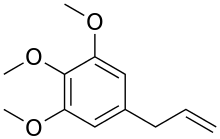
Elemicin
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
487-11-6 |
| PubChem (CID) | 10248 |
| ChemSpider |
9830 |
| KEGG |
C10451 |
| ChEMBL |
CHEMBL458690 |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.954 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H16O3 |
| Molar mass | 208.25 g/mol |
| 3D model (Jmol) | Interactive image |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Elemicin is a phenylpropene, a natural organic compound, and is a constituent of several plant species' essential oils.[1][2]
Natural occurrence
Elemicin is a constituent of the oleoresin and the essential oil of Canarium luzonicum (also referred to as elemi). Elemicin is named after this tree. One study found it to comprise 2.4% of the fresh essential oil.[1] Elemicin is also present in the oils of the spices nutmeg and mace, with it comprising 2.4% and 10.5% of those oils respectively.[2]
Isolation
Elemicin was first isolated from elemi oil using vacuum distillation. Specifically, the substance was collected between 162-165 °C at a reduced pressure of 10 torr.[3][4]
Preparation
Elemicin has been synthesized from syringol and allyl bromide using Williamson ether synthesis and Claisen rearrangement.[5][6] The electrophilic aromatic substitution entering the para-position was made possible by secondary Cope rearrangement.[7] This is due to syringol's allyl aromatic ether being blocked by ethers in both ortho-positions. When blocked the allyl group migrates to the para-position, in this case with yields above 85%.[8]
Uses
Elemicin has been used to synthesize the alkaloid mescaline.[9]
Pharmacology
Raw nutmeg causes anticholinergic-like effects, which are attributed to elemicin and myristicin.[10][11]
See also
References
- 1 2 Villanueva, M. A.; Torres, R. C.; Baser, K. H. C.; Özek, T.; Kürkçüoglu, M. (1993). "The Composition of Manila Elemi Oil". Flavour and Fragrance Journal (pdf). 8: 35–37. doi:10.1002/ffj.2730080107.
- 1 2 Leela, N. (2008). Chemistry of Spices. Calicut, Kerala, India: Biddles Ltd. pp. 165–188 [170]. ISBN 9781845934057.
- ↑ Editor (1908). "Constituents of Essential Oils. Elemicin, a High-boiling Constituent of Elemi Oil, and the Displacement of Alkyloxygroups in the Benzene Nucleus by Hydrogen". Journal of the Chemical Society, Abstracts. 94 (A493): 557–558. doi:10.1039/CA9089400493.
- ↑ Semmler, Friedrich (1908). "Zur Kenntnis der Bestandteile der ätherischen Öle. (Über das Elemicin, einen hochsiedenden Bestandteil des Elemiöls, und über Ersetzung von Alkyloxy-gruppen am Benzolkern durch Wasserstoff.)". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft. 41 (2): 1768–1775. doi:10.1002/cber.19080410240.
- ↑ F. Mauthner (1918). "Die Synthese des Elemicins und Isoelemicins". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 414 (2): 250–255. doi:10.1002/jlac.19184140213.
- ↑ Editor (1918). "Synthesis of Elemicin and of isoElemicin". Journal of the Chemical Society, Abstracts. 114: i428. doi:10.1039/CA9181400421.
- ↑ Thomas, Laue (2005). Named Organic Reactions, 2nd Edition. Wolfsburg, Germany: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. pp. 58–60 [59]. ISBN 0470010401.
- ↑ Adams, Rodger (1944). Organic Reactions, Volume II (PDF). Newyork: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. pp. 2–44 [44]. doi:10.1002/0471264180.or002.01.
- ↑ Hahn, Georg; Wassmuth, Heinrich (1934). "Über β-[Oxyphenyl]-äthylamine und ihre Umwandlungen, I. Mitteil.: Synthese des Mezcalins". Berichte der deutschen chemischen Gesellschaft (A and B Series). 67 (4): 696–708. doi:10.1002/cber.19340670430.
- ↑ McKenna, A.; Nordt, S. P.; Ryan, J. (2004). "Acute Nutmeg Poisoning". European Journal of Emergency Medicine. 11 (4): 240–241. doi:10.1097/01.mej.0000127649.69328.a5. PMID 15249817.
- ↑ Shulgin, A. T.; Sargent, T.; Naranjo, C. (1967). "The Chemistry and Psychopharmacology of Nutmeg and of Several Related Phenylisopropylamines" (pdf). Psychopharmacology Bulletin. 4 (3): 13. PMID 5615546.