Tsonga language
| Tsonga | |
|---|---|
| Xitsonga | |
| Native to | Mozambique, South Africa, Swaziland, Zimbabwe |
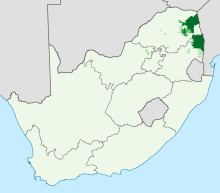
| Region | Limpopo, Mpumalanga, Gauteng, Kwa-Zulu Natal, North-West Province, Gaza Province, Maputo Province, Maputo City, Manica, Inhambane, Chikombezi, Malipati, Chiredzi |
| Ethnicity | Tsonga |
Native speakers |
13 million (2006–2011)[1] 3.4 L2 speakers in South Africa (2002)[2] |
|
Latin (Tsonga alphabet) Tsonga Braille | |
| Signed Tsonga | |
| Official status | |
Official language in |
South Africa Zimbabwe (as 'Shangani') |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-1 |
ts |
| ISO 639-2 |
tso |
| ISO 639-3 |
tso |
| Glottolog |
tson1249[3] |
S.53 (S.52)[4] | |
| Linguasphere |
99-AUT-dc incl. varieties 99-AUT-dca... |
Tsonga (Xitsonga) is a southern African Bantu language spoken by the Tsonga people. It was officially created in 1875 at the Valdezia Mission Station and Elim/Waterval/ Shirley Mission Stations by two Swiss missionaries, Reverend Paul Berthoud and Reverend Ernest Creux. Prior to the arrival of the Missionaries at Valdezia, the Tsonga people in that region that includes, Bungeni, Chavani, Mbhokota, Shirley, Riverplaats, Elim, Waterval, Nwaxinyamani and adjacent areas did not speak one language, but rather, they spoke a diverse of east coast dialects all related to modern Tsonga language. The Swiss Missionaries combined all these east coast dialects, such as Xigwamba, XiNkuna, Xihlengwe, XiTembe, XiValoyi, XiNyembani, Xitswa, XiRonga, and XiChopi to form a new unified superlanguage which they called 'Thonga', but they later modified it and renamed Xitsonga or simply Tsonga.
The Swiss Missionaries refused to recognise Tswa and Ronga as independent languages from Xitsonga because, according to them, Tswa and Ronga are 99% related to Xitsonga. At Valdezia Mission Station and the Elim Mission Station, Tswa and Ronga were swallowed, incorporated and disappeared into Xitsonga. But in Mozambique, Tswa, Ronga and Xitsonga continue to exist as independent languages. The only differences between Tswa, Ronga and Xitsonga in Mozambique is that Ronga and Tswa are highly influenced by the Portuguese language as Maputo and Matola are the homelands of the Ronga and Tswa people. While the homelands of Xitsonga speakers in Mozambique starts 75 km north of Maputo, Xitsonga, Tswa and Ronga are 99% similar to one another, and it is difficult for a non-Xitsonga speaker to see a difference between the three dialects.
Etymology
The name "Tsonga" is the root of Xitsonga (culture, language or ways of the Tsonga), Mutsonga (a Tsonga person), Vatsonga (Tsonga people), etc. In the language of the Vatsonga themselves, the root never appears by itself. It is Tsonga for the ease and accessibility of the wider international community.
As for the origins of the name, there are three theories. The first states that Tsonga is another pronunciation for Dzonga, which means south and also the name of one of the dialects of Xitsonga. The second theory is that is comes from Thonga, the Zulu way of saying "slave" (hlonga in Xitsonga). Why the people would be called slaves is unclear. The other Zulu explanation is that Zulu people have difficulty pronouncing "r", thus their "r" tends to be "l". However, "rh" in Tsonga becomes "th" in Zulu. An example is rhuma (Tsonga word for "send") becomes thuma (Zulu word for the same action). The third and most accepted is that it is another pronunciation for "Rhonga", the root for the word "vurhonga" for east or the direction where the sun rises. Vurhonga also means morning in Xitsonga. Rhonga (commonly and wrongly spelt as Ronga) is one of the Tsonga languages. The physical evidence of most Tsonga people residing along the eastern coast of Africa in the south, extending inland in a westward direction, makes this explanation especially inviting.
Languages and dialects
Tsonga people and languages are: Chopi, Gwamba, Ndau, Ronga, Tonga and Tswa.
Among these languages, three language groups can be identified. These are S50 (Tswa-Ronga group), S60 (Chope group), and Ndau language (S15), currently falling under the Shona group (S10). In total there are six recognised languages.
