monarchies of Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania joined with Germany in World War II against the Kingdom of Yugoslavia, the Western allies and the Soviet Union. As the Axis powers came to a defeat in the war, communist partisans in occupied Yugoslavia and occupied Albania seized power and ended the monarchies. Communists in Bulgaria, Hungary and Romania removed their monarchies with strong backing by the Soviet Union, which had many troops and supporters placed there during the course of the war. Through this, Peter II of Yugoslavia, Simeon II of Bulgaria and Michael I of Romania all lost their thrones. King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy had switched sides during the war in favour of the western allies, but a referendum in 1946 ended the short reign of his son King Umberto II and the Italian monarchy ceased to exist. A unique result of the war was that Emperor Hirohito of Japan, who had held a debated but important role in Japan's warfare against the Allied powers, was reduced in stature from a divine monarch to a figurehead by the occupying United States, instead of losing his throne altogether.
Throughout Greece's eventful modern history, the monarchy was toppled and restored several times between and after the two World Wars. The last king, Constantine II, was forced into exile after a coup in 1967 and the republic was proclaimed in 1973 by the then ruling military dictatorship. Final abolition of the monarchy was confirmed overwhelmingly after constitutional legality was restored, by free referendum in 1974.
The independence of the Indian subcontinent from direct British rule in 1947 posed a unique problem. From 1858, when the British government had assumed direct rule over the subcontinent, it had been governed as a quasi-federation, with most of the subcontinent (known as British India), under the direct rule of the British sovereign. The remainder of the subcontinent, however, was under a form of indirect rule through its division and subdivision into over 500 subnational monarchies, known as princely states; each was ruled by a prince in a subsidiary alliance with the British government. The princely states ranged from powerful and largely independent principalities such as Hyderabad or Mysore, with a high level of autonomy, to tiny fiefdoms a few dozen acres in size. The resulting imperial structure was broadly similar to that of the German Empire before the First World War.
In 1947, it was agreed the Indian subcontinent would be partitioned into the independent British dominions of India and Pakistan, with the princely states acceding to one nation or the other. The accession process proceeded smoothly, with the notable exception of four of the most influential principalities. The Muslim ruler of the Hindu-majority state of Junagadh ruler acceded to Pakistan, but his decision was overruled by the Indian government, while Hyderabad chose to be independent, but was forcibly annexed to India in 1948. The Hindu ruler of Jammu and Kashmir, among the largest and most powerful of the principalities, but with a Muslim-majority population, initially held off on a decision. In the autumn of 1947, an invading force from Pakistan frightened the ruler into acceding to India. The ruler of Kalat, in Baluchistan, declared his independence in 1947, after which the state was forcibly merged with Pakistan, resulting in an insurgency persisting to this day. With the promulgation of the Indian constitution in 1950, India abolished its monarchy under the British crown and became a republic within the Commonwealth of Nations, followed by Pakistan in 1956; as a result of both developments, the majority of the princes formally lost their sovereign rights. A few remaining principalities in Pakistan retained their autonomy until 1969, when they finally acceded to Pakistan. The Indian government formally derecognised its princely families in 1971, followed by Pakistan in 1972.
Many monarchies were abolished in the middle of the 20th century or later as part of the process of decolonisation. The monarchies of India, Ghana, Nigeria, Kenya, Tanganyika, Uganda, Guyana, and Malawi were abolished shortly after they became independent of the United Kingdom, while remaining within the Commonwealth. That of Ireland was not abolished when Ireland became independent of the United Kingdom in the 1920s, but by the Republic of Ireland Act of 1948, which came into force in 1949. Some Commonwealth realms waited a little longer before abolishing their monarchies: Pakistan became a republic in 1956 and South Africa in 1961. Gambia abolished its monarchy in 1970, while Sierra Leone became a republic in 1971, as did Sri Lanka in 1972, Malta in 1974, Trinidad and Tobago in 1976, and Fiji in 1987. The latest country to become a Commonwealth republic was Mauritius in 1992.
