De Fryske Marren
| De Fryske Marren | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
|
Canal through Joure | |||
| |||
.png) Location in Friesland | |||
| Coordinates: 52°58′N 5°47′E / 52.967°N 5.783°ECoordinates: 52°58′N 5°47′E / 52.967°N 5.783°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | Friesland | ||
| Established | 1 January 2014[1] | ||
| Government[2] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Burgemeester | Arie Aalberts (CDA) | ||
| Area[3] | |||
| • Total | 559.93 km2 (216.19 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 361.83 km2 (139.70 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 198.10 km2 (76.49 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[4] | 2 m (7 ft) | ||
| Population (May 2014)[5] | |||
| • Total | 51,229 | ||
| • Density | 142/km2 (370/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postcode | Parts of 8400 and 8500 range | ||
| Area code | 0513, 0514 | ||
| Website |
www | ||
De Fryske Marren is a municipality of Friesland in the northern Netherlands. It was established 1 January 2014 and consists of the former municipalities of Gaasterlân-Sleat, Lemsterland, Skarsterlân and parts of Boarnsterhim, all four of which were dissolved on the same day.[1][6] The municipality is located in the province of Friesland, in the north of the Netherlands, and has a population of 51,229 and a combined area of 559.93 km2 (216.19 sq mi).
History
Municipal mergers are commonplace in the Netherlands: over the course of the 20th century the number of municipalities was reduced by more than half, from 1,121 in 1900 to 537 in 2000.[7] Several of the municipalities that were amalgamated into De Friese Meren were themselves the result of mergers as well: Gaasterlân-Sleat, Skarsterlân and Boarnsterhim were created during a series of mergers that took effect 1 January 1984. Government policy at the time of the creation of De Friese Meren was that new mergers should have local support and be initiated by the effected municipalities themselves.[8]
The municipalities of Gaasterlân-Sleat, Lemsterland and Skarsterlân were all rural municipalities with a relatively highly developed tourism industry. In 2007 the first two evaluated their functioning as municipalities and both concluded they could benefit from a municipal merger. The following year all three municipal councils decided they were in favour of investigating the benefits of a merger. The report from this study was publicly available for eight weeks and resulted in two negative replies. One of these was from the municipality of Heerenveen, which suggested a merger between them and Lemsterland and Skarsterlân or, alternatively, only parts of Skarsterlân. The province of Friesland, home to these municipalities, rejected these options, although the final draft of the merger proposal specified that two towns from Skarsterlân, Nieuwebrug and Haskerdijken, would become part of Heerenveen, while the rest would be included in De Friese Meren.[9][10] A second merging discussion involved the dissolution of Boarnsterhim. The municipal council of Boarnsterhim concluded the municipality was too small to warrant the continued existence of a separate municipality. In the final advice regarding its dissolution it was suggested that the current municipality be split into four parts; one of these, the town of Terherne, would be included in De Friese Meren. The other three parts were divided among three preexisting municipalities: The northern part, including the actual town of Boarnsterhim, was assigned to Leeuwarden, the southern part to Heerenveen and the western part to Súdwest-Fryslân.[11] After approval by both the House of Representatives and the Senate, the creation of De Friese Meren became law in June 2013 and took effect 1 January 2014.[1][6]
Etymology
De Friese Meren is the name specified for the municipality in the law that establishes it.[6] This is the same name that has been proposed for the municipality since the initial plans of its conception were tabled by the predecessor municipalities of Gaasterlân-Sleat, Lemsterland and Skarsterlân. The name is Dutch for "The Frisian Lakes", in reference to the lakes in the area.[10] By law, any municipality in the Netherlands can change its name with at least a one-year notice; accordingly, as the website for the soon-to-be municipality notes, its name could be changed from De Friese Meren to another name as early as 1 January 2015, a year after its creation.[12][13] 1 July 2015 it was officially renamed De Fryske Marren.