Chope Group
- Chopi (Chope, Copi, Tshopi, Txopi) dialects are Copi, Khambani, Lambwe, Lenge (Lengue), Ndonge and Tonga.
- Tonga (Nyembane, Nyembani, Inhambane).
Ndau Group
- Ndau (Ndzawu, Njao, Sofala, South-East Shona) dialects are Changa (Shanga, Xanga), Danda, Dondo, Gova, Ndau, and
Tswa-Ronga Group
- Ronga (Rhonga) dialects are Kalanga, Konde, Putru, and Ssonge.
- Gwamba (Gwapa) dialects are Bila (Vila), Changana (Shangaan, Shangani), Djonga (Dzonga, Jonga), Hlanganu (Langanu, Nhlanganu), Hlave (Mbayi, Nkuna, Pai), Kande, Khosa, Luleke, N'walungu (Ngwalungu), Nkuma, Songa, Valoyi, Xika, and Xonga.
- Tswa (Tshwa) dialects are Dzibi (Dzivi), Dzibi-Dzonga (Dzivi-Dzonga), Tshwa, Hlengwe (Lengwe, Lhenge), Khambani, Makwakwe-Khambani, Mandla, Ndxhonge, and Nhayi (Nyai, Nyayi).
Some dialects are subdialects but have been mentioned here for completeness. For example, Valoyi and Luleke comprise the N'walungu dialect. There is no Gwamba dialect as Gwamba is another name for Xitsonga itself. Formally Xitsonga has been called Gwamba. Tswa-Ronga dialects not considered part of the family include Pulana (Xipulana, Sepulane).
It has been said that the two dialects that unite all Tswa-Ronga languages are Nkuna and Khosa (HP Junod, Matimu ya Vatsonga).
For "language of", the various languages and dialects may use one or more of the prefixes: Bi-, Chi-, Ci-, Gi-, Ici-, Ki-, Ma-, Shee-, Shi-, Txi-, Va-, Wa-, and Xi-. For "people of", they use either "Ba-" or "Va-".
It is to be noted that the current standard language was largely based on the Dzonga dialect, thus languages like Copi, Tonga and Ndau divert further.




Official status
Tsonga is an official language in South Africa. It has been suggested to be made official in Zimbabwe according to the new constitution. All Tswa-Ronga languages are recognised in Mozambique. It is not official in Swaziland.
Phonology
Tsonga has a distinction between modal and breathy voiced consonants: /bʱ, bvʱ, vʱ, dʱ, ɖʐʱ, dʒʱ, ɡʱ/ vs /b, bv, v, d, ɖʐ, dʒ, ɡ/ among the obstruents (the one exception being /ɮ/), and /m̤, n̤, ŋ̈, r̤, ȷ̈, w̤/ vs /m, n, ŋ, r, j, w/ among the sonorants (the one exception being /ɲ/).
Unlike some of the Nguni languages, Tsonga has very few words with click consonants, and these vary in place between dental and postalveolar. Examples are: ngqondo (mind), gqoka (wear/dress), guqa (kneel), riqingo (phone), qiqi (earring), qamba (compose), Mugqivela (Saturday).
Tsonga also has "whistled" sibilants similar to Shona "sw/sv", tsw/tsv", "dzw/dzv".
Grammar
The grammar is generally typical of Bantu languages with a subject–verb--object order. The structure changes to subject—object—verb when addressing another person:
| Tsonga | English |
|---|---|
| Ndza ku rhandza | I you love (I love you) |
| Wa ndzi rhandza | You love me |
| Ha ku tiva | We know you |
| Va ndzi tiva | They know me |
Tenses
Present tense
The present tense is formed by simply using the personal pronoun along with the verb.
Ndzi lava mali – I want money,
Hi tirha siku hinkwaro – We work all day,
Mi(u) lava mani? – Who are you looking for?
U kota ku famba – S/He knows how to walk.
Present progressive
Generally, to indicate ongoing actions in the present one takes the personal pronoun, drops the 'i' and adds 'a'.
Ndzi nghena (e)ndlwini – I am entering the house,
Ha tirha sweswi – We are working right now,
Ma hemba – You(pl.) are lying,
Wa hemba – You(sing.) are lying,
Wa hemba – S/He is lying,
With the plural 'va'(they) there is no difference. Thus 'va hemba' = they lie AND they are lying.