That of Egypt was abolished in 1953, after the revolution of 1952, which caused King Farouk I to abdicate in favour of his infant son Fuad II. The monarchy of Tunisia ended in 1957 when Muhammad VIII al-Amin lost his throne and that of Iraq when King Faisal II was killed and a republic proclaimed. The monarchy of Yemen was abolished in 1962 when King Muhammad al-Shami was overthrown in a coup, although he continued to resist his opponents until 1970. King Idris of Libya was overthrown by a military coup led by Muammar Gaddafi in 1969. The monarchy of Afghanistan was abolished in 1973 after a coup d'état overthrew King Mohammed Zahir Shah. That of Iran was abolished by the Islamic revolution of 1979 overthrowing Mohammad Reza Pahlavi. In Ethiopia, Emperor Haile Selassie I was overthrown in 1974 as a result of a leftist coup. King Palden Thondup Namgyal of Sikkim lost his throne in 1975 when the country became a state of India following a referendum. Political upheaval and Communist insurrection put an end to the monarchies of Indochina after World War II: a short-lived attempt to leave a monarchical form of government in post-colonial South Vietnam came to naught in 1955, a military coup overthrew the kingless monarchy in Cambodia in 1970 and a Communist takeover ended the monarchy in Laos in 1975. Cambodia's monarchy later saw an unexpected rebirth under an internationally mediated peace settlement with former king Norodom Sihanouk being restored as a figurehead in 1993.
Brazil rejected an attempt to restore its monarchy in the 1990s. Unsuccessful efforts to restore the monarchies of some of the Balkan states in the former Eastern Bloc continue. Former King Michael of Romania and Prince Alexander of Serbia have been allowed to return, gained some popularity, played largely apolitical public roles, but never came close to being restored to their ancestral thrones. However, in Bulgaria, Simeon Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, who was deposed from the Bulgarian throne in 1946, was elected and recently served as the Prime Minister of his country from 2001 to 2005. The only formerly socialist country to have held a referendum on the monarchy was Albania where the claimant to his father's throne, the self-styled Leka I, lost by a huge margin.
In a 1999 referendum, the voters of Australia rejected a proposal to abolish their monarchy in favour of a specific republican model. The proposal was rejected in all states, with only the Australian Capital Territory voting in favour.
21st century
On 24 December 2007, the Nepalese government decided in an accord to abolish the monarchy after the elections to be held in April 2008.[4] The Nepalese monarchy was formally abolished on 28 May 2008, causing King Gyanendra to lose his throne.
Monarchies abolished in the 20th–21st centuries
| Country |
Last Monarch |
Year |
Annotations | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1900s | |||||
| Dendi | Askia Malla | 1901 | Ousted by French, the country became a part of French West Africa. | ||
| Ashanti | Prempeh I | 1902 | Ousted by British, the country became a part of Gold Coast (British colony). | ||
| Oyo | Adeyemi I Alowolodu | 1905 | Last monarch died, the country became a part of British Southern Nigeria Protectorate. | ||
| Mwali | 1909 | The country was incorporated into French Third Republic. | |||
| 1910s | |||||
| Portugal | Manuel II | 1910 | Republican Coup d'État. | ||
| Korea | Sunjong | Native monarchy abolished; replaced by rule by Japan, a monarchy, through 1945. | |||
| Angoche | Ousted by Portuguese, the country was incorporated into Portugal. | ||||
| Nri | Eze Nri Òbalíke | 1911 | Ousted by British, the country became a part of Southern Nigeria Protectorate. | ||
| Kasanje | The country was incorporated into Portuguese West Africa. | ||||
| China | Xuantong | 1912 | Xinhai Revolution – Emperor ousted by warlords and republicans. | ||
| Ndzuwani | Saidi Mohamed bin Saidi Omar | The country was incorporated into French Third Republic. | |||