Population centres
The municipality consists of 51 settlements[9] of which Joure is the seat of government. The 51 cities, towns and villages are: Akmarijp, Bakhuizen, Balk, Bantega, Boornzwaag, Broek, Delfstrahuizen, Dijken, Doniaga, Echten, Echtenerbrug, Eesterga, Elahuizen, Follega, Goingarijp, Harich, Haskerhorne, Idskenhuizen, Joure, Kolderwolde, Langweer, Legemeer, Lemmer, Mirns, Nijehaske, Nijemirdum, Oldeouwer, Oosterzee, Oudega, Oudehaske, Oudemirdum, Ouwster-Nijega, Ouwsterhaule, Rijs, Rohel, Rotstergaast, Rotsterhaule, Rottum, Ruigahuizen, Scharsterbrug, Sint Nicolaasga, Sintjohannesga, Sloten, Snikzwaag, Sondel, Terherne, Terkaple, Teroele, Tjerkgaast, Vegelinsoord and Wijckel.
Topography
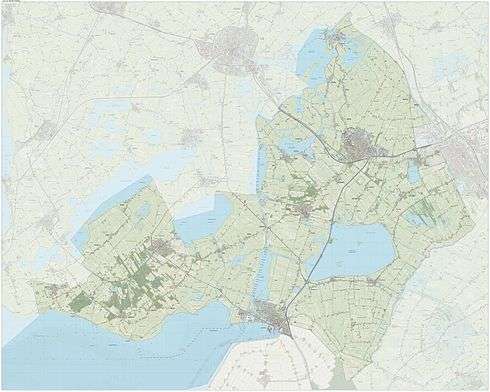
Dutch topographic map of the municipality of De Fryske Marren, June 2015
References
- 1 2 3 "Herindeling" [New subdivisions] (in Dutch). Uitvoeringsorganisatie De Friese Meren. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ "College B&W" [Board of mayor and aldermen] (in Dutch). Gemeente De Friese Meren. Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 12 March 2014.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 8501AA". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 25 August 2013.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 26 June 2014. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- 1 2 3 Wet van 19 juni 2013 tot wijziging van de gemeentelijke indeling in een deel van de provincie Fryslân [Act of 19 June 2013 to change the municipal division in a part of the province of Fryslân], Act No. 286 of 19 June 2013 (in Dutch). Retrieved on 26 August 2013.
- ↑ Ekamper, Peter; van der Erf, Rob; van der Gaag, Nicole; Henkes, Kène; van Imhoff, Evert; van Poppel, Frans (2003). "Chapter: Provincies en gemeenten, 1850–2000" [Provinces and municipalities, 1850–2000]. Bevolkingsatlas van Nederland: demografische ontwikkelingen van 1850 tot heden [Population atlas of the Netherlands: demographic developments from 1850 to now] (link to PDF) (in Dutch). Rijswijk: Uitgeverij Elmar. pp. 21–27. ISBN 9038913648. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- ↑ "Gemeentelijke herindeling" [Municipal mergers]. rijksoverheid.nl (in Dutch). Government of the Netherlands. Retrieved 28 August 2013.
- 1 2 Wijziging van de gemeentelijke indeling in een deel van de provincie Fryslân [Change of the municipal subdivision in parts of the province of Fryslân] (Report) (in Dutch). Tweede Kamer der Staten-Generaal. 20 December 2012. Kamerstuk 33496 nr. 3. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
- 1 2 Herindelingsadvies De Friese Meren [Advice about the municipal division of De Friese Meren] (Technical report) (in Dutch). 27 April 2011.
- ↑ Herindelingsadvies Boarnsterhim, Heerenveen, Leeuwarden, Súdwest-Fryslân en Skarsterlân [Advice about the municipal division of Boarnsterhim, Heerenveen, Leeuwarden, Súdwest-Fryslân en Skarsterlân] (Technical report) (in Dutch). March 2012. p. 27. Retrieved 27 August 2013.
- ↑ Article 158, Gemeentewet [Municipalities Act], Act No. 96 of 14 February 1992 (in Dutch). Retrieved on 8 April 2013.
- ↑ "Wat wordt de nieuwe naam van de gemeente?" [What will be the name of the new municipality?] (in Dutch). Uitvoeringsorganisatie De Friese Meren. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
External links
 Media related to De Fryske Marren at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to De Fryske Marren at Wikimedia Commons- Official website
 |
Súdwest-Fryslân | Leeuwarden |  | |
| |
Heerenveen Weststellingwerf | |||
| ||||
| | ||||
| IJsselmeer | Noordoostpolder (FL) | Steenwijkerland (OV) |