Past tense
This is for in one of three ways, depending on the word.
(i) Generally, one drops the 'a' from the verb and adds the prefix '-ile'
Ndzi nghenile ndlwini – I entered the house,
Hi tirhile siku hinkwaro – We worked all day,
U hembile – You lied,
U hembile – S/He lied,
Va hembile – They lied.
(ii) With verbs that end with -ala, in the past change to -ele or -ale.
ku rivala – to forget,
Ndzi rivele – I Forgot, U rivele – you forgot, Va rivele – they forgot,
Ku nyamalala – To disappear,
U nyamalarile – S/he – disappeared,
Words used to describe a state of being also use the past tense.
Ku karhala – To be tired,
Ndzi karhele – I am tired, U karhele – S/He is tired, Va karhele – They are tired.
(iii) In many cases merely changing the last 'a' in the verb to an 'e' indicates past action.
Ku fika – To arrive,
U fike tolo – S/He arrived yesterday,
Ndzi fike tolo – I arrived yesterday,
Hi tirhe siku hinkwaro – We worked all day,
Ndzi nghene (e)ndlwini – I entered the house.
Future tense
This is formed by the adding 'ta' in between the personal pronoun and the verb.
Ndzi ta nghena (e)ndlwini – I will enter the house,
Hi ta tirha siku hinkwaro – We will work all day,
Va ta tirha siku hinkwaro – They will work all day,
Mi ta tirha siku hinkwaro – You(pl.) will work all day.
Noun classes
Tsonga has several classes, much like other Bantu languages, which are learned through memorisation mostly. These are:
| 1 | mu | mufana/boy | murhangeri/leader | |
| 2 | va | vafana/boys | varhangeri/leaders | vanhu/people |
| 3 | mu | nseve/arrow | nenge/leg | nambu/river |
| 4 | mi | miseve/arrows | milenge/legs | milambu/rivers |
| 5 | ri | tiko/country | rito/word | vito/name |
| 6 | ma | matiko/countries | marito/words | mavito/names |
| 7 | xi | Xikwembu/God | xilo/thing | xitulu/chair |
| 8 | swi | Swikwembu/gods | swilo/things | switulu/chairs |
| 9 | yi (N) | yindlu/house | mbyana/dog | homu/cow |
| 10 | ti(N) | tiyindlu/houses | timbyana/dogs | tihomu/cows |
| 11 | ri | rihlaya/jaw | rivambu/rib | rintiho – finger |
| 14 | vu | vutomi/life | vumunhu/humanness | vululami – righteousness |
| 15 | ku | ku tshemba/trust | ku dya/ to eat | ku biha/ugliness |
| 21 | dyi | dyimunhu/abnormally huge person | dyiyindlu/abnormally huge house |
Personal pronouns
Personal pronouns in Tsonga are very similar to those of many other Bantu languages, with a few variations.
These may be classified as first person (the speaker), second person (the one spoken to), and third person (the one spoken about). They are also classified by grammatical number, i.e., singular and plural. There is no distinction between subject and object.
Each pronoun has a corresponding concord or agreement morpheme.
| 1st sg. | 2nd sg. | 3rd sg. | 1st pl. | 2nd pl. | 3rd pl. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pronoun | mina | wena | yena | hina | n'wina | vona |
| Agreement morpheme | ndzi, ndza | u, wa | u, wa | hi, ha | mi, ma | va |
| Example sentences | Mina ndzi vona huku. ("I see a chicken.") Mina ndza yi vona huku. ("I see it—the chicken.") | Wena u vona huku. ("You see a chicken.") Wena wa yi vona huku. ("You see it—the chicken.") | Yena u vona huku. ("He/she sees a chicken.") Yena wa yi vona huku. ("He/she sees it—the chicken.") | Hina hi vona huku. ("We see a chicken.") Hina ha yi vona huku. ("We see it—the chicken.") | N'wina mi vona huku. ("You see a chicken.") N'wina ma yi vona huku. ("You see it—the chicken.") | Vona va vona huku. ("They see a chicken.") Vona va yi vona huku. ("They see it—the chicken.") |
Verbs
All verbs have the prefix "ku" and end with an 'a' in the infinitive, with a couple of exceptions.
| Tsonga | English |
|---|---|
| ku chava | To fear |
| ku tsaka | To rejoice |
| ku rhandza | to love |
The main exception to this is the verb "ku ri" – "to say" It corresponds to "ti" in many other bantu languages. Examples of its usage include:
u ri yini? – What do you say? (What are you saying?)
ndzi ri ka n'wina – I say to you all.