| Kongo | Manuel III | 1914 | Position abolished by Portuguese after an unsuccessful revolt. | ||
| Sultanate of Sulu | Sultan Jamalul-Kiram II | 1915 | Split into American Insular Government over the Philippine islands, British North Borneo and the Dutch East Indies. | ||
| Darfur | Ali Dinar | 1916 | Darfur formally re-incorporated into Anglo-Egyptian Sudan. | ||
| China | Hongxian | Monarchy abandoned, shortly after the outbreak of the National Protection War. | |||
| Russia | Nicholas II | 1917 | Russian Revolution of 1917. | ||
| Finland | Finnish Declaration of Independence. | ||||
| Montenegro | Nicholas I | 1918 | Referendum deposed King and united Montenegro with Serbia. | ||
| Germany | William II | All on account of German defeat in World War I and the following German Revolution. | |||
| Prussia | |||||
| Bavaria | Ludwig III | ||||
| Württemberg | William II | ||||
| Saxony | Frederick Augustus III | ||||
| Hesse | Ernest Louis | ||||
| Baden | Frederick II | ||||
| Saxe-Weimar-Eisenach | William Ernest | ||||
| Mecklenburg-Schwerin | Frederick Francis IV | ||||
| Mecklenburg-Strelitz | Adolphus Frederick VI | ||||
| Oldenburg | Frederick Augustus II | ||||
| Brunswick | Ernst Augustus | ||||
| Anhalt | Joachim Ernst | ||||
| Saxe-Coburg and Gotha | Charles Edward | ||||
| Saxe-Meiningen | Bernhard III | ||||
| Saxe-Altenburg | Ernst II | ||||
| Waldeck-Pyrmont | Friedrich | ||||
| Lippe | Leopold IV | ||||
| Schaumburg-Lippe | Adolf II | ||||
| Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt | Günther Victor | ||||
| Schwarzburg-Sondershausen | |||||
| Reuss Elder Line | Heinrich XXIV | ||||
| Reuss Younger Line | Heinrich XXVII | ||||
| Austria | Charles I | Charles I "renounced participation" in state affairs, but did not abdicate. Monarchy officially abolished by the Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye, on 10 September 1919. | |||
| Finland | Frederick Charles I | Monarchy never in effect. | |||
| Lithuania | Mindaugas II | ||||
| Poland | Ruled by Regency Council | ||||
| Hungary | Charles IV | Monarchy restored in 1920, although the throne remained vacant with a Regent. | |||
| Serbia | Peter I | Country transformed to Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes. | |||
| Ukraine | Pavlo Skoropadskyi | Removed from power, following an uprising led by Symon Petliura and the withdrawal of German forces from Kiev. | |||
| 1920s | |||||
| Bukhara (Uzbekistan) | Mohammed Alim Khan | 1920 | |||
| Khiva (Uzbekistan) | Abdallah Khan | ||||
| Syria | Faisal I | Monarchy deposed, following the Siege of Damascus. | |||
| Ottoman Empire | Mehmed VI | 1922 | Sultanate abolished in 1922. | ||
| Wituland | Fumo `Umar ibn Ahmad | 1923 | Sultanate abolished by British, the country was incorporated into Kenya Colony. | ||
| Greece | George II | 1924 | Restored 1935 and later abolished again in 1974 (see below). | ||
| Mongolia | Bogd Khan | Communist People's Republic proclaimed after Khan's death. | |||
| Albania | William I | 1925 | Monarchy restored in 1928 (Albanian Kingdom). | ||
| Mohammerah | Khaz'al al-Ka'bi | 1925 | Sheikhdom abolished by Persia | ||
| Orungu | Rogombé-Nwèntchandi | 1927 | Position abolished by French. | ||
| 1930s | |||||
| Spain | Alfonso XIII | 1931 | Later restored (see below). | ||
| Jimma | Abba Jofir | 1932 | Ousted by Ethiopians, Jimma incorporated into Ethiopia. | ||
| Albania | Zog I | 1939 | Throne usurped by Victor Emmanuel III, after Italian invasion. | ||
| 1940s | |||||
| Albania | Victor Emmanuel III | 1943 | Relinquished throne after Italian armistice. | ||
| Croatia | Tomislav II | Abdicated after withdrawal of Italian support. | |||
| Iceland | Christian X | 1944 | Union with Denmark terminated. | ||
| Montenegro | Ruled by Governor | Monarchy abolished after takeover by Yugoslav Partisans | |||
| Yugoslavia | Peter II | 1945 | Communist reconstruction. | ||
| Manchukuo | Kāngdé | Merged into the Republic of China after abolition of the Empire. | |||
| Vietnam | Bảo Đại | Monarchy abolished after the Surrender of Japan. | |||