In many instances the "ri" is often omitted and thus "ku" on its own can also mean "say".
Va ri ndza penga – They say I'm crazy.
Va ri yini? – What do they say? (What are they saying?)
Proverbs
Like many other languages, Xitsonga has many proverbs; these appear in different classes. They appear in a group of animals, trees and people.
| Tsonga | English | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| N'wana wa mfenhe a nga tsandziwi hi rhavi | The child of baboon does not fail a branch | A wiseman's child can do anything. |
| U nga teki mali u bohela enengeni wa mpfuvu | Do not tie money in the leg of hippopotamus | Do not lend your money to people who do not pay back. |
| U nga dlayi nyoka u yi ndzuluta, ta micele ta ku vona | Do not kill a snake and swing it, the ones inside the holes are watching you | Do not do unnecessary bad things to someone, other people are watching you. |
| Kuwa ro tshwuka ri na xivungu endzeni. | A fig fruit which is pink, it has a worm inside. | Most of very beautiful women they have bad habits. |
| N'wana wa nyoka i nyoka. | The child of snake is a snake. | A child of a bad person, might be a very bad person. |
| Ndlopfu a yi fi hi rivambu rin'we | An elephant does not die of one (broken) rib | When in trouble, a man should try all efforts to find a solution. |
| Mbuti ya xihaha a yi tswaleli entlhambini | A secretive goat does not give birth in a midst. | Keep a secret do not say it where there are many people |
| Matimba ya ngwenya i mati | The strength of crocodile is water. | A man has power when he is supported by his people |
| N'hwarimbirhi yin'we yi ta tshwa nkanga | If one tries to do more than one thing at the same time, one might not prosper. | |
| N'wana wo ka a nga rili u ta fela a dzobyeni | A child who does not cry will die unnoticed at the back of his mother. | If you do not raise your voice (in a form of a complaint), you will not be heard. |
| Mbuti yi dya laha yi nga bohiwa kona | A goat eats where it is tied. | A person must use properties of a place where he is working. |
| Ku tlula ka mhala ku letela n'wana wa le ndzeni | The way an impala jumps, it influences its unborn child. | Whatever bad things a mother does, her daughter will also do. |
| I malebvu ya nghala. | It is a lion's beard. | A thing may not be as scary as it looks. |
| Nomu a wu taleriwi hi nambu | A mouth can cross any river. | A mouth can say all words of promises. |
| Mavoko ya munhu a ma mili nhova/byanyi | Grass cannot grow on a human being's hands. | You must work hard (in every possible way) to succeed. |
| Xandla famba, xandla vuya. | Let the hand go and let the hand come back. | A giving hand is a receiving hand. |
| Humba yi olele nkuma | The snail has collected ashes | A person has died |
| Mbyana loko yi lava ku ku luma ya n'wayitela. | A dog smiles when it intends to bite something. | A person can do (or intend to do) bad things to you, while he is smiling. |
| Ku hiwa hi Thomo ku suka e palamendhe ya le tilweni. | To be given by Thomo (king's name) from heavenly parliament. | To be blessed by God. |
| Vana va munhu va tsemelana nhloko ya njiya. | Siblings are sharing the head of locust. | Siblings must share good things. |
| Mhunti yo tlulatlula Mangulwe u ta yi khoma. | An antelope which is jumping around next to Mangulwe (dog's name), he will catch it. | Any girl who has been seen by this boy, she will accept his proposal (used by a boy when he is in love with a girl). |
| Tolo a nga ha vuyi. | Yesterday will not come back. | Wishing to bring interesting old things of old days to nowadays. |
| Nghala yi vomba exihlahleni. | A lion roars in the bush. | A warrior is seen in a war. |
| Ku hundza muti ri xile | To pass a home during the day | To be stupid |
| Tinghala timbirhi ta chavana. | Two lions fear each other. | Two powerful nations fear each other. |