| Hungary | Miklós Horthy as Regent | 1946 | Decision of the parliament without a referendum. | ||
| Italy | Umberto II | Referendum; official result: 54.3% in favour of republic. | |||
| Bulgaria | Simeon II | Referendum held to decide whether the monarchy would be retained; results falsified by the communist government: 95% in favour of republic. | |||
| Sarawak | Charles Vyner Brooke | White Rajahs hand over power to British crown. | |||
| Romania | Michael I | 1947 | Forced out by the communists. | ||
| Ireland | George VI | 1949 | Abolished the last "Monarchy of Ireland", the King of the United Kingdom. | ||
| 1950s | |||||
| India | George VI | 1950 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Mysore | HH Maharaja Sir Jayachamaraja Wodeyar | 1950 | The Kingdom of Mysore merged with the Republic of India in 1950 | ||
| Tibet | Tenzin Gyatso | 1951 | Incorporated into the People's Republic of China. | ||
| Egypt | Fuad II | 1953 | Republic proclaimed one year after the 1952 Revolution. | ||
| Vietnam | Bảo Đại | 1954 | Vietnam partitioned through the Geneva Accords. | ||
| Vietnam | Bảo Đại | 1955 | Referendum in South Vietnam. | ||
| Pakistan | Elizabeth II | 1956 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Tunisia | Muhammad VIII al-Amin | 1957 | coup d'état | ||
| Iraq | Faisal II | 1958 | |||
| 1960s | |||||
| Ghana | Elizabeth II | 1960 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| South Africa | 1961 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy pursuant to 1960 referendum; official result: 53% in favor of republic. | |||
| Rwanda | Kigeli V | coup d'état, followed by referendum; official result: 80% in favor of abolishing monarchy. | |||
| Tanganyika | Elizabeth II | 1962 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Yemen | Muhammad al-Badr | coup d'état | |||
| Nigeria | Elizabeth II | 1963 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Uganda | |||||
| Kenya | 1964 | ||||
| Zanzibar | Jamshid bin Abdullah | Zanzibar Revolution | |||
| Burundi | Ntare V | 1966 | coup d'état | ||
| Malawi | Elizabeth II | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | |||
| Fadhli Sultanate | Nasser bin Abdullah bin Hussein bin Ahmed Alfadhli | 1967 | The countries were incorporated into newly created People's Republic of South Yemen. | ||
| Qu'aiti Sultanate | Ghalib II bin Awadh bin Saleh Al Qu'aiti | ||||
| Sultanate of Upper Yafa | Muhammad ibn Salih Harharah | ||||
| Sultanate of Lower Yafa | Mahmud ibn Aidrus Al Afifi | ||||
| Muflahi Sheikhdom | al Qasim ibn Abd ar Rahman | ||||
| Audhali Sultanate | Salih ibn al Husayn ibn Jabil Al Audhali | ||||
| Emirate of Beihan | Saleh al Hussein Al Habieli | ||||
| Dathina Sheikhdom | |||||
| Emirate of Dhala | Shafaul ibn Ali Shaif Al Amiri | ||||
| Wahidi Sultanate of Balhaf | |||||
| Sheikhdom of Shaib | Yahya ibn Mutahhar al-Saqladi | ||||
| Alawi Sheikhdom | Salih ibn Sayil Al Alawi | ||||
| Aqrabi Sheikhdom | Mahmud ibn Muhammad Al Aqrabi | ||||
| Wahidi Sultanate of Haban | Husayn ibn Abd Allah Al Wahidi | ||||
| Qutaibi Sheikhdom | |||||
| Hadrami Sheikhdom | |||||
| Mausatta Sheikhdom | |||||
| Busi Sheikhdom | |||||
| Dhabi Sheikhdom | |||||
| Haushabi Sultanate | Faisal bin Surur Al Haushabi | ||||
| Kathiri Sultanate | Al Husayn ibn Ali | ||||
| Mahra Sultanate | |||||
| Sultanate of Lahej | Ali bin Abd al Karim al Abdali | ||||
| Lower Aulaqi Sultanate | Nasir ibn Aidrus Al Awlaqi | ||||
| Upper Aulaqi Sultanate | Awad ibn Salih Al Awlaqi | ||||
| Upper Aulaqi Sheikhdom | Amir Abd Allah ibn Muhsin al Yaslami Al Aulaqi | ||||
| Maldives | Muhammad Fareed Didi | 1968 | Independence referendum. | ||
| Libya | Idris I | 1969 | coup d'état | ||
| 1970s | |||||
| Cambodia | Norodom Sihanouk | 1970 | Later restored (see below). | ||
| The Gambia | Elizabeth II | 1971 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Guyana | |||||
| Sierra Leone | |||||
| Ceylon | 1972 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy, state name changed into "Sri Lanka". | |||
| Afghanistan | Mohammed Zahir Shah | 1973 | coup d'état | ||