| Timpfuvu timbirhi a ti tshami xidziveni xin'we. | Two hippos cannot stay in the same deep water. | Enemies cannot stay in the same place. |
| Vuhosi a byi peli nambu. | Chiefdom does not cross the river. | Chiefdom stays in the same family, cannot be passed to other families. |
| A ndzi ku hi laha ku nga na mpfula ku sala ndzhongo. | I thought is where the rain has poured and left fertile soil. | I thought it was good things. |
| I matutu vana va ntavasi | It is plenty. | |
| Ku tshwa nomo | To have a burnt mouth | Referring to someone who constantly lies, e.g. Jephrey Cuma u tshwe nomo. |
| N'wana u tseme mubya | A disobedient child | |
| Ximitantsengele xi tshemba nkolo | He who swallows a large stone has confidence in the size of his throat. | When you start something you must have power (courage) to complete it. |
| Mutlhontlhi wa tinyarhi ti vuya hi yena | The one who challenges buffaloes they will chase him. | He who provokes other people, will face the consequences. |
| Loko u tsundzuka mhelembe khandziya ensinyeni | When you think of rhino, climb a tree. | When you think of something, act immediately. |
| Ku ba ndlopfu hi xibakele | To hit an elephant with a fist | To make a very slight impression. |
| Ku banana hi rhambu ra mfenhe | To hit each other with a baboon's bone | To exchange gifts with relatives only. |
| Ku banana hi rhanga ro hisa | To hit each other with a hot 'pumpkin' | To accuse each other. |
| U nga hlawuli nkuku wa mhangele | One must not choose the male of the guinea-fowl (similar to "Don't count your chickens before they are hatched"). | This proverb is said to a young husband who might be tempted to prepare something for their babies before their birth, since you do not know if the baby is a male or female. |
| Tinhlanga ta le ndzhaku ti tiviwa hi mutlhaveri wa tona. | The tattooing marks made on the back are known by the tattooer (not by the tattooed) | You do not know what may happen when you have turned your back. |
| Xihlovo a xi dungiwi loko u heta ku nwa mati | Do not close the well after having drunk. | Do not mess up things after using them, you might need them tomorrow. |
| U nga sahi nsinya hi vuxika, u ta tshwa hi mumu hi malanga | Do not cut the tree in winter, you will burn by sun in summer. | Do not mess up things when you do not need them, you will suffer when you need them. |
| Mhunti yi biwa ya ha ri na mahika | An antelope is killed while is sighing | A problem must be solved immediately. |
| Xirhami xi vuyisa na n'wana evukatini | Chillness causes a girl to come back to her parents' house from her husband's house. | It is very cold. |
Numerals
| Tsonga | English |
|---|---|
| N'we | one |
| Mbirhi | two |
| Nharhu | three |
| Mune | four |
| Ntlhanu | five |
| Tsevu | six |
| Nkombo | seven |
| Nhungu | eight |
| Kaye | nine |
| Khume | ten |
| Khume (na) n'we / Khumen'we | eleven |
| Khume (na) mbirhi / Khumembirhi | twelve |
| Khume (na) nharhu / Khumenharhu | thirteen |
| Makhume mambirhi / Makumembirhi | twenty |
| Makhume manharhu / Makumenharhu | thirty |
| Mune wa makhume / Makumemune | forty |
| Ntlhanu wa makhume / Makumentlhanu | fifty |
| Dzana | hundred |
| Gidi | thousand |
Months of the Year
| Tsonga | English |
|---|---|
| Sunguti | January |
| Nyenyenyani | February |
| Nyenyankulu | March |
| Dzivamisoko | April |
| Mudyaxihi | May |
| Khotavuxika | June |
| Mawuwani | July |
| Mhawuri | August |
| Ndzati | September |
| Nhlangula | October |
| Hukuri | November |
| N'wendzamhala | December |
Vocabulary
Xitsonga, like many other African languages, have been influenced by various European colonial languages. Xitsonga includes words borrowed from English, Afrikaans, and Portuguese. Also, because of the influence of other more dominant neighbouring languages, Xitsonga has taken some words, especially click words, from isiZulu actually its (Nguni/ngoni).