| Ethiopia | Haile Selassie I | 1974 | |||
| Greece | Constantine II | referendum; official result: 69% against monarchy | |||
| Malta | Elizabeth II | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | |||
| Laos | Savang Vatthana | 1975 | Communist takeover | ||
| Sikkim | Palden Thondup Namgyal | Referendum; official result: 97% to become a state of India. | |||
| Trinidad and Tobago | Elizabeth II | 1976 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| Iran | Mohammad Reza Pahlavi | 1979 | Iranian Revolution | ||
| Central Africa | Bokassa I | coup d'état | |||
| 1980s | |||||
| Southern Rhodesia | Elizabeth II | 1980 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. An unrecognised government had unilaterally declared independence as Rhodesia in 1965 and proclaimed a republic in 1969; it was renamed Zimbabwe Rhodesia in 1979 but returned to United Kingdom control as Southern Rhodesia in December 1979. Southern Rhodesia subsequently gained independence as Zimbabwe. | ||
| Rwenzururu | Charles Mumbere | 1982 | Forced to abdicate by the government of Uganda; declaration of independence of Rwenzururu was annulled. | ||
| Fiji | Elizabeth II | 1987 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. Elizabeth II remained recognized as Paramount Chief by the Great Council of Chiefs until the council's de-establishment on 14 March 2012. | ||
| 1990s | |||||
| Mauritius | Elizabeth II | 1992 | Abolished Commonwealth monarchy. | ||
| 2000s | |||||
| Nepal | King Gyanendra | 2008 | Monarchy abolished on 28 May 2008, replaced with a secular federal republic.[5] | ||
Current monarchies that were abolished and then restored
| Country |
Year Abolished |
Annotations |
Year Restored | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| England, and Ireland | 1649 | Commonwealth of England established | 1660 | |
| Spain | 1873 | First Spanish Republic established | 1874 | |
| 1931 | Second Spanish Republic established, then restored in 1947 (de jure), initially under the regency of Francisco Franco | 1975 (de facto) | ||
| Ankole | 1967 | Four traditional Ugandan monarchies abolished by government under new constitution of Milton Obote | 1993 | |
| Buganda | ||||
| Bunyoro | ||||
| Toro | ||||
| Cambodia | 1970 | Khmer Republic established, in 1975 it was overthrown by the Khmer Rouge and Democratic Kampuchea was established. In 1979, the People's Republic of Kampuchea was established, whose name was changed to the State of Cambodia. | 1993 | |
| Rwenzururu, a part of Uganda | 1982 | Abolished by the government. | 2009 (de facto) | |
See also
- List of Abdications by Date
- List of countries by date of transition to republican system of government
- List of monarchs who lost their thrones before the 17th century
- List of monarchs who lost their thrones in the 17th century
- List of monarchs who lost their thrones in the 18th century
- List of monarchs who lost their thrones in the 19th century
- List of monarchs who lost their thrones in the 20th and 21st centuries (by individual instead of by institution as above)
- List of extinct states
- Debate on the monarchy in Canada
- Republicanism in the United Kingdom
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines constitutional referendum, 2009
- Tuvaluan constitutional referendum, 2008
References
- ↑ Maya Jasanoff (2012). Liberty's Exiles: American Loyalists in the Revolutionary World. Random House. p. 357.
- ↑ The Ottoman Empire and Russian Empire are counted amongst Europe, the German Empire is counted as a single monarchy.
- ↑ The Republic of Turkey is counted amongst Europe, the Union of Socialist Soviet Republics as a single republic, the Irish Free State as an independent monarchy (see also Irish head of state from 1936 to 1949), Vatican City as an elective monarchy, the Kingdom of Hungary as a nominal monarchy.
- ↑ "South Asia | Nepalese monarchy to be abolished". BBC News. 24 December 2007. Retrieved 2011-07-21.
- ↑ "World | South Asia | Nepal votes to abolish monarchy". BBC News. 28 May 2008. Retrieved 2011-07-21.