Words borrowed from English
- Thelevhixini (Mavonakule) – television
- Rhediyo (Xiyanimoya) – Radio
- Xitulu – chair (Stool)
- Wachi (Xikomba-nkarhi) – watch (to tell time)
- Movha (Xipandza-mananga) – car (automobile)
- Sokisi – socks
- Nghilazi – glass
- Tliloko – clock(bell)
- Masipala – municipal (plural: vamasipala)
- Makhiya/swikhiya (Xilotlela) – keys
Words borrowed from Afrikaans
- lekere – sweets (lekkers)
- fasitere – window (venster)
- lepula – spoon (lepel)
- kereke – church (kerk)
- buruku – trousers (broek)
- domu – idiot (dom)
- tafula – table (tafel)
- xipuku – ghost (spook)
Words borrowed from isiZulu:
- riqingho – phone
- ku qonda – to head towards (not standard = ku kongoma)
- ku gcina – to end (not standard = ku hetelela)
- ku zama – to try (not standard = ku ringeta)
Writing system
Xitsonga Latin Alphabet
Xitsonga uses the Latin alphabet. However, certain sounds are spelled using a combination of letters, which either do not exist in Indo-European languages, or may be meant to distinguish the language somewhat.
An example of this is the letter "x" taken from Portuguese orthography, which is pronounced /ʃ/. Therefore, the following words, [ʃuʃa], [ʃikolo], [ʃilo], are written in Tsonga as -xuxa, xikolo, and xilo.
Other spelling differences include the letter "c", which is pronounced /t͡ʃ/. However, where the emphasis of a word is on the following vowel the letter is hardened by adding "h" this the Tsonga word -chava(fear)
A sound equivalent to the Welsh "ll" (/ɬ/) is written "hl" in Tsonga, e.g. -hlangana(meet), -hlasela(attack), -hleka(laugh)
A whistling sound common in the language is written "sw" or "sv" in Zimbabwean chishona. This sound actually belongs to the "x-sw" class within the language. E.g.:
- sweswi (now)
- xilo(thing) – swilo(things)
- xikolo(school) – swikolo(schools)
- Xikwembu(God) – swikwembu(gods)
Another whistling sound is spelled "dy" but has no English equivalent, the closest being the "dr" sound in the English word "drive"
Xitsonga has been standardised as a written language. However, there are many dialects within the language that may not pronounce words as written. For example, the Tsonga bible uses the word "byela"(tell), pronounced bwe-la, however a large group of speakers would say "dzvela" instead.
The Lord's Prayer as written in the Xitsonga Bible (Bibele)
Tata wa hina la nge matilweni,
vito ra wena a ri hlawuriwe;
a ku te ku fuma ka wena;
ku rhandza ka wena a ku endliwe misaveni;
tani hi loko ku endliwa matilweni;
u hi nyika namuntlha vuswa bya hina
bya siku rin'wana ni rin'wana;
u hi rivalela swidyoho swa hina,
tani hi loko na hina hi rivalela lava hi dyohelaka;
u nga hi yisi emiringweni
kambe u hi ponisa eka Lowo biha,
hikuva ku fuma, ni matimba, no ku twala i swa wena
hi masiku ni masiku.
Amen.
Xiyinhlanharhu xa Mipfawulo
The sintu writing system, Isibheqe Sohlamvu/Ditema tsa Dinoko, also known technically in Xitsonga as Xiyinhlanharhu xa Mipfawulo,[5] is used for all Xitsonga varieties. The class 7/8 noun pairs above are represented as follows:
| xilo |
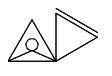 [ʃiːlɔ] |
swilo |
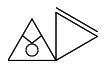 [ʂiːlɔ] |
|---|---|---|---|
| xikolo |
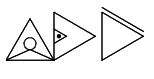 [ʃikʼɔːlɔ] |
swikolo |
 [ʂikʼɔːlɔ] |
| xikwembu |
 [ʃikwʼɛmbu] |
swikwembu |
 [ʂikwʼɛmbu] |
References
- ↑ Tsonga at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015)
- ↑ Webb, Vic. 2002. "Language in South Africa: the role of language in national transformation, reconstruction and development." Impact: Studies in language and society, 14:78
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin; Bank, Sebastian, eds. (2016). "Tsonga". Glottolog 2.7. Jena: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ↑ Jouni Filip Maho, 2009. New Updated Guthrie List Online
- ↑ "IsiBheqe". isibheqe.org. 2015-08-23. Retrieved 2015-08-28.
Further reading
- van Wyk, E. B.; Odendal, F. F.; Nkatini, N. L. (2012) [1988], "Comparison between the phonetic systems of Afrikaans and Tsonga", South African Journal of Linguistics, Taylor & Francis Group, 7 (1): 38–45, doi:10.1080/10118063.1989.9723787
External links
| Tsonga edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| Look up Tsonga in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